|
Flateyjarbók
''Flateyjarbók'' (; "Book of Flatey") is an important medieval Icelandic manuscript. It is also known as GkS 1005 fol. and by the Latin name ''Codex Flateyensis''. It was commissioned by Jón Hákonarson and produced by the priests and scribes Jón Þórðarson and Magnús Þórhallsson. Description ''Flateyjarbók'' is the largest medieval Icelandic manuscript, comprising 225 written and illustrated vellum leaves. It contains mostly sagas of the Norse kings as found in the ''Heimskringla'', specifically the sagas about Olaf Tryggvason, St. Olaf, Sverre, Hákon the Old, Magnus the Good, and Harald Hardrada. But they appear here expanded with additional material not found elsewhere (some of it being very old) along with other unique differences. Most—but not all—of the additional material is placed within the royal sagas, sometimes interlaced. Additionally, the manuscript contains the only copy of the eddic poem '' Hyndluljóð'', a unique set of annals from creation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnús Þórhallsson
Magnús Þórhallsson was an Icelandic priest who was one of two scribes (the other being Jón Þórðarson) who wrote the manuscript Flateyjarbók for Jón Hákonarson. Magnús was responsible for the second part of the manuscript after Jón Þórðarson left Iceland for Norway in the spring of 1388. Magnús also added three leaves to the front of the codex and rubricated and illuminated the entire manuscript. Ólafur Halldórsson has described his work as "among the most beautiful in medieval Icelandic manuscripts." Very little of Magnús's life is known. A priest named Magnús Þórhallsson, assumed to be the same person, is the first witness named in two letters written on 2 April 1397 concerning land purchased by Þorsteinn Snorrason, abbot of Helgafell. In light of this, Magnús is thought to have been a priest there at that time. It is assumed that Magnús trained at a different school or scriptorium from Jón Þórðarson, as their handwriting differs markedly. Where Mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grœnlendinga Saga
''Grœnlendinga saga'' () (spelled ''Grænlendinga saga'' in modern Icelandic and translated into English as the Saga of the Greenlanders) is one of the sagas of Icelanders. Like the ''Saga of Erik the Red'', it is one of the two main sources on the Norse colonization of North America. The saga recounts events that purportedly happened around 1000 and is preserved only in the late 14th century ''Flateyjarbók'' manuscript. The ''Saga of the Greenlanders'' starts with Erik the Red, who leaves Norway and colonizes Greenland. It then relates six expeditions to North America, led respectively by Bjarni, Leif, Thorvald, Thorstein and his wife Gudrid, Karlsefni, and Freydís. Bjarni and his crew discover three lands by chance during their voyage to Greenland, but they never set foot on the lands themselves. Leif learns about Bjarni's encounters and, after buying Bjarni's ship, sails to the lands to explore them. During his adventures, Leif names the three lands Helluland, Markland, and V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
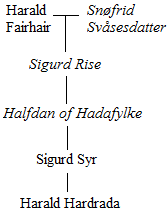
Harald Hardrada
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' (; modern no, Hardråde, roughly translated as "stern counsel" or "hard ruler") in the sagas, was King of Norway from 1046 to 1066. Additionally, he unsuccessfully claimed both the Danish throne until 1064 and the English throne in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald had spent around fifteen years in exile as a mercenary and military commander in Kievan Rus' and as a chief of the Varangian Guard in the Byzantine Empire. When he was fifteen years old, in 1030, Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad together with his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson (later Saint Olaf). Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to the Danish king Cnut the Great two years prior. In the battle, Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan Rus' (the sagas' ). He thereafter spent some time in the army of Grand Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Færeyinga Saga
The Færeyinga saga (), the saga of the Faroe Islands, is the story of how the Faroe Islanders were converted to Christianity and became a part of Norway. Summary It was written in Iceland shortly after 1200. The author is unknown and the original manuscript is lost to history, but passages of the original manuscript have been copied in other sagas, especially in three manuscripts: ''Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar en mesta'', ''Flateyjarbók'', and a manuscript registered as AM 62 fol. The different sagas differ somewhat on the first settlement of the Faroes. Historians have understood from the beginning of ''Færeyinga Saga'' in ''Flateyjarbók'' that Grímur Kamban settled in the Faroes when Harald Fairhair was king of Norway (c.872-930 AD). This does not correspond with the writings of the Irish monk Dicuil. However, the version from ''Ólafs saga Tryggvasonar'' does correspond with the writings of Dicuil. The opening text is, "There was a man named Grímr Kamban; he first settled i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyndluljóð
''Hyndluljóð'' (Old Norse: 'The Lay of Hyndla') is an Old Norse poem often considered a part of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in its entirety only in ''Flateyjarbók'', but some stanzas are also quoted in the ''Prose Edda'', where they are said to come from ''Völuspá hin skamma''. __NOTOC__ ''Hyndluljóð'' is believed to be a relatively late Eddic poem, dating to the second half of the 12th century or later, although including much older traditions, such as that of the 4th c. Gothic king Ermanaric. In the poem, the goddess Freyja meets the völva Hyndla and they ride together towards Valhalla. Freyja rides on her boar Hildisvíni and Hyndla on a wolf. Their mission is to find out the pedigree of Óttarr so that he can touch his inheritance, and the lay consists mostly of Hyndla reciting a number of names from Óttarr's ancestry. Because of the reference in the ''Prose Edda'' to ''Völuspá hin skamma'', since Sophus Bugge's first edition of the Eddic poems, stanza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Árni Magnússon Institute For Icelandic Studies
The Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies ( is, Stofnun Árna Magnússonar í íslenskum fræðum ) is an institute of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Iceland which conducts research in Icelandic and related academic studies, in particular the Icelandic language and Icelandic literature, to disseminate knowledge in those areas, and to protect and develop the collections that it possesses or those placed in its care. It is named after Árni Magnússon, a 17th–18th century collector of medieval Icelandic manuscripts. The Árni Magnússon Institute () was an academic institute located in Reykjavík, Iceland. The institute had the task of preserving and studying mediaeval Icelandic manuscripts containing Landnáma, Heimskringla and the Icelandic sagas. On 1 September 2006, this institute was merged with the Icelandic Language Institute, the University of Iceland Institute of Lexicography, the Sigurður Nordal Institute, and the Place-Name Institute of Ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breiðafjörður
Breiðafjörður (, ''wide fjord'') is a large shallow bay, about 50 km wide and 125 km long, in the west of Iceland. It separates the region of the Westfjords (Vestfirðir) from the Snæfellsnes peninsula to the south. Breiðafjörður is encircled by mountains, including Kirkjufell and the glacier Snæfellsjökull on the Snæfellsnes peninsula, and the Látrabjarg bird cliffs at the tip of the Westfjords. Numerous smaller fjords extend inland from Breiðafjörður, the largest being Hvammsfjörður at its southeastern corner. An interesting feature of the bay is that the land to the north was formed about 15 million years ago, whereas the land to the south was formed less than half that time ago. Nature Breiðafjörður has a spectacular land and seascape consisting of shallow seas, small fjords and bays, and intertidal areas, dotted with about 3,000 islands, islets and skerries. The area contains about half of Iceland's intertidal area and tides can be six metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brynjólfur Sveinsson
Brynjólfur Sveinsson (14 September 1605 – 5 August 1675) served as the Lutheran Bishop of the see of Skálholt in Iceland. His main influence has been on modern knowledge of Old Norse literature. Brynjólfur is also known for his support of the career of the Icelandic poet and hymn writer Hallgrímur Pétursson. Brynjólfur Sveinsson is currently pictured on the banknote. Brynjólfur was born in Önundarfjörður in the Westfjords of northwestern Iceland. He studied at the University of Copenhagen from 1624 to 1629 and was Provost of Roskilde University from 1632 to 1638. In 1643, he named the collection of Old Norse mythological and heroic poems ''Edda''. Brynjólfur attributed the manuscript to Sæmundr fróði, but the scholarly consensus is that whoever wrote the Eddic poems, whether in the sense of being the compiler or the poet, it could not have been Sæmundr. It is believed that the manuscript has multiple authorship from over a long span of time. In 1650 King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatey, Breiðafjörður
Flatey () is an island of the western islands, a cluster of about forty large and small islands and islets located in Breiðafjörður on the northwestern part of Iceland. Flatey and its surrounding islands are, as a creation, believed to have forged from under the weight of a great glacier during the previous Ice age. In terms of size, Flatey is some two kilometers long and about one kilometer wide, of which most is flat land (hence its name, meaning "flat island" in Icelandic), with scarcely any hills to be found. The island has a seasonal habitation; most houses there are occupied only during summer. In winter, the island's total population is five people. In spite of this, Flatey used to be one of the main cultural centres of Iceland, with its no-longer existing monastery (founded in 1172) standing on the highest point of the island as its beacon of knowledge. In the middle of the 19th century, Flatey was still a cultural and artistic centre but doubled as a hub of commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styrbjarnar þáttr Svíakappa
''Styrbjarnar þáttr Svíakappa'' (''The Tale of Styrbjörn the Swedish Champion'') is a short story, a ''þáttr'' on the Swedish claimant and Jomsviking Styrbjörn the Strong preserved in the ''Flatey Book'' (GKS 1005 fol 342-344, ca 1387-1395). It is inserted together with '' Hróa þáttr heimska'' in the description of Olaf Haraldsson's wooing of the Swedish princess Ingegerd Olofsdotter. Their purpose appears to be to present the Swedish court, its traditions and Þorgnýr the Lawspeaker. In the story, Styrbjörn becomes the leader of the Jomsvikings and makes war against the Danes, until he makes peace with the Danish king Haraldr Gormsson who in return gave Styrbjörn his daughter and 100 ships. However, Styrbjörn is not happy with the agreement and attacks Denmark with an even larger fleet and forces king Harald to give him 200 ships and the king himself as a hostage. Styrbjörn goes back to Sweden to take the Swedish throne. Styrbjörn has sacrificed to Thor, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Völsa þáttr
''Vǫlsa þáttr'' is a short story which is only extant in the ''Flateyjarbók'' codex, where it is found in a chapter of ''Óláfs saga helga''. It is probably from the fourteenth century but takes place in 1029, when Scandinavia was still largely pagan, and it appears to preserve traditions of a pagan phallos cult, the ''vǫlsi'' (see also blót). The worship It relates that an old man and an old woman lived with their brisk son and intelligent daughter on a promontory far from other people. They also had a male and a female thrall. When the thrall had butchered a horse and was to throw away the horse's penis, the boy ran past, took it, and went to the place where his mother, sister, and the slave woman were sitting. There he joked at the slave woman, telling her the organ would not be dull between her legs, whereupon the slave woman laughed. The daughter asked her brother to throw away the disgusting object, but her old mother rose and said it was a useful thing that should n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
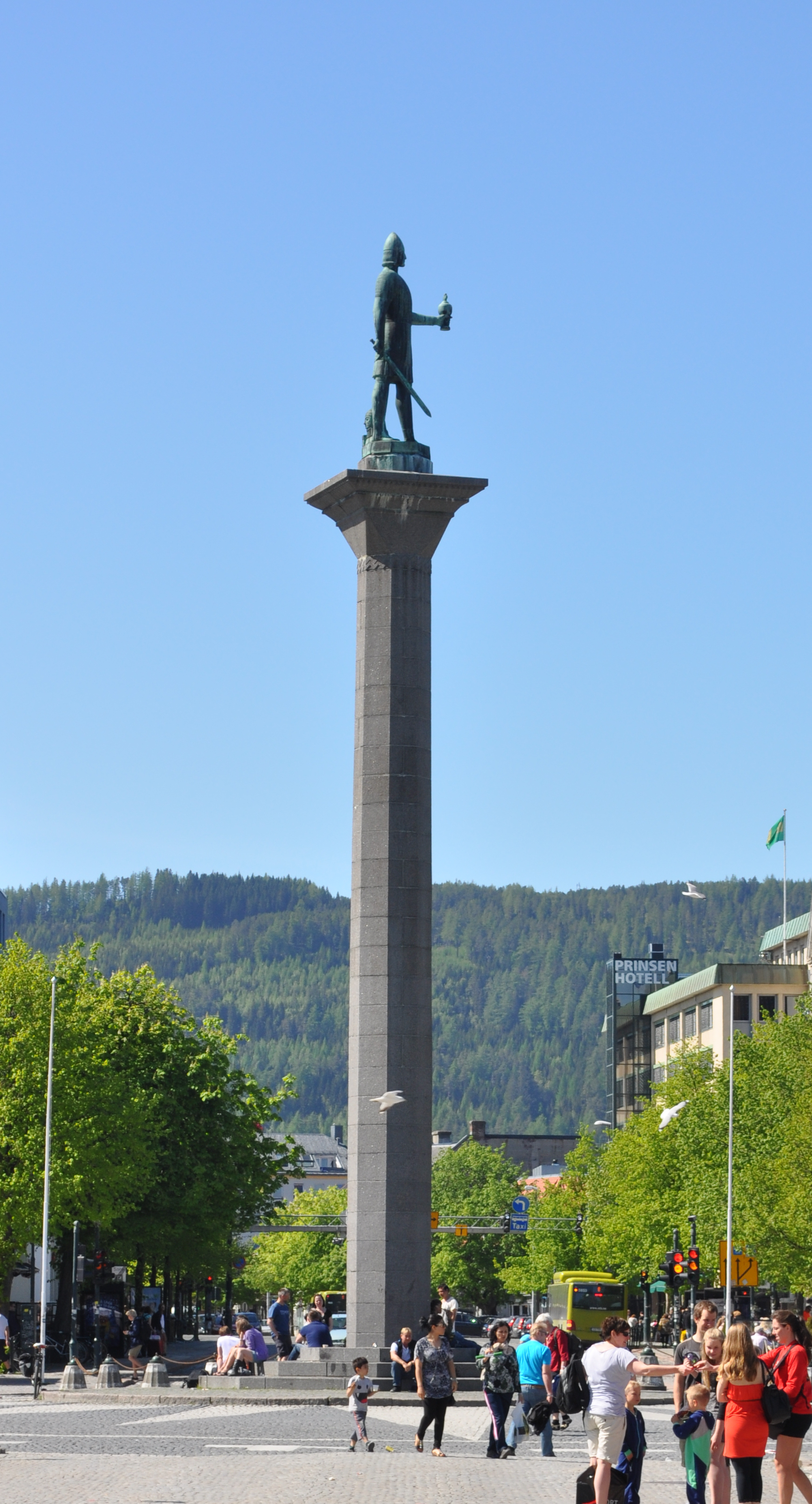
Olaf Tryggvason
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken (Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King of Norway. He is numbered as Olaf I. Olaf is seen as an important factor in the conversion of the Norse to Christianity. He is said to have built the first Christian church in Norway, in 995, and to have founded the city of Trondheim in 997. A statue of Olaf Tryggvason is located in the city's central plaza. Historical information on Olaf is sparse. He is mentioned in some contemporary English sources, and some skaldic poems. The oldest narrative source mentioning him briefly is Adam of Bremen's ''Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' of ''circa'' 1070. In the 1190s, two Latin versions of ''"Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar"'' were written in Iceland, by Oddr Snorrason and by Gunnlaugr Leifsson – these are now lost, but are thought to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Iceland_M74A1908.jpg)

