|
Datu
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, especially in Mindanao, Sulu and Palawan, but it was used much more extensively in early Philippine history, particularly in the regions of Central and Southern Luzon, the Visayas and Mindanao. It is a cognate of the title ''ratu'' in several other Austronesian languages. Overview In early Philippine history, datus and a small group of their close relatives formed the "apex stratum" of the traditional three-tier social hierarchy of lowland Philippine societies. Only a member of this birthright aristocracy (called "''maginoo''", "''nobleza''", "''maharlika''", or "''timagua''" by various early chroniclers) could become a datu; members of this elite could hope to become a datu by demonstrating prowess in war or exceptional leadership. In large c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madja-as
The Confederation of Madya-as was a legendary pre-colonial supra-baranganic polity on the island of Panay in the Philippines. It was mentioned in Pedro Monteclaro's book titled Maragtas. It was supposedly created by Datu Sumakwel to exercise his authority over all the other datus of Panay. Like the Maragtas and the Code of Kalantiaw, the historical authenticity of the confederation is disputed, as no other documentation for Madya-as exists outside of Monteclaro's book. However, the notion that the Maragtas is an original work of fiction by Monteclaro is disputed by a 2019 Thesis, named "Mga Maragtas ng Panay: Comparative Analysis of Documents about the Bornean Settlement Tradition" by Talaguit Christian Jeo N. of the De La Salle UniversityMga Maragtas ng Panay Comparative Analysis of Docume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Barangay
In early Philippine history, Barangay is the term historically used by scholars to describe the complex sociopolitical units which were the dominant organizational pattern among the various peoples of the Philippine archipelago , . in the period immediately before the arrival of European colonizers. The term originally referred to both a house on land and a boat on water, containing families, friends and dependents. These sociopolitical units were sometimes also referred to as barangay states, but are more properly referred to using the technical term "polity", rather than "state", so they are usually simply called "barangays", but evidence suggests a considerable degree of independence as a type of "city states" ruled by datus, rajahs and lakans and sultans. Some barangays were well-organized independent villages, consisting of thirty to a hundred households. Other barangays — most notably those in Maynila, Tondo, Panay, Pangasinan, Cebu, Bohol, Butuan, Cotabato, and Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindanau; fil, Kasultanan ng Maguindanao; ar, سلطنة ماجينداناو) was a sultanate that ruled parts of the island of Mindanao, in the southern Philippines, especially in modern-day Maguindanao province, Soccsksargen, Zamboanga Peninsula and Davao Region. Its known historical influence stretches from the peninsula of Zamboanga to the bay of Sarangani. During the era of European colonization, the Sultanate maintained friendly relations with British and Dutch traders. History Before the founding of the Sultanate of Maguindanao, according to the Yuan Dynasty annals, Nanhai Zhi (At year 1304), a polity known as Wenduling 文杜陵 was its predecessor-state. This Wenduling was invaded by then Hindu Brunei, called Pon-i (present-day Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
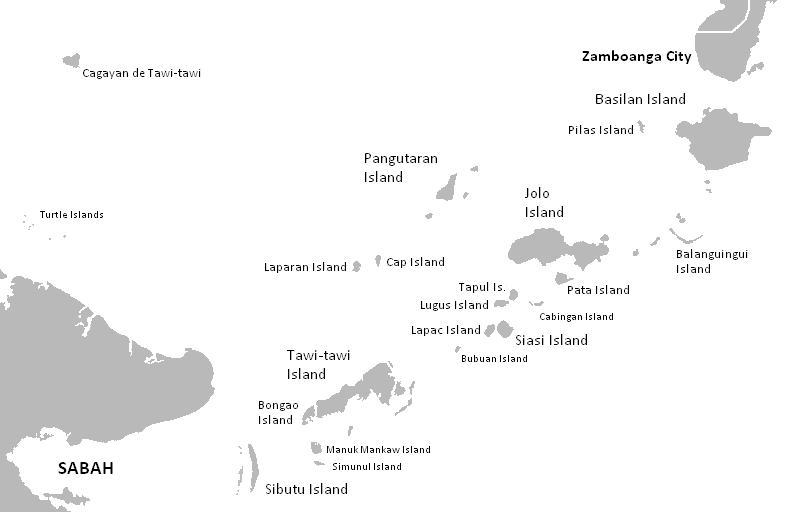
Sultanate Of Sulu
The Sultanate of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Kasultanan sin Sūg'', كاسولتانن سين سوڬ; malay language, Malay: ''Kesultanan Sulu''; fil, Sultanato ng Sulu; Chavacano: ''Sultanato de Sulu/Joló''; ar, سلطنة سولك) was a Muslim Sovereign state, state that ruled the Sulu Archipelago, parts of Mindanao and certain portions of Palawan in today's Philippines, alongside parts of present-day Sabah, North Kalimantan, North and East Kalimantan in north-eastern Borneo. The sultanate was founded either on 17 November 1405 or 1457 by Johore-born explorer and religious scholar Sharif ul-Hāshim of Sulu, Sharif ul-Hashim. ''Paduka Mahasari Maulana al Sultan Sharif ul-Hashim'' became his full regnal name, ''Sharif-ul Hashim'' is his abbreviated name. He settled in Buansa, Sulu. After the marriage of Abu Bakr and a local ''dayang-dayang'' (princess) Paramisuli, he founded the sultanate. The sultanate gained its independence from the Bruneian Empire in 1578. At i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tondo (historical Polity)
In History of the Philippines (900–1521), early Philippine history, the Tagalog people, Tagalog settlement at Tondo (; Baybayin: ) was a major trade hub located on the northern part of the List of islands in the Greater Manila Area, Pasig River delta, on Luzon island.Abinales, Patricio N. and Donna J. Amoroso, State and Society in the Philippines. Maryland: Rowman and Littlefield, 2005. as referred to in http://malacanang.gov.ph/75832-pre-colonial-manila/#_ftn1 Together with Maynila, the polity (''bayan'') on the southern part of the Pasig River delta, it established a shared monopoly on the trade of Chinese goods throughout the rest of the Philippine archipelago, making it an established force in trade throughout Southeast Asia and East Asia. Tondo is of particular interest to Filipino historians and historiography, historiographers because it is one of the oldest historically documented settlements in the Philippines. Scholars generally agree that it was mentioned in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th to the 12th century AD. Srivijaya was the first polity to dominate much of western Maritime Southeast Asia. Due to its location, the Srivijaya developed complex technology utilizing maritime resources. In addition, its economy became progressively reliant on the booming trade in the region, thus transforming it into a prestige goods-based economy. The earliest reference to it dates from the 7th century. A Tang dynasty Chinese monk, Yijing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in year 671 for six months. The earliest known inscription in which the name Srivijaya appears also dates from the 7th century in the Kedukan Bukit inscription found near Palembang, Sumatra, dated 16 June 682. Between the late 7th and early 11th century, Srivijaya rose t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajahnate Of Butuan
Butuan also called the Butan Rajanate and the Kingdom of Butuan (; Butuanon: ; ; ) was a precolonial Philippine polity centred on the northern Mindanao island in the modern city of Butuan in what is now the southern Philippines. It was known for its mining of gold, its gold products and its extensive trade network across the Nusantara area. The kingdom had trading relationships with the ancient civilizations of Japan, China, India, Indonesia, Persia, Cambodia and areas now comprised in Thailand. The balangay (large outrigger boats) that have been found along the east and west banks of the Libertad river (old Agusan River) have revealed much about Butuan's history. As a result, Butuan is considered to have been a major trading port in the Caraga region during the pre-colonial era. Historiography Chinese records Evidence indicates that Butuan was in contact with the Song dynasty of China by at least 1001 AD. The Chinese annal ''Song Shih'' recorded the first appearance of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajahnate Of Maynila
In early Philippine history, the Tagalog Bayan ("country" or "city-state") of Maynila ( tl, Bayan ng Maynila; Pre-virama Baybayin: ) was a major Tagalog city-state on the southern part of the Pasig River delta, where the district of Intramuros currently stands.Abinales, Patricio N. and Donna J. Amoroso, State and Society in the Philippines. Maryland: Rowman and Littlefield, 2005. Historical accounts indicate that the city-state was led by sovereign rulers who were referred to with the title of ''raja'' ("king"). Other accounts also refer to it as the "Kingdom of Luzon", although some historians suggest that this might rather refer to the Manila Bay region as a whole. The earliest oral traditions suggest that Maynila was founded as a Muslim principality in as early as the 1250s, supposedly supplanting an even older pre-Islamic settlement. However, the earliest archeological findings for organized human settlements in the area dates to around 1500s. By the 16th century, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., Order of precedence, precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically Hereditary title, hereditary and Patrilinearity, patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Bisayan languages, Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three Island groups of the Philippines, principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, it consists of several islands, primarily surrounding the Visayan Sea, although the Visayas are also considered the northeast extremity of the entire Sulu Sea. Its inhabitants are predominantly the Visayan peoples. The major islands of the Visayas are Panay, Negros (Philippines), Negros, Cebu Island, Cebu, Bohol Island, Bohol, Leyte and Samar. The region may also include the provinces of Palawan, Romblon, and Masbate whose populations identify as Visayan and whose languages are more closely related to other Visayan languages than to the major languages of Luzon. There are three administrative Regions of the Philippines, regions in the Visayas: Western Visayas (pop. 7.9 million), Central V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the fourth most populous island in the world. It is the 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands of Masbate, Palawan and Romblon are also included, although these three are sometimes grouped with another of the island groups, the Visayas. Etymology The name ''Luz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . The etymologically related English term "county" denoted the territories associated with the countship. Definition The word ''count'' came into English from the French ''comte'', itself from Latin ''comes''—in its accusative ''comitem''—meaning “companion”, and later “companion of the emperor, delegate of the emperor”. The adjective form of the word is "comital". The British and Irish equivalent is an earl (whose wife is a "countess", for lack of an English term). In the late Roman Empire, the Latin title ''comes'' denoted the high rank of various courtiers and provincial officials, either military or administrative: before Anthemius became emperor in the West in 467, he was a military ''comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |