Sultanate of Sulu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sultanate of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Kasultanan sin Sūg'', كاسولتانن سين سوڬ;
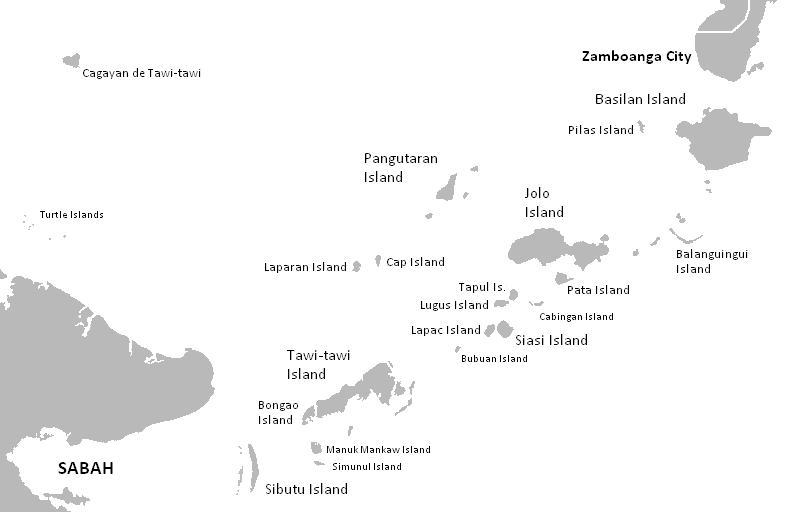 The present area of the Sultanate of Sulu was once under the influence of the
The present area of the Sultanate of Sulu was once under the influence of the
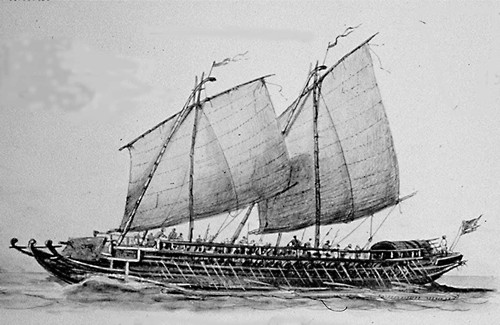
 The Sulu sultanate became notorious for its so-called "Moro Raids" or acts of piracy directed toward Spanish settlements in the Visayan areas with the aim of capturing slaves and other goods from these coastal towns. The Tausug pirates used boats known collectively by Europeans as ''proas'' (predominantly the ''
The Sulu sultanate became notorious for its so-called "Moro Raids" or acts of piracy directed toward Spanish settlements in the Visayan areas with the aim of capturing slaves and other goods from these coastal towns. The Tausug pirates used boats known collectively by Europeans as ''proas'' (predominantly the ''
 In the 18th century, Sulu's dominion covered most of northeastern part of Borneo. However areas like Tempasuk and Abai had never really shown much allegiance to its earlier ruler, Brunei, subsequently similar treatment was given to Sulu. Dalrymple, who made a treaty of allegiance in 1761 with Sulu, had to make a similar agreement with the rulers of Tempasuk and Abai on the north Borneo coast in 1762. The Sultanate of Sulu totally gave up its domain over Palawan to Spain in 1705 and Basilan to Spain in 1762. The territory ceded to Sulu by Brunei initially stretched south to Tapean Durian (now Tanjong Mangkalihat) (another source mentioned the southernmost boundary is at Dumaring), near the Straits of Macassar (now Kalimantan). From 1726 to 1733, the Sulu sultanate restarted their tributary relationship with China, now the
In the 18th century, Sulu's dominion covered most of northeastern part of Borneo. However areas like Tempasuk and Abai had never really shown much allegiance to its earlier ruler, Brunei, subsequently similar treatment was given to Sulu. Dalrymple, who made a treaty of allegiance in 1761 with Sulu, had to make a similar agreement with the rulers of Tempasuk and Abai on the north Borneo coast in 1762. The Sultanate of Sulu totally gave up its domain over Palawan to Spain in 1705 and Basilan to Spain in 1762. The territory ceded to Sulu by Brunei initially stretched south to Tapean Durian (now Tanjong Mangkalihat) (another source mentioned the southernmost boundary is at Dumaring), near the Straits of Macassar (now Kalimantan). From 1726 to 1733, the Sulu sultanate restarted their tributary relationship with China, now the
 The Sulu sultanate later came under the control of Spain in Manila. In 1885,
The Sulu sultanate later came under the control of Spain in Manila. In 1885,
 The sultanate's political power was relinquished in March 1915 after American commanders negotiated with Sultan Jamalul Kiram on behalf of Governor-General
The sultanate's political power was relinquished in March 1915 after American commanders negotiated with Sultan Jamalul Kiram on behalf of Governor-General
/ref> Lakandula was the uncle of the Muslim king of Manila, Rajah Sulayman, and they had a grandmother from Sulu in the person of the Tausug princess, Laila Mechanai, wife of Sultan Bolkiah of Brunei and ancestor of
 The dispute is based on a territorial claim by the
The dispute is based on a territorial claim by the 
 The Chinese set up a trading network between
The Chinese set up a trading network between
 After the destruction of the pirate haunts of
After the destruction of the pirate haunts of
 The two main social classes of the sultanete were as follows:
*
The two main social classes of the sultanete were as follows:
*
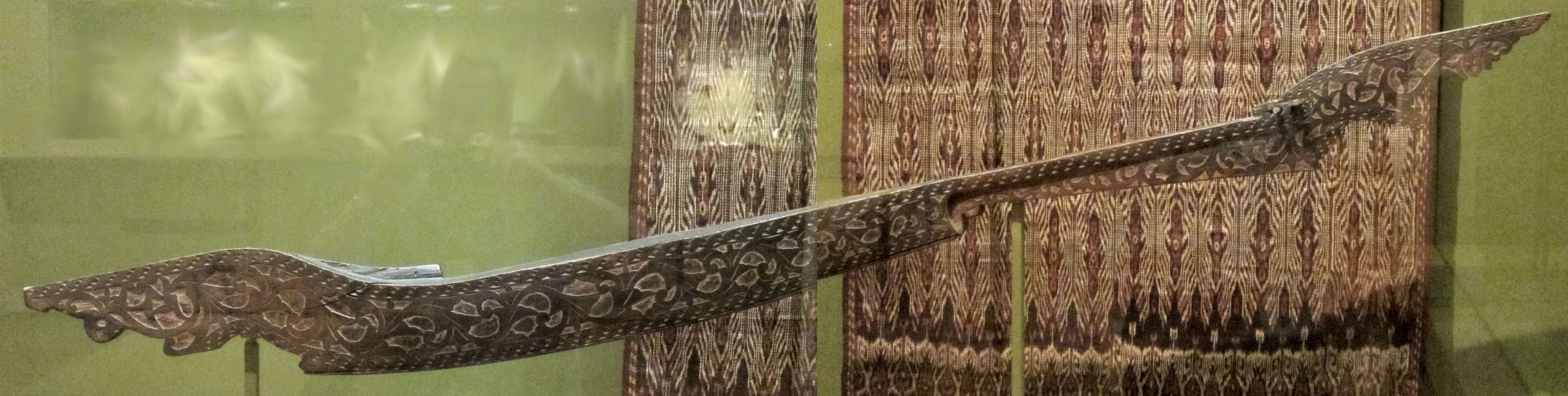 The Sultanate of Sulu, along with the rest of Mindanao, has a long tradition of decorative arts known as ''okir'' or ''ukkil''. ''Ukkil'' is the Tausug word for "wood carving" or "engraving". The Tausug and
The Sultanate of Sulu, along with the rest of Mindanao, has a long tradition of decorative arts known as ''okir'' or ''ukkil''. ''Ukkil'' is the Tausug word for "wood carving" or "engraving". The Tausug and
File:18th Century Flag of Sulu.svg, Flag of Sulu sultanate according to
Line of succession of the Sultans of Sulu of the Modern Era
as published in the Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines
Philippine Provincial Government of Sulu – The official list of Sultans
on WorldStatesMen.org {{authority control
Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
: ''Kesultanan Sulu''; fil, Sultanato ng Sulu; Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speakers. ...
: ''Sultanato de Sulu/Joló''; ar, سلطنة سولك) was a Muslim state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
that ruled the Sulu Archipelago, parts of Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
and certain portions of Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in ...
in today's Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, alongside parts of present-day Sabah
Sabah () is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indone ...
, North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and East Kalimantan
East Kalimantan (Indonesian: ) is a province of Indonesia. Its territory comprises the eastern portion of Borneo. It had a population of about 3.03 million at the 2010 census (within the current boundary), 3.42 million at the 2015 census, and 3. ...
in north-eastern Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
.
The sultanate was founded either on 17 November 1405 or 1457 by Johore
Johor (; ), also spelled as Johore, is a state of Malaysia in the south of the Malay Peninsula. Johor has land borders with the Malaysian states of Pahang to the north and Malacca and Negeri Sembilan to the northwest. Johor shares maritime bor ...
-born explorer and religious scholar Sharif ul-Hashim. ''Paduka Mahasari Maulana al Sultan Sharif ul-Hashim'' became his full regnal name
A regnal name, or regnant name or reign name, is the name used by monarchs and popes during their reigns and, subsequently, historically. Since ancient times, some monarchs have chosen to use a different name from their original name when they ac ...
, ''Sharif-ul Hashim'' is his abbreviated name. He settled in Buansa, Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
. After the marriage of Abu Bakr and a local ''dayang-dayang'' (princess) Paramisuli, he founded the sultanate. The sultanate gained its independence from the Bruneian Empire
Bruneian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Brunei
* A person from Brunei, or of Bruneian descent. For information about the Bruneian people, see Demographics of Brunei and Culture of Brunei. For specific Bruneians, see List of Bruneians.
...
in 1578.
At its peak, it stretched over the islands that bordered the western peninsula of Zamboanga in Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
in the east to Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in ...
in the north. It also covered areas in the northeast of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
, stretching from Marudu Bay, to Tepian Durian (in present-day Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
). Another source stated the area included stretched from Kimanis
Kimanis (Chinese: 金馬利) is a town and also a parliamentary constituency in Papar District, West Coast Division of Sabah, Malaysia. It is located approximately 45 kilometres south of the city of Kota Kinabalu, halfway between Papar and B ...
Bay, which also overlaps with the boundaries of the Bruneian Sultanate
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by the ...
. Following the arrival of western powers
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
such as the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, French, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, the Sultan thalassocracy
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples ...
and sovereign political powers were relinquished by 1915 through an agreement that was signed with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. In the second half of the 20th century, Filipino government extended official recognition of the head of the royal house of the sultanate, before the ongoing succession dispute.
In Kakawin Nagarakretagama, the Sultanate of Sulu is referred to as Solot, one of the countries in the Tanjungnagara archipelago (Kalimantan-Philippines), which is one of the areas that is under the influence of the mandala area of the Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
kingdom in the archipelago.
History
Pre-establishment
 The present area of the Sultanate of Sulu was once under the influence of the
The present area of the Sultanate of Sulu was once under the influence of the Bruneian Empire
Bruneian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Brunei
* A person from Brunei, or of Bruneian descent. For information about the Bruneian people, see Demographics of Brunei and Culture of Brunei. For specific Bruneians, see List of Bruneians.
...
before it gained its own independence in 1578. During the 13th century the people of Sulu began migrating to present-day Zamboanga and the Sulu archipelago from their homelands in northeastern Mindanao. Scott (1994) mentions the origins of the Sulu as being the descendants of ancient Butuanons and Surigaonons from the Rajahnate of Butuan
Butuan also called the Butan Rajanate and the Kingdom of Butuan (; Butuanon: ; ; ) was a precolonial Philippine polity centred on the northern Mindanao island in the modern city of Butuan in what is now the southern Philippines. It was known f ...
, which was then Hindu like pre-islamic Sulu. They moved south and established a spice trading port in pre-Islamic Sulu. Sultan Batarah Shah Tengah, who ruled as sultan in 1600, was said to be an actual native of Butuan. The Butuanon-Surigaonon origins of the Tausugs is suggested by the relationship of their languages, as the Butuanon, Surigaonon and Tausug languages are all grouped under the Southern sub-family of Visayan. Later, the earliest known settlement in this area soon to be occupied by the sultanate was in Maimbung
Maimbung, officially the Municipality of Maimbung ( Tausūg: كاومن سين ماءيمبوڠ; tl, Bayan ng Maimbung), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,59 ...
, Jolo
Jolo ( tsg, Sūg) is a volcanic island in the southwest Philippines and the primary island of the province of Sulu, on which the capital of the same name is situated. It is located in the Sulu Archipelago, between Borneo and Mindanao, and has ...
. During this time, Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
was called Lupah Sug
In the Philippine history, the ''Lupah Sug'' ( Jawi: سوگ; ''Sūg'') was a predecessor state before the establishment of Sultanate of Sulu.
History
Hindu principality of Maimbung
Sulu that time was called ''Lupah Sug'' and ruled by the In ...
. The principality of Maimbung, populated by Buranun people (or ''Budanon'', literally means "mountain-dwellers"), was first ruled by a certain rajah
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested fr ...
who assumed the title Rajah Sipad the Older. According to Majul, the origins of the title ''rajah sipad'' originated from the Hindu sri
Shri (; , ) is a Sanskrit term denoting resplendence, wealth and prosperity, primarily used as an honorific.
The word is widely used in South and Southeast Asian languages such as Marathi, Malay (including Indonesian and Malaysian), Javanes ...
pada, which symbolises authority. The principality was instituted and governed using the system of rajahs. Sipad the Older was succeeded by Sipad the Younger.
Some Chams
The Cham (Cham: ''Čaṃ'') or Champa people (Cham: , ''Urang Campa''; vi, Người Chăm or ; km, ជនជាតិចាម, ) are an Austronesian ethnic group. From the 2nd century to 1832 the Cham populated Champa, a contiguous territo ...
who migrated to Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
were called Orang Dampuan. The Champa civilization and the port-kingdom of Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
engaged in commerce with each other which resulted in merchant Chams settling in Sulu where they were known as Orang Dampuan from the 10th–13th centuries. In contrast to their cousins in the Butuan Rajahnate that considered themseleves diplomatic competitors against Champa for China trade, (under Butuan's Rajah Kiling); instead, Sulu freely traded with the Champa civilization. The Orang Dampuans from Champa however were eventually slaughtered by envious native Sulu Buranuns due to the wealth of the Orang Dampuan. The Buranun were then subjected to retaliatory slaughter by the Orang Dampuan. Harmonious commerce between Sulu and the Orang Dampuan was later restored. The Yakans were descendants of the Taguima-based Orang Dampuan who came to Sulu from Champa. Sulu received civilization in its Indic form from the Orang Dampuan.
During the reign of Sipad the Younger, a mystic named ''Tuan'' Mashā′ikhaMashā′ikha is an Arabic term which originated from ''mashā′ikh'', which means "an intelligent or pious man". arrived in Jolo in 1280 AD. Little is known to the origins and early biography of Tuan Mashā′ikha, except that he is a Muslim "who came from foreign lands" at the head of a fleet of Muslim traders, or he was issued from a stalk of bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, bu ...
