|
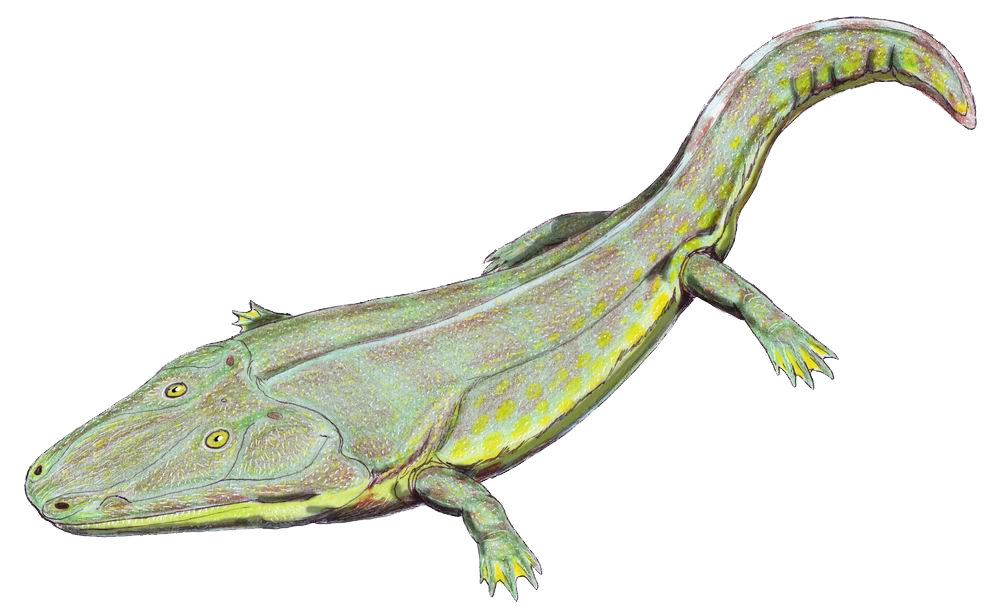
Fleming Fjord Formation
The Fleming Fjord Formation, alternatively called the Fleming Fjord Group is an Upper Triassic geological formation in the northeastern coast of Jameson Land, Greenland. It consists of terrestrial sediments and is known for its fossil content. Description It is of Norian to Rhaetian age and is subdivided into three members; at the base the Edderfugledal Member, followed by the Malmros Klint Member with the Ørsted Dal Member at the top. It was deposited in a large shallow to ephemeral lake. Paleobiota The fauna of Fleming Fjord is diverse, including sauropodomorph dinosaurs, pterosaurs, temnospondyls, mammaliaforms, aetosaurs, and other taxa. Freshwater unionid bivalves and conchostracans have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Fish Lungfish, actinopterygian, and chondrichthyan teeth have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Amphibians Reptiles Besides the forms described below, a diverse ichnofauna of small and large tracks has also been reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropodomorpha
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had long necks and tails, were quadrupedal, and became the largest animals to ever walk the Earth. The '' prosauropods,'' which preceded the sauropods, were smaller and were often able to walk on two legs. The sauropodomorphs were the dominant terrestrial herbivores throughout much of the Mesozoic Era, from their origins in the Late Triassic (approximately 230 Ma) until their decline and extinction at the end of the Cretaceous. Description Sauropodomorphs were adapted to browsing higher than any other contemporary herbivore, giving them access to high tree foliage. This feeding strategy is supported by many of their defining characteristics, such as: a light, tiny skull on the end of a long neck (with ten or more elongated cervical vertebrae) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptychoceratodus
''Ptychoceratodus'' is an extinct genus of lungfish living from Early Triassic to Middle Jurassic. It was established by Otto Jaekel for one species (''P. runcinatus''), transferred from ''Ceratodus'' genus. Type species is ''P. serratus'' from the Middle Triassic of Switzerland and Germany. ''Ptychoceratodus'' had two pairs of massive dental plates, bearing 4-6 acute ridges. Its skull roof was composed from massive, plate-like bones. In the central part of skull roof was localized an unossified fenestra. Most of the ''Ptychoceratodus'' findings are isolated dental plates, some associated with jaws. Other parts of skull or postcranial skeleton are relatively rarely found as fossils. The anatomy of skull is the best recognized in ''P. serratus'', whereas less complete cranial material is available also for ''P. concinuus, P. phillipsi,'' and ''P. rectangulus''. Although ''Ptychoceratodus'' is known exclusively from the Triassic and Jurassic, there were also Cretaceous specimens ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratodus
''Ceratodus'' (from el, κέρας , 'horn' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') was a wide-ranging genus of extinct lungfish. Fossil evidence dates back to the Early Triassic. A wide range of fossil species from different time periods have been found around the world in places such as the United States, Argentina, Greenland, England, Germany, Egypt, Madagascar, China, and Australia.Agnolin, F. L., Mateus O., Milàn J., Marzola M., Wings O., Adolfssen J. S., & Clemmensen L. B. (2018). Ceratodus tunuensis, sp. nov., a new lungfish (Sarcopterygii, Dipnoi) from the Upper Triassic of central East Greenland. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. e1439834 ''Ceratodus'' is believed to have become extinct sometime around the beginning of the Eocene Epoch. The closest living relative of ''Ceratodus'' is thought to be the Queensland lungfish, ''Neoceratodus forsteri'', which means "new ''Ceratodus''" in Greek. Species * ''C. latissimus'' Agassiz, 1837 ( type) * ''C. eruciferus'' Cope, 1876 (''nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are jawed vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, scales, and a heart with its chambers in series. Extant chondrichthyes range in size from the 10 cm (3.9 in) finless sleeper ray to the 10 m (32 ft) whale shark. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, except in Holocephali, where the notochord stays intact. In some deepwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from ''Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conchostracans
Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated Bivalvia, bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classified in the former order (biology), order Conchostraca, which later proved to be paraphyly, paraphyletic and was subsumed into the superorder Diplostraca. Clam shrimp now make up three of the seven orders in Diplostraca, Cyclestherida, Laevicaudata, and Spinicaudata, in addition to the fossil family Leaiidae. Characteristics Both valves of the shell are held together by a strong closing muscle. The animals react to danger by contracting the muscle, so that the valves close tightly and the crustacean, as if dead, lies motionlessly at the bottom of the pool. In most species the head is anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsoventrally compressed. The Sessility (zoology), sessile compound eyes are close together and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ... that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into Ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unionidae
The Unionidae are a family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionida, the bivalve molluscs sometimes known as river mussels, or simply as unionids. The range of distribution for this family is world-wide. It is at its most diverse in North America, with about 297 recognised taxa, but China and Southeast Asia also support very diverse faunas. Freshwater mussels occupy a wide range of habitats, but most often occupy lotic waters, i.e. flowing water such as rivers, streams and creeks. Origin and early diversification The recent phylogenetic study reveals that the Unionidae most likely originated in Southeast and East Asia in the Jurassic, with the earliest expansions into North America and Africa (since the mid-Cretaceous) followed by the colonization of Europe and India (since the Paleocene). Life history Unionidae burrow into the substrate, with their posterior margins exposed. They pump water through the incurrent aperture, obtaining oxygen and food. They remove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammaliaformes
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade that contains the crown group mammals and their closest Extinction, extinct relatives; the group adaptive radiation, radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent common ancestor of Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals; the latter is the clade originating with the most recent common ancestor of extant Monotremata, Marsupialia, and Placentalia. Besides Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals, Mammaliaformes includes Docodonta and ''Hadrocodium'' as well as the Triassic ''Tikitherium'', the earliest known member of the group. Mammaliaformes is a term of phylogenetic nomenclature. In contrast, the assignment of organisms to Mammalia has traditionally been founded on traits and, on this basis, Mammalia is slightly more inclusive than Mammaliaformes. In particular, trait-based taxonomy generally includes ''Adelobasileus'' and ''Sinoconodon'' in Mammalia, though they fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |