|
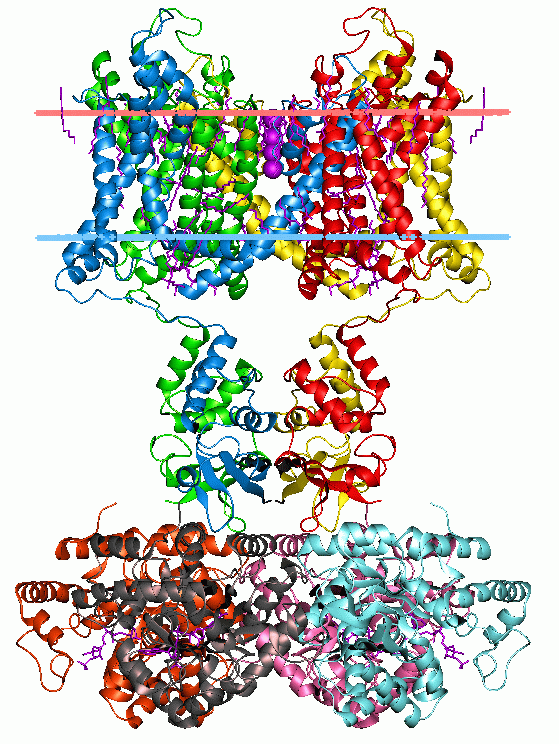
Archaeosortase
An archaeosortase is a protein that occurs in the cell membranes of some archaea. Archaeosortases recognize and remove carboxyl-terminal protein sorting signals about 25 amino acids long from secreted proteins. A genome that encodes one archaeosortase may encode over fifty target proteins. The best characterized archaeosortase target is the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein, an extensively modified protein with O-linked glycosylations, N-linked glycosylations, and a large prenyl-derived lipid modification toward the C-terminus. Knockout of the archaeosortase A (artA) gene, or permutation of the motif Pro-Gly-Phe (PGF) to Pro-Phe-Gly in the S-layer glycoprotein, blocks attachment of the lipid moiety as well as blocking removal of the PGF-CTERM protein-sorting domain. Thus archaeosortase appears to be a transpeptidase, like sortase, rather than a simple protease. Archaeosortases are related to exosortases, their uncharacterized counterparts in Gram-negative bacteria. The na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosortase
Exosortase refers to a family of integral membrane proteins that occur in Gram-negative bacteria that recognizes and cleaves the carboxyl-terminal sorting signal PEP-CTERM. The name derives from a predicted role analogous to sortase, despite the lack of any detectable sequence homology, and a strong association of exosortase genes with exopolysaccharide or extracellular polymeric substance biosynthesis loci. Many archaea have an archaeosortase, homologous to exosortases rather than to sortases. Archaeosortase A recognizes the signal PGF-CTERM, found at the C-terminus of some archaeal S-layer proteins. Following processing by archaeosortase A, the PGF-CTERM region is gone, and a prenyl-derived lipid anchor is present at the C-terminus instead. Exosortase has not itself been characterized biochemically. However, site-directed mutagenesis work on archaeosortase A, an archaeal homolog of exosortases, strongly supports the notion of a Cys active site and convergent evolution C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sortase
Sortase refers to a group of prokaryotic enzymes that modify surface proteins by recognizing and cleaving a carboxyl-terminal sorting signal. For most substrates of sortase enzymes, the recognition signal consists of the motif LPXTG (Leu-Pro-any-Thr-Gly), then a highly hydrophobic transmembrane sequence, followed by a cluster of basic residues such as arginine. Cleavage occurs between the Thr and Gly, with transient attachment through the Thr residue to the active site Cys residue, followed by transpeptidation that attaches the protein covalently to cell wall components. Sortases occur in almost all Gram-positive bacteria and the occasional Gram-negative bacterium (e.g. ''Shewanella putrefaciens'') or Archaea (e.g. '' Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum''), where cell wall LPXTG-mediated decoration has not been reported. Although sortase A, the "housekeeping" sortase, typically acts on many protein targets, other forms of sortase recognize variant forms of the cleavage motif, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomboid Protease
The rhomboid proteases are a family of enzymes that exist in almost all species. They are proteases: they cut the polypeptide chain of other proteins. This proteolytic cleavage is irreversible in cells, and an important type of cellular regulation. Although proteases are one of the earliest and best studied class of enzyme, rhomboids belong to a much more recently discovered type: the intramembrane proteases. What is unique about intramembrane proteases is that their active sites are buried in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, and they cleave other transmembrane proteins within their transmembrane domains. About 30% of all proteins have transmembrane domains, and their regulated processing often has major biological consequences. Accordingly, rhomboids regulate many important cellular processes, and may be involved in a wide range of human diseases. Intramembrane proteases Rhomboids are intramembrane serine proteases. The other types of intramembrane protease are aspartyl- an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramembrane Protease
Intramembrane proteases (IMPs), also known as intramembrane-cleaving proteases (I-CLiPs), are enzymes that have the property of cleaving transmembrane domains of integral membrane proteins. All known intramembrane proteases are themselves integral membrane proteins with multiple transmembrane domains, and they have their active sites buried within the lipid bilayer of cellular membranes. Intramembrane proteases are responsible for proteolytic cleavage in the cell signaling process known as regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP). Intramembrane proteases are not evolutionarily related to classical soluble proteases, having evolved their catalytic sites by convergent evolution. Although only recently discovered, intramembrane proteases are of significant research interest because of their major biological functions and their relevance to human disease. Classification There are four groups of intramembrane proteases, distinguished by their catalytic mechanism: *Metalloproteases: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferax Volcanii
''Haloferax volcanii'' is a species of organism in the genus ''Haloferax'' in the Archaea. Description and significance Microbiologist Benjamin Elazari Volcani first discovered ''Haloferax volcanii'', a self-named extremophile, in the 1930s. ''H. volcanii'' is a halophilic mesophile archaeon that can be isolated from hypersaline environments such as: the Dead Sea, the Great Salt Lake, and oceanic environments with high sodium chloride concentrates. ''Haloferax volcanii'' is noteworthy because it can be cultured without much difficulty, rare for an extremophile. ''H. volcanii'' is chemoorganotrophic, metabolizing sugars as a carbon source. It is primarily aerobic, but is capable of anaerobic respiration under anoxic conditions. Recently an isolate of this species was studied by researchers at University of California, Berkeley, as part of a project on the survival of haloarchaea on Mars. Genome structure The genome of ''H. volcanii'' consists of a large (4 Mb), multicopy chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate (catalytic site). Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their function. The active si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas '' homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to parallel evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the -arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid. History Arginine was first isolated in 1886 from yellow lupin seedlings by the German chemist Ernst Schulze and his assistant Ernst Steiger. He named it from the Greek ''árgyros'' (ἄργυρος) meaning "silver" due to the silver-white appearance of arginine nitrate crystals. In 1897, Schulze and Ernst Winterstein (1865–1949) determined the structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |