|
Equity (typeface)
Ehrhardt is an Serif#Old-style, old-style serif typeface released by the British branch of the Monotype Imaging, Monotype Corporation in 1938. Ehrhardt is a modern adaptation of metal type, printing types of "stout Dutch character" from the Dutch Baroque tradition sold by the Ehrhardt Type foundry, foundry in Leipzig. These were cut by the Hungarians in Romania, Hungarian-Transylvanian pastor and punchcutting, punchcutter Miklós Tótfalusi Kis, Miklós (Nicholas) Tótfalusi Kis while in Amsterdam in the period from 1680 to 1689. From 1937 to 1938, Monotype re-cut the type for modern-day usage, and it has become a popular book typeface. Ehrhardt has a slightly condensed design, giving it a strongly vertical, crisp appearance. Historical background Miklós Tótfalusi Kis, Miklós Kis, a Transylvanian Protestant pastor and schoolteacher, became deeply interested in printing after being sent to Amsterdam to help print a Hungarian Protestant translation of the Bible. This was a peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serif
In typography, a serif () is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface (or serifed typeface), and a typeface that does not include them is sans-serif. Some typography sources refer to sans-serif typefaces as "grotesque" (in German, ) or "Gothic", and serif typefaces as "roman". Origins and etymology Serifs originated from the first official Greek writings on stone and in Latin alphabet with inscriptional lettering—words carved into stone in Roman antiquity. The explanation proposed by Father Edward Catich in his 1968 book ''The Origin of the Serif'' is now broadly but not universally accepted: the Roman letter outlines were first painted onto stone, and the stone carvers followed the brush marks, which flared at stroke ends and corners, creating serifs. Another theory is that serifs were devised to neate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
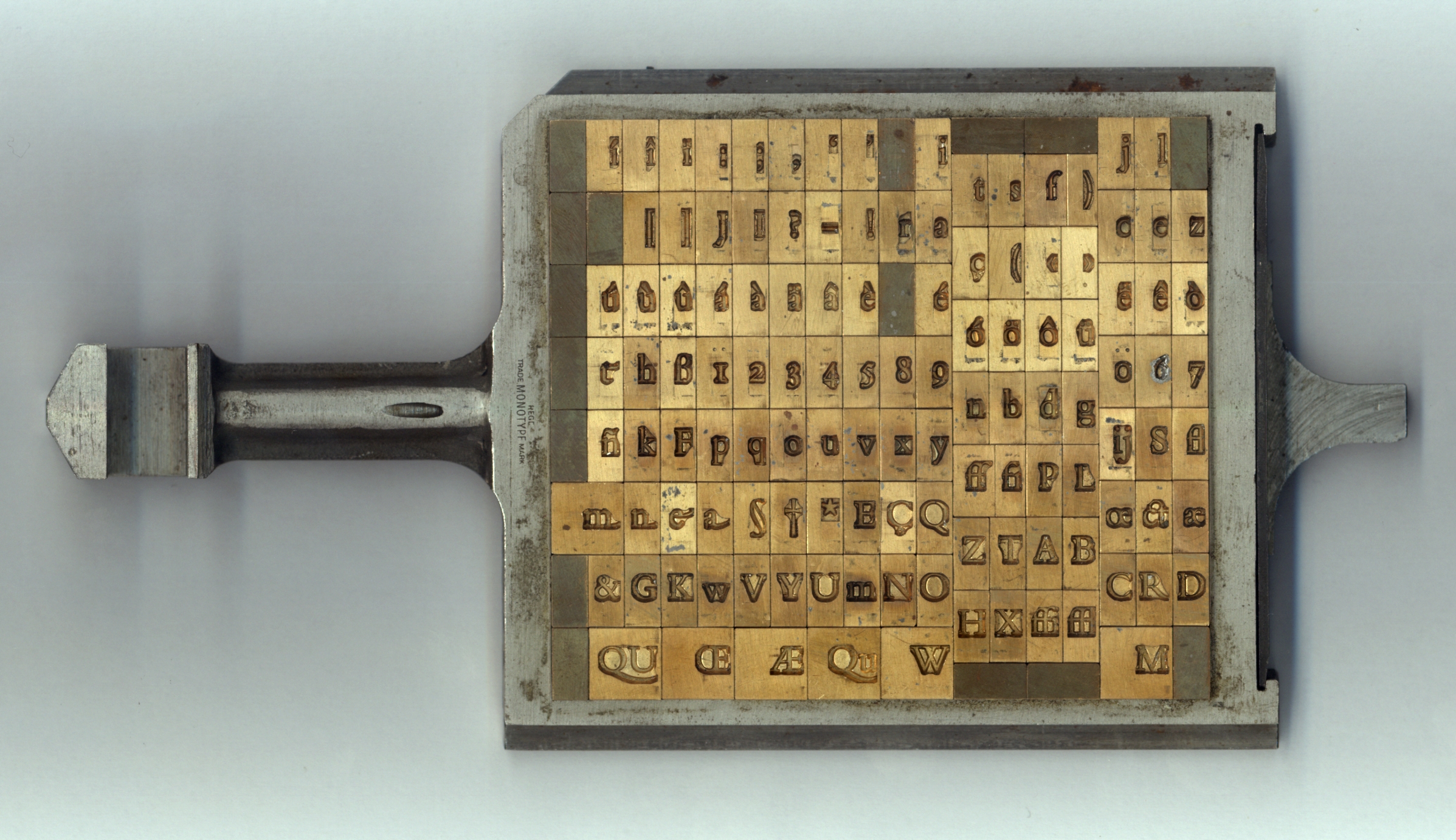
Matrix (printing)
In the manufacture of metal type used in letterpress printing, a matrix (from the Latin meaning ''womb'' or ''a female breeding animal'') is the mould used to cast a letter, known as a sort. Matrices for printing types were made of copper. However, in printmaking the matrix is whatever is used, with ink, to hold the image that makes up the print, whether a plate in etching and engraving or a woodblock in woodcut. Description In letterpress or "cold metal" typesetting, used from the beginning of printing to the late nineteenth century, the matrix of one letter is inserted into the bottom of an adjustable-width hand mould, the mould is locked and molten type metal is poured into a straight-sided vertical cavity above the matrix. When the metal has cooled and solidified the mould is unlocked and the newly cast metal sort is removed. The matrix can then be reused to produce more copies of the sort.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design.'' John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. (pp 58� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Janson
Anton Janson (January 17, 1620 in Wanden/Wauden? in Friesland – November 18, 1687 in Leipzig) was a Dutch type founder and printer. The typeface Janson Janson is the name given to a set of old-style serif typefaces from the Dutch Baroque period, and modern revivals from the twentieth century. Janson is a crisp, relatively high-contrast serif design, most popular for body text. Janson is based ... is named after him, although it can also be attributed to Hungarian punch-cutter and printer ''Miklós (Nicholas) Kis'' (1650–1702). References *Carter, Rob, Day, Ben, Meggs, Philip. ''Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Second Edition.'' Van Nostrand Reinhold, Inc: 1993 . *Meggs, Philip B. and McKelvey, Roy. ''Revival of the Fittest: Digital Versions of Classic Typefaces.'' RC Publications: 2000. . * Molnár, József. ''Misztótfalusi Kis Miklós''. Európai Protestáns Szabadegyetem: 2000. . 1620 births 1687 deaths Dutch typographers and type designers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest city in the state of Hesse after Frankfurt am Main, Wiesbaden, and Kassel. Darmstadt holds the official title "City of Science" (german: link=no, Wissenschaftsstadt) as it is a major centre of scientific institutions, universities, and high-technology companies. The European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) and the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) are located in Darmstadt, as well as Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI Centre for Heavy Ion Research, where several chemical elements such as bohrium (1981), meitnerium (1982), hassium (1984), darmstadtium (1994), roentgenium (1994), and copernicium (1996) were discovered. The existence of the following elements were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stempel Type Foundry
D. Stempel AG was a German typographic foundry founded by David Stempel (1869–1927), in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Many important font designers worked for the Stempel foundry, including Hans Bohn, Warren Chappell, F. H. Ehmcke, Friedrich Heinrichsen, Hanns Th. Hoyer, F. W. Kleukens, Erich Meyer, Hans Möhring, Hiero Rhode, Wilhelm Schwerdtner, Herbert Thannhaeuser, Martin Wilke, Rudolf Wolf, Victor Hammer, Hermann Zapf, and Gudrun Zapf von Hesse. With the introduction of ''Memphis'' in 1929, the foundry was the first to cast modern slab serif typefaces. From 1900 to 1983, Stempel had an exclusive relationship with Mergenthaler Linotype Company, as one of just a few producers of matrices for the Linotype machine worldwide and the only one in Europe. Starting in 1925, Stempel types were distributed in the United States by Continental Type Founders Association. Linotype AG became the majority stockholder in 1941. In 1977, Stempel began manufacturing Phototypes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Colour
Type color, or colour, is an element of typography that describes how dense or heavy the text appears on the page. Finding the correct balance of type color and white space can make text more easily readable. The term ''type color'' should not be confused with the usual meaning of color, (i.e. red, yellow, blue); instead it has more to do with the blackness or boldness of the text on the page. A bold font creates more contrast on the page, therefore creates more emphasis. Using a bold font is therefore one way that type color can be adjusted. There are four different decisions a typographer can make that affect the type color. These are the letter spacing, the way the specific font or type is designed, word spacing, and line spacing (leading). Text will appear darker or blacker if the letters are kerned more closely, or if there is less spacing between the lines of text. Other elements that affect type color can be harder to grasp, such as the rhythm of the type, the contrast, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font. For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal line which lies below the ''v'' created by the two lines converging. In the letter ''p'', it is the stem reaching down past the ''o''. In most fonts, descenders are reserved for lowercase characters such as ''g'', ''j'', ''q'', ''p'', ''y'', and sometimes ''f''. Some fonts, however, also use descenders for some numerals (typically ''3'', ''4'', ''5'', ''7'', and ''9''). Such numerals are called old-style numerals. (Some italic fonts, such as Computer Modern italic, put a descender on the numeral ''4'' but not on any other numerals. Such fonts are not considered old-style.) Some fonts also use descenders for the tails on a few uppercase letters such as ''J'' and ''Q''. The parts of characters that extend above the x-height of a font are called ascenders. Descenders a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-height
upright 2.0, alt=A diagram showing the line terms used in typography In typography, the x-height, or corpus size, is the distance between the baseline and the mean line of lowercase letters in a typeface. Typically, this is the height of the letter ''x'' in the font (the source of the term), as well as the letters ''v'', ''w'', and ''z''. (Curved letters such as ''a'', ''c'', ''e'', ''m'', ''n'', ''o'', ''r'', ''s'', and ''u'' tend to exceed the x-height slightly, due to overshoot; ''i'' has a dot that tends to go above x-height.) One of the most important dimensions of a font, x-height defines how high lowercase letters without ascenders are compared to the cap height of uppercase letters. Display typefaces intended to be used at large sizes, such as on signs and posters, vary in x-height. Many have high x-heights to be read clearly from a distance. This, though, is not universal: some display typefaces such as Cochin and Koch-Antiqua intended for publicity uses have low x- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Garamond
Claude Garamont (–1561), known commonly as Claude Garamond, was a French type designer, publisher and punch-cutter based in Paris. Garamond worked as an engraver of punches, the masters used to stamp matrices, the moulds used to cast metal type. He worked in the tradition now called old-style serif design, which produced letters with a relatively organic structure resembling handwriting with a pen but with a slightly more structured and upright design. Considered one of the leading type designers of all time, he is recognised to this day for the elegance of his typefaces. Many old-style serif typefaces are collectively known as Garamond, named after the designer. Garamond was one of the first independent punchcutters, specialising in type design and punch-cutting as a service to others rather than working in house for a specific printer. His career therefore helped to define the future of commercial printing with typefounding as a distinct industry to printing books. Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garamond
Garamond is a group of many serif typefaces, named for sixteenth-century Parisian engraver Claude Garamond, generally spelled as Garamont in his lifetime. Garamond-style typefaces are popular and particularly often used for book printing and body text. Garamond's types followed the model of an influential typeface cut for Venetian printer Aldus Manutius by his punchcutter Francesco Griffo in 1495, and are in what is now called the old-style of serif letter design, letters with a relatively organic structure resembling handwriting with a pen, but with a slightly more structured, upright design. Following an eclipse in popularity in the eighteenth and nineteenth century, many modern revival faces in the Garamond style have been developed. It is common to pair these with italics based on those created by his contemporary Robert Granjon, who was well known for his proficiency in this genre. However, although Garamond himself remains considered a major figure in French printing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of English Studies
The Institute of English Studies (abbreviated as IES) is a centre of excellence in the research, promotion and facilitation in the field English Literature and Language. With a specialisation in book history, palaeography and textual scholarship, the IES facilitates the advanced study and research of English Studies in the national and international academic community. The Institute, located in Senate House, London, is one of the nine institutes that together comprise the School of Advanced Study, University of London. History The Institute was founded as the Centre for English Studies in 1991. Institute status was conferred by the University Council on 2 December 1998, and it officially became known as the Institute of English Studies on New Year's Day, 1999. The Institute faced closure in 2014, but a successful campaign in 2014 resulted in the reversal of this decision. Networks The Institute is partner in a number of important research networks and collaborations. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_FFM_Schriftgießerei_D.Stempel_AG.jpg)



