|
Antiprotozoal Agent
Antiprotozoal agents ( ATC code: ATC P01) is a class of pharmaceuticals used in treatment of protozoan infection. A paraphyletic group, protozoans have little in common with each other. For example, ''Entamoeba histolytica'', a unikont eukaryotic organism, is more closely related to ''Homo sapiens'' (humans), which also belongs to the unikont phylogenetic group, than it is to ''Naegleria fowleri'', a "protozoan" bikont. As a result, agents effective against one pathogen may not be effective against another. Antiprotozoal agents can be grouped by mechanism or by organism. Recent papers have also proposed the use of viruses to treat infections caused by protozoa. Medical uses Antiprotozoals are used to treat protozoal infections, which include amebiasis, giardiasis, cryptosporidiosis, microsporidiosis, malaria, babesiosis, trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, and toxoplasmosis. Currently, many of the treatments for these infections are limited by their toxicity. Outda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification System is a drug classification system that classifies the active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties. Its purpose is an aid to monitor drug use and for research to improve quality medication use. It does not imply drug recommendation or efficacy. It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology (WHOCC), and was first published in 1976. Coding system This pharmaceutical coding system divides drugs into different groups according to the organ or system on which they act, their therapeutic intent or nature, and the drug's chemical characteristics. Different brands share the same code if they have the same active substance and indications. Each bottom-level ATC code stands for a pharmaceutically used substance, or a combination of substances, in a single indication (or u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by ''Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tract in both immunocompetent (i.e., individuals with a normal functioning immune system) and immunocompromised (e.g., persons with HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders) individuals, resulting in watery diarrhea with or without an unexplained cough. In immunosuppressed individuals, the symptoms are particularly severe and can be fatal. It is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated water; recent evidence suggests that it can also be transmitted via fomites contaminated with respiratory secretions. ''Cryptosporidium'' is commonly isolated in HIV-positive patients presenting with diarrhea. Despite not being identified until 1976, it is one of the most common waterborne diseases and is found worldwide. The infection beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer more generally to any organic molecule that contains amino sugar substructures. Aminoglycoside antibiotics display bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobes and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen but generally not against Gram-positive and anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria.ME Levison, MD, 2012, Aminoglycosides, The Merck Manua accessed 22 February 2014. Streptomycin is the first-in-class aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is derived from ''Streptomyces griseus'' and is the earliest modern agent used against tuberculosis. Streptomycin lacks the common 2-deoxystreptamine moiety (image right, below) present in most other members of this class. Other examples of aminoglycosides include the deoxystreptamine-containi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithine Decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer. Reaction mechanism Lysine 69 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) binds the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate to form a Schiff base. Ornithine displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base attached to orthonine, which decarboxylates to form a quinoid intermediate. This intermediate rearranges to form a Schiff base attached to putrescine, which is attacked by lysine to release putrescine product and reform PLP-bound ODC. This is the first step and the rate-limiting step in humans for the production of polyamines, compounds required for cell division. Structure image:Ornithine Decarboxylase Publication View.png, 270px, 3D crystal structure of ornithine decarboxylase.; ; rendered viPyMOL The active form of ornithine decarboxyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eflornithine
Eflornithine, sold under the brand name Vaniqa among others, is a medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) and excessive hair growth on the face in women. Specifically it is used for the 2nd stage of sleeping sickness caused by '' T. b. gambiense'' and may be used with nifurtimox. It is taken intravenously (injection into a vein) or topically. It has also been given orally on at least some rare occasions for the treatment of African trypanosomiasis. Common side effects when applied as a cream include rash, redness, and burning. Side effects of the injectable form include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, and seizures. It is unclear if it is safe to use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is recommended typically for children over the age of 12. Eflornithine was developed in the 1970s and came into medical use in 1990. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States the injectable form can be obtained fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-protist
Anti-protist or antiprotistal refers to an anti-parasitic and anti-infective agent which is active against protists. Unfortunately due to the long ingrained usage of the term antiprotozoal, the two terms are confused, when in fact protists are a supercategory. Therefore, there are protists that are not protozoans. Beyond "animal-like" (heterotrophic, including parasitic) protozoans, protists also include the "plant-like" (autotrophic) protophyta and the "fungi-like" saprophytic molds. In current biology, the concept of a "protist" and its three subdivisions has been replaced. See also * Amebicide An amebicide (or amoebicide) is an agent that is destructive to amoeba, especially parasitic amoeba that cause amoebiasis. Entamoeba * Metronidazole, or a related drug such as Tinidazole, Secnidazole or Ornidazole, is used to destroy amoebae that h ... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Antiprotist Agent Biocides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and ''protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
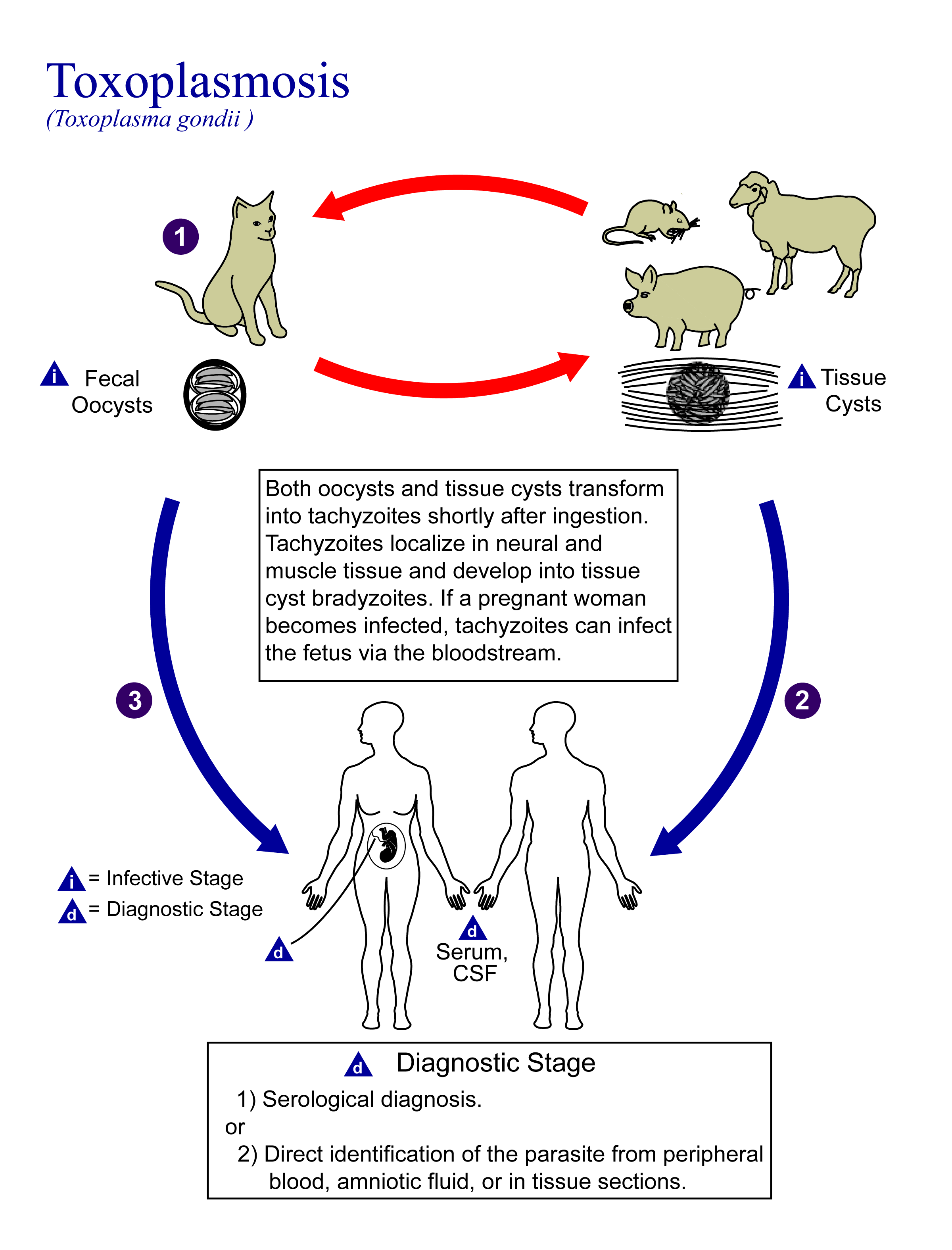
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver. Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty, malnutrition, deforestation, and urbanization. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Additionally, visceral disease can be diagnosed by blood tests. Leishmaniasis can be partl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagas Disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily ''Triatominae'', known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change over the course of the infection. In the early stage, symptoms are typically either not present or mild, and may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches, or swelling at the site of the bite. After four to eight weeks, untreated individuals enter the chronic phase of disease, which in most cases does not result in further symptoms. Up to 45% of people with chronic infections develop heart disease 10–30 years after the initial illness, which can lead to heart failure. Digestive complications, including an enlarged esophagus or an enlarged colon, may also occur in up to 21% of people, and up to 10% of people may experience nerve damage. is commonly spread to humans and other mammals by the bite of a kissing bug. The disease may also be spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus ''Trypanosoma''. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other diseases occur in other animals. African trypanosomiasis, which is caused by either ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' or ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'', threatens some 65 million people in sub-Saharan Africa, especially in rural areas and populations disrupted by war or poverty. The number of cases has been going down due to systematic eradication efforts: in 1998 almost 40,000 cases were reported but almost 300,000 cases were suspected to have occurred; in 2009, the number dropped below 10,000; and in 2018 it dropped below 1000. Chagas disease causes 21,000 deaths per year mainly in Latin America. Signs and symptoms The tsetse fly bite erupts into a red chancre sore and within a few weeks, the person can experience fever, swollen lymph gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |