|
Etymology Of The Word Arab
The proper name ''Arab'' or ''Arabian'' (and cognates in other languages) has been used to translate several different but similar-sounding words in ancient and classical texts which do not necessarily have the same meaning or origin. The etymology of the term is closely linked to that of the place name ''Arabia''. Semitic etymology The root of the word has many meanings in Semitic languages including ''desert'', ''nomad'', ''merchant'', ''raven'' and ''comprehensible'' with all of these having varying degrees of relevance to the emergence of the name. It is also possible that some forms were metathetical from root "moving around", and hence, it is alleged, "nomadic." The plurality of meanings results partly from the assimilation of the proto-Semitic '' ghayin'' with in some languages. In Hebrew the word ' thus has the same triconsonantal root as the root meaning "west" ( ') "setting sun" or "evening" ( ', '). The direct Arabic cognate of this is ' ("west", etc.) rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At , the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen, as well as the southern portions of Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the classical era, the southern portions of modern-day Syria, Jordan, and the Sinai Peninsula were also considered parts of Arabia (see Arabia Petraea). The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and Arabian Desert but spread across the rest of the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa after the spread of Islam. The English word ''bedouin'' comes from the Arabic ''badawī'', which means "desert dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ''ḥāḍir'', the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky sands of the Middle East. They are traditionally divided into tribes, or clans (known in Arabic as ''ʿašāʾir''; or ''qabāʾil'' ), and historically share a common culture of herding camels and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Christian Bedouins present in the Fertile Crescent. Bedouins have been referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
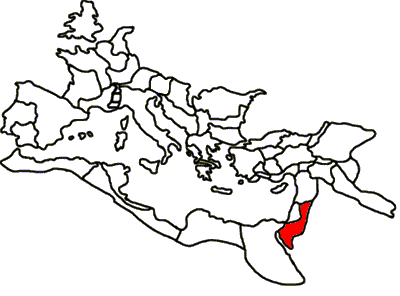
Nabatean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east. The old meaning, which was in use up to the early 20th century, covered almost the entire length of what today is called the Jordan Rift Valley, running in a north–south orientation between the southern end of the Sea of Galilee and the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba of the Red Sea at Aqaba– Eilat. This included the Jordan River Valley between the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea, the Dead Sea itself, and what today is commonly called the Arava Valley. The contemporary use of the term is restricted to this southern section alone. Geography The Arabah is in length, from the Gulf of Aqaba to the southern shore of the Dead Sea. Topographically, the region is divided into three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Petraea and Arabia Deserta. The term's meaning evolved during its history of usage. During the Early Middle Ages, the term came to be associated with the tribes of Arabia. The oldest known source mentioning "Saracens" in relation to Islam dates back to the 7th century, in the Greek-language Christian tract ''Doctrina Jacobi''. Among other major events, the tract discusses the Muslim conquest of the Levant, which occurred after the rise of the Rashidun Caliphate following the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Roman-Catholic church and European Christian leaders used the term during the Middle Ages to refer to Muslims—usually Arabs, Turks, and Iranians. By the 12th century, "Saracen" had become synonymous with "Muslim" in Medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaanite Languages
The Canaanite languages, or Canaanite dialects, are one of the three subgroups of the Northwest Semitic languages, the others being Aramaic and Ugaritic, all originating in the Levant and Mesopotamia. They are attested in Canaanite inscriptions throughout the Levant, Mesopotamia, Anatolia and the East Mediterranean, and after the founding of Carthage by Phoenician colonists, in coastal regions of North Africa and Iberian Peninsula also. Dialects have been labelled primarily with reference to Biblical geography: Hebrew ( Israelian, Judean/Biblical, Samaritan), Phoenician/Punic, Amorite, Ammonite, Philistine, Moabite, Sutean and Edomite; the dialects were all mutually intelligible, being no more differentiated than geographical varieties of Modern English. This family of languages has the distinction of being the first historically attested group of languages to use an alphabet, derived from the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, to record their writings, as opposed to the far earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the Assyrians from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 630) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC but there is no evidence yet discovered that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gindibu
Gindibu (Akkadian: ; ) was a king of the Qedarite Arabs. Reign Background Gindibu ruled over an Arab kingdom located around the Wādī Sirḥān. The kingdom of Gindibu bordered on the powerful kingdoms of Aram-Damascus and Israel in the west, although Gindibu himself was independent of Damascene hegemony. Battle of Qarqar Although Gindibu's kingdom was not on the Assyrian campaign routes and therefore was not in danger of being attacked by the Assyrians, the rise of Neo-Assyrian power in the 9th century BCE meant that the desert and border routes where Gindibu had economic interests were under threat of Assyrian interference, due to which he allied with his powerful neighbours, the kings Bar-Hadad II of Aram-Damascus and Ahab of Israel, against the Assyrian Empire. Fearing disruptions by the Assyrians, Gindibu led 1000 camelry troops at the battle of Battle of Qarqar in 853 BCE on the side of the alliance led by Aram-Damascus and Israel against Shalmaneser III of Assyria. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arava (other)
Arava, Aravah or Arabah may refer to: Places *Arava, Estonia, a village in Anija Commune, Harju County, Estonia *Arava(h) (Hebrew) or Arabah (Arabic), a section of the Great Rift Valley between the Dead Sea and the Gulf of Aqaba in Israel and Jordan Other uses *Arava Institute for Environmental Studies, an Israeli study programme *Arava Power Company, an Israeli solar energy company *Arava Shahaf (born 1990), Israeli footballer * Arava spider, a huntsman spider found in the southern Arava Valley of Israel and Jordan *Arava, a brand name for the antirheumatic drug leflunomide *IAI Arava, a plane manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries *Aravah (Sukkot), a willow branch, one of the Four Species used on the Jewish holiday of Sukkot See also *Arraba (other) *Araba (other) Araba may refer to: Places and jurisdictions * the Ancient Arab Kingdom of Hatra, a Roman-Parthian buffer state in modern Iraq * Basque name of Álava, a province and medieval bishopric (now La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algarve
The Algarve (, , ; from ) is the southernmost NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities ( ''concelhos'' or ''municípios'' in Portuguese). The region has its administrative centre in the city of Faro, where both the region's international airport (IATA: FAO) and public university, the University of Algarve, are located. The region coincides with Faro District and is subdivided into two zones, one to the West ( Barlavento) and another to the East ( Sotavento). Tourism and related activities are extensive and make up the bulk of the Algarve's summer economy. Production of food, which includes fish and other seafood, as well as different types of fruit and vegetables, such as oranges, figs, plums, carob pods, almonds, avocados, tomatoes, cauliflowers, strawberries, and raspberries, are also economically important in the region. Although Lisbon surpasses the Algarve in terms of tourism reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abi Ishaq
ʿAbd-Allāh ibn Abī Isḥāq al-Ḥaḍramī (Arabic, عَبْدُ اللّهِ بْنُ أَبِي إِسْحَاقَ الْحَضْرَمِيُّ), (died AD 735 / AH 117)Kees Versteegh, ''Arabic Grammar and Qur'anic Exegesis in Early Islam'', pg. 17. Leiden: Brill Publishers, 1993. was an Arab from Yemen and is considered the first grammarian of the Arabic language.Monique Bernards, "Pioneers of Arabic Linguistic Studies." Taken from ''In the Shadow of Arabic: The Centrality of Language to Arabic Culture'', pg. 213. Ed. Bilal Orfali. Leiden: Brill Publishers, 2011. He compiled a prescriptive grammar by referring to the usage of the Bedouins, whose language was seen as especially pure (see also iʿrāb, aʿrāb). He is also considered the first person to use linguistic analogy in Arabic. Two students of Ibn Abi Ishaq's were Harun ibn Musa and Abu 'Amr ibn al-'Ala'. His student al-Thaqafi seems to have had more prescriptive views while al-'Ala's were more descriptive. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)