|
Exosortase
Exosortase refers to a family of integral membrane proteins that occur in Gram-negative bacteria that recognizes and cleaves the carboxyl-terminal sorting signal PEP-CTERM. The name derives from a predicted role analogous to sortase, despite the lack of any detectable sequence homology, and a strong association of exosortase genes with exopolysaccharide or extracellular polymeric substance biosynthesis loci. Many archaea have an archaeosortase, homologous to exosortases rather than to sortases. Archaeosortase A recognizes the signal PGF-CTERM, found at the C-terminus of some archaeal S-layer proteins. Following processing by archaeosortase A, the PGF-CTERM region is gone, and a prenyl-derived lipid anchor is present at the C-terminus instead. Exosortase has not itself been characterized biochemically. However, site-directed mutagenesis work on archaeosortase A, an archaeal homolog of exosortases, strongly supports the notion of a Cys active site and convergent evolution C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeosortase
An archaeosortase is a protein that occurs in the cell membranes of some archaea. Archaeosortases recognize and remove carboxyl-terminal protein sorting signals about 25 amino acids long from secreted proteins. A genome that encodes one archaeosortase may encode over fifty target proteins. The best characterized archaeosortase target is the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein, an extensively modified protein with O-linked glycosylations, N-linked glycosylations, and a large prenyl-derived lipid modification toward the C-terminus. Knockout of the archaeosortase A (artA) gene, or permutation of the motif Pro-Gly-Phe (PGF) to Pro-Phe-Gly in the S-layer glycoprotein, blocks attachment of the lipid moiety as well as blocking removal of the PGF-CTERM protein-sorting domain. Thus archaeosortase appears to be a transpeptidase, like sortase, rather than a simple protease. Archaeosortases are related to exosortases, their uncharacterized counterparts in Gram-negative bacteria. The na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sortase
Sortase refers to a group of prokaryotic enzymes that modify surface proteins by recognizing and cleaving a carboxyl-terminal sorting signal. For most substrates of sortase enzymes, the recognition signal consists of the motif LPXTG (Leu-Pro-any-Thr-Gly), then a highly hydrophobic transmembrane sequence, followed by a cluster of basic residues such as arginine. Cleavage occurs between the Thr and Gly, with transient attachment through the Thr residue to the active site Cys residue, followed by transpeptidation that attaches the protein covalently to cell wall components. Sortases occur in almost all Gram-positive bacteria and the occasional Gram-negative bacterium (e.g. ''Shewanella putrefaciens'') or Archaea (e.g. '' Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum''), where cell wall LPXTG-mediated decoration has not been reported. Although sortase A, the "housekeeping" sortase, typically acts on many protein targets, other forms of sortase recognize variant forms of the cleavage motif, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Targeting
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein-sorting Transpeptidase
A protein-sorting transpeptidase is an enzyme, such as the sortase SrtA of Staphylococcus aureus, that cleaves one or more target proteins produced by the same cell, as part of a specialized pathway of protein targeting. The typical prokaryotic protein-sorting transpeptidase is characterized as a protease, but does not simply hydrolyze a peptide bond. Instead, the larger, N-terminal portion of the cleaved polypeptide is transferred onto another molecule, such as a precursor of the peptidoglycan cell wall in Gram-positive bacteria. The term sortase is properly reserved for the set of cysteine protease enzymes sortase A, sortase B, and members of additional classes, all of which share homology. However, a growing number of additional protein sorting systems has been described in prokaryotes, involving sorting enzymes that lack any homology to sortase and that appear to have arisen separately by convergent evolution. Although the sortases are the best described members of the protein- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
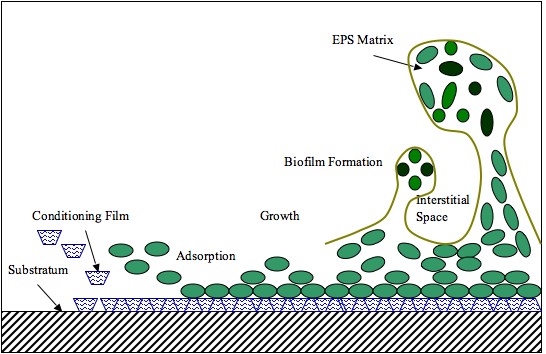
Floc (biofilm)
A floc is a type of microbial aggregate that may be contrasted with biofilms and granules, or else considered a specialized type of biofilm. Flocs appear as cloudy suspensions of cells floating in water, rather than attached to and growing on a surface like most biofilms. The floc typically is held together by a matrix of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), which may contain variable amounts of polysaccharide, protein, and other biopolymers. The formation and the properties of flocs may affect the performance of industrial water treatment bioreactors such as activated sludge The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air (or oxygen) and microorganism ... systems where the flocs form a ''sludge blanket''. Floc formation may benefit the constituent microorganisms in a number of ways, including protection fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exopolysaccharide
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, Lipopolysaccharides, and minerals. Components EPSs are mostly composed of polysaccharides (exopolysaccharides) and proteins, but include other macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and humic substances. EPSs are the construction material of bacterial settlements and either remain attached to the cell's outer surface, or are secreted into its growth medium. These compounds are important in biofilm formation and cells' attachment to surfaces. EPSs c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Polymeric Substance
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, Lipopolysaccharides, and minerals. Components EPSs are mostly composed of polysaccharides (exopolysaccharides) and proteins, but include other macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and humic substances. EPSs are the construction material of bacterial settlements and either remain attached to the cell's outer surface, or are secreted into its growth medium. These compounds are important in biofilm formation and cells' attachment to surfaces. EPSs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-layer
An S-layer (surface layer) is a part of the cell envelope found in almost all archaea, as well as in many types of bacteria. The S-layers of both archaea and bacteria consists of a monomolecular layer composed of only one (or, in a few cases, two) identical proteins or glycoproteins. This structure is built via self-assembly and encloses the whole cell surface. Thus, the S-layer protein can represent up to 15% of the whole protein content of a cell. S-layer proteins are poorly conserved or not conserved at all, and can differ markedly even between related species. Depending on species, the S-layers have a thickness between 5 and 25 nm and possess identical pores with 2–8 nm in diameter. The terminology “S-layer” was used the first time in 1976. The general use was accepted at the "First International Workshop on Crystalline Bacterial Cell Surface Layers, Vienna (Austria)" in 1984, and in the year 1987 S-layers were defined at the European Molecular Biology Organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