and was considered a prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
, thus well respected by the people. Other reports, however, insisted that Tuan Mashā′ikha together with his parents, Jamiyun Kulisa and Indra Suga, were sent to Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
(who is known as ''Iskandar Zulkarnain'' in Malay Annals). However, Najeeb Mitry Saleeby, a Lebanese American doctor who wrote ''A History of Sulu'' in 1908 and other studies of the Moros, dismisses this claim by concluding that Jamiyun Kulisa and Indra Suga were mythical names. According to ''tarsila'', during the coming of Tuan Mashā′ikha, the people of Maimbung worshipped tombs and stones of any kind. After he preached Islam in the area, he married Sipad the Younger's daughter, Idda Indira Suga and bore three children: Tuan Hakim, Tuan Pam and 'Aisha. Tuan Hakim, in turn, begot five children. From the genealogy of Tuan Mashā′ikha, another titular system of aristocracy called "tuanship" started in Sulu. Apart from the Idda Indira Suga, Tuan Mashā′ikha also married into another "unidentified woman" and begot Moumin. Tuan Mashā′ikha died in 710 A.H. (equivalent to 1310 AD), and was buried in Bud Dato near Jolo, with an inscription of ''Tuan Maqbālū''.
A descendant of Tuan Mashā′ikha named Tuan May also begot a son named ''Datu'' Tka. The descendants of Tuan May did not assume the title ''tuan'', instead, they started to use ''datu
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, especial ...
''. It is the first time ''datu'' was used as a political institution. During the coming of Tuan Mashā′ikha, the Tagimaha people (literally means "the party of the people") coming from Basilan
Basilan, officially the Province of Basilan ( cbk, Provincia de Basilan; yka, Wilayah Basilanin; tsg, Wilaya' sin Basilan; fil, Lalawigan ng Basilan), is an island province of the Philippines located primarily in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Reg ...
and several places in Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
, also arrived and settled in Buansa. After the Tagimaha came the Baklaya people (which means "seashore dwellers"), believed to be originated from Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
, and settled in Patikul
Patikul, officially the Municipality of Patikul ( Tausūg: ''Kawman sin Patikul''; tl, Bayan ng Patikul), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 79,564 people.
The ...
. After these came the Bajau people
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exony ...
(or ''Samal'') from Johor
Johor (; ), also spelled as Johore, is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia in the south of the Malay Peninsula. Johor has land borders with the Malaysian states of Pahang to the north and Malacca and Negeri Sembilan ...
. The Bajau were accidentally driven towards Sulu by a heavy monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
, some of them to the shores of Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
and others to Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
. The population of Buranun, Tagimaha, and Baklaya in Sulu created three parties with distinct system of government and subjects. In the 1300s the Chinese annals, ''Nanhai zhi'', reported that Brunei invaded or administered the Philippine kingdoms of Butuan
Butuan (pronounced ), officially the City of Butuan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Butuan; Butuanon: ''Dakbayan hong Butuan''; fil, Lungsod ng Butuan), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Caraga, Philippines. It is the ''de facto'' ca ...
, Sulu and Ma-i
Ma-i or Maidh (also spelled Ma'I, Mai, Ma-yi or Mayi; Baybayin: ; Hanunoo: ; Hokkien ; Mandarin ) was an ancient sovereign state located in what is now the Philippines.
Its existence was first documented in 971 in the Song dynasty documents ...
(Mindoro) which would regain their independence at a later date. According to the Nagarakretagama
The ''Nagarakretagama'' or ''Nagarakṛtāgama'', also known as ''Desawarnana'' or ''Deśavarṇana'', is an Old Javanese eulogy to Hayam Wuruk, a Javanese king of the Majapahit Empire. It was written on lontar as a ''kakawin'' by Mpu Prapan ...
, the Majapahit Empire under Emperor Hayam Wuruk, invaded Sulu at year 1365. However, in 1369, the Sulus rebelled and regained independence and in vengeance, assaulted the Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
Empire and its province ''Po-ni'' (Brunei), and had invaded the Northeast Coast of Borneo and thereafter went to the capital, looting it of treasure and gold. In the sacking of Brunei, the Sulus had stolen 2 sacred pearls from the Bruneian king. A fleet from the Majapahit capital succeeded in driving away the Sulus, but ''Po-ni'' was left weaker after the attack. Since Chinese historiographies later recorded there to be a Maharaja of Sulu, it is assumed that it was unable to be reconquered by Majapahit and it was a rival to that state. By 1390 AD, Rajah Baguinda
Rajah Baguinda Ali, also known as Rajah Baginda Ali, Rajah Baginda, Raha Baguinda, or ''Rajah Baguinda'', was a prince from a Minangkabau kingdom in Sumatra, Indonesia called "Pagaruyung". (Baginda/Baguinda is a Minangkabau honorific for ''prin ...
Ali, a prince of the Pagaruyung Kingdom
Pagaruyung (ڤاڬارويوڠ; also Pagarruyung, Pagar Ruyung and, Malayapura or Malayupura) was the seat of the Minangkabau kings of Western Sumatra, though little is known about it. Modern Pagaruyung is a village in ''Tanjung Emas'' subdist ...
arrived at Sulu and married into the local nobility. At least in 1417, when Sulu rivaled Majapahit, according to Chinese annals, three kings (or monarchs) ruled three civilised kingdoms in the island. Patuka Pahala (Paduka Batara) ruled the eastern kingdom (The Sulu Archipelago), he was the most powerful; the west kingdom was ruled by Mahalachi (Maharajah Kamal ud-Din) (Ruler of Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
in Indonesia); and the kingdom near the cave (or Cave King) was Paduka Patulapok (From Palawan Island). The Bajau settlers were distributed among the three kingdoms. During this time, Sulu had avenged itself from Majapahit Imperialism by encroaching upon the Majapahit Empire as the alliance of the 3 Sulu kings had territory that reached Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo.
In 2019, ...
, specifically East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and North Kalimantan, which were former Majapahit provinces.
Moumin's descendants, the son of Tuan Mashā′ikha populated Sulu. After some time, a certain Timway Orangkaya Su'il was mentioned by the second page of tarsila, that he received four Bisaya slaves (People from the Kedatuan of Madja-as) from Manila (presumably Kingdom of Maynila) as a sign of friendship between the two countries. The descendants of Timway Orangkaya Su'il then inherited the title timway, which means "chief". On tarsila's third page, it accounts the fact that the slaves were the ancestors of the inhabitants in the island to Parang, Lati, Gi'tung, and Lu'uk respectively.
The fourth page then narrates the coming of the Buranun (addressed in the ''tarsila'' as "the Maimbung people") Tagimaha, Baklaya, then the drifted Bajau immigrants from Johor. The condition of Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
before the arrival of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
can be summarised as such: The island was inhabited by several cultures, and was reigned over by three independent kingdoms ruled by the Buranun, Tagimaha, and Baklaya peoples. Likewise, the socio-political systems of these kingdoms were characterised by several distinct institutions: rajahship, datuship, tuanship and timwayship. The arrival of Tuan Mashā′ikha afterwards established a core Islamic community in the island.
Islamisation and establishment
At the end of the 14th century, a notable Arab judge and religious scholar named Karim ul-MakhdumMay be interchange to ''Karimul Makhdum'', ''Karimal Makdum'' or ''Makhdum Karim'' among others. Makhdum came from the Arabic word ''makhdūmīn'', which means "master". fromMecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
arrived in the Malacca Sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Melaka; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswa ...
. He preached Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
to the people, and thus many citizens, including the ruler of Malacca, converted to Islam. Chinese Muslims, Arabs, Persians, Malays, and Indian Muslims introduced Sulu and other Muslim sultanates to Islam. Chinese Muslim merchants participated in the local commerce, and the sultanate had diplomatic relations with China during the time of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
(1368–1644), being involved in the tribute system. The Sulu leader Paduka Pahala
Paduka Pahala (died 1417) was East King of Sulu, most famous for being the first king from the area of the modern day Philippines to be buried in China. He ruled one of the three Kingdoms on Sulu during his time.
Journey to China and Demise of ...
and his sons moved to China, where he died, and Chinese Muslims brought up his sons in Dezhou
Dezhou () is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It borders the provincial capital of Jinan to the southeast, Liaocheng to the southwest, Binzhou to the northeast, and the province of Hebei t ...
, where their descendants live and have the surnames An and Wen.
In 1380 AD,Another uncertain date in Philippine Islamic history is the year of arrival of Karim ul-Makhdum. Though other Muslim scholars place the date as simply "''the end of 14th century''", Saleeby calculated the year as 1380 AD corresponding to the description of the ''tarsilas'', in which Karim ul-Makhdum's coming is 10 years before Rajah Baguinda's. The 1380 reference originated from the event in Islamic history when a huge number of ''makhdūmīn'' started to travel to Southeast Asia from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. See Ibrahim's "Readings on Islam in Southeast Asia." Karim ul-Makhdum arrived in Simunul island from Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
, again with Arab traders. Apart from being a scholar, he operated as a trader; some see him as a Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Tho ...
originating from Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
.
He preached Islam in the area, and was thus accepted by the core Muslim community. He was the second person who preached Islam in the area, following Tuan Mashā′ikha. To facilitate easy conversion of nonbelievers, he established a mosque in Tubig-Indagan, Simunul, which became the first Islamic temple to be constructed in the area, as well as the first in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. This later became known as Sheik Karimal Makdum Mosque
The Sheik Karimol Makhdum Mosque is located in Barangay Tubig Indangan, Simunul, Tawi-Tawi, the Philippines. It is the oldest mosque in the Philippines and in Southeast Asia, according to local folklore, it was built by an Arab trader named Sh ...
. He died in Sulu, although the exact location of his grave is unknown. In Buansa, he was known as Tuan Sharif Awliyā. On his alleged grave in Bud Agad, Jolo, an inscription was written as "Mohadum Aminullah Al-Nikad". In Lugus
Lugus was a deity of the Celtic pantheon. His name is rarely directly attested in inscriptions, but his importance can be inferred from place names and ethnonyms, and his nature and attributes are deduced from the distinctive iconography of Gall ...
, he is referred to as Abdurrahman. In Sibutu
Sibutu, officially the Municipality of Sibutu, is a municipality in the province of Tawi-Tawi, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 34,243 people.
History
Due to an administrative error in the Treaty of Paris, wh ...
, he is known by his name.
The different of beliefs on his grave locations came about due to the fact that Karim ul-Makhdum travelled to several islands in the Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea ( fil, Dagat Sulu; Tausug: ''Dagat sin Sūg''; Chavacano: ''Mar de Sulu''; Cebuano: ''Dagat sa Sulu''; Hiligaynon: ''Dagat sang Sulu''; Karay-a: ''Dagat kang Sulu''; Cuyonon: ''Dagat i'ang Sulu''; ms, Laut Sulu) is a body o ...
to preach Islam. In many places in the archipelago, he was beloved. It is said that the people of Tapul built a mosque honouring him and that they claim descent from Karim ul-Makhdum. Thus, the success of Karim ul-Makhdum of spreading Islam in Sulu threw a new light in Islamic history in the Philippines. The customs, beliefs and political laws of the people changed and customised to adopt the Islamic tradition.
In 1417, the Sulu sultanate began a tributary relationship with the Ming Empire
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
. However, Sulu abruptly stopped sending tributes to the Ming in 1424. Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was an Venetian scholar and explorer. He joined the expedition to the Spice Islands led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan under the flag of the emperor Charles V and after Magellan's death in the Philippine Islands, ...
, in his journals, records that the sultan of Brunei went and invaded Sulu in order subjugate the nation and retrieve the two sacred pearls Sulu pillaged from Brunei during earlier times. A sultan of Brunei, Sultan Bolkiah married a princess (''dayang-dayang'') of Sulu, Puteri Laila Menchanai, and they became the grandparents of the Muslim prince of Maynila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
, Rajah Matanda
Rajah Ache ( Abecedario: ''Rája Aché'' pronounced ''Aki''), better known by his title Rajah Matanda (1480–1572), was one of the rulers of Maynila, a pre-colonial Indianized and Islamized Tagalog polity along the Pasig River in what is now ...
, as Manila was a Muslim city-state and vassal to Brunei before the Spanish colonized them and converted them from Islam to Christianity. Islamic Manila ended after the failed attack of Tarik Sulayman
Tarik Sulayman, also spelled Tarik Soliman (from Arabic طارق سليمان ''Tāriq Sulaiman''), is the most popular of several names attributed by Kapampangan historians to the individual that led the forces of Macabebe against the Spanish fo ...
, a Muslim Kapampangan commander, in the failure of the Conspiracy of the Maharlikas The Tondo Conspiracy of 1587, popularly known as the Conspiracy of the Maginoos (Spanish: ''La Conspiración de las Maginoos''), also known as the Revolt of the Lakans, was a revolt planned by Tagalog nobles known as maginoos, led by Don Agustin de ...
, when the formerly Muslim Manila nobility attempted a secret alliance with the Japanese shogunate and Bruneiean sultanate (together with her Manila and Sulu allies) to expel the Spaniards from the Philippines. The Spanish had native allies against the former Muslims they conquered like Hindu Tondo which resisted Islam when Brunei invaded and established Manila as a Muslim city-state to supplant Hindu Tondo.
Maritime power
 The Sulu sultanate became notorious for its so-called "Moro Raids" or acts of piracy directed toward Spanish settlements in the Visayan areas with the aim of capturing slaves and other goods from these coastal towns. The Tausug pirates used boats known collectively by Europeans as ''proas'' (predominantly the ''
The Sulu sultanate became notorious for its so-called "Moro Raids" or acts of piracy directed toward Spanish settlements in the Visayan areas with the aim of capturing slaves and other goods from these coastal towns. The Tausug pirates used boats known collectively by Europeans as ''proas'' (predominantly the ''lanong
''Lanong'' were large outrigger warships used by the Iranun and the Banguingui people of the Philippines. They could reach up to in length and had two biped shear masts which doubled as boarding ladders. They also had one to three banks of oars ...
'' and ''garay'' warships), which varied in design and were much lighter than the Spanish galleons and could easily out-sail these ships, and also often carried large swivel guns or ''lantaka
The ''Lantaka'' (Baybayin: pre virama: ''ᜎᜆᜃ'': post virama: ''ᜎᜈ᜔ᜆᜃ'') also known as ''rentaka'' (In Malay) was a type of bronze portable cannon or swivel gun, sometimes mounted on merchant vessels and warships in Maritime So ...
'' and also carried a crew of pirates from different ethnic groups throughout Sulu, such as the Iranun
The Iranun are a Moro ethnic group native to Mindanao, Philippines (in Maguindanao del Norte: Barira, Buldon, Parang, Matanog, Sultan Mastura, and Sultan Kudarat; North Cotabato: Alamada, Banisilan, Carmen, Libungan, and Pigcawayan; L ...
, Bajaus and Tausugs alike. By the 18th century, the Sulu pirates had become the virtual masters of the Sulu seas and the surrounding areas, wreaking havoc on Spanish settlements. This prompted the Spaniards to build a number of fortifications across the Visayan islands of Cebu and Bohol; churches were built on higher ground, and watchtowers were built along coastlines to warn of impending raids.
The maritime supremacy of Sulu was not directly controlled by the sultan, independent ''datu''s and warlords waged their own wars against the Spaniards and even with the capture of Jolo on numerous occasions by the Spaniards, other settlements like Maimbung
Maimbung, officially the Municipality of Maimbung ( Tausūg: كاومن سين ماءيمبوڠ; tl, Bayan ng Maimbung), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,59 ...
, Banguingui
Banguingui, also known as Sama Banguingui or Samal Banguingui (alternative spellings include Bangingi’, Bangingi, Banguingui, Balanguingui, and Balangingi) is a distinct ethnolinguistic group native to Balanguingui Island but also dispersed ...
and Tawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim M ...
were used as assembly areas and hideouts for pirates.
The sultanate's control over the Sulu seas was at its height around the late 17th to early 18th centuries were Moro raids became very common for the Visayans and Spaniards.
In Sulu and in the Mindanao interior, the slave trade flourished and majority of these slaves that were being imported and exported were of Visayan ethnicity; the term ''Bisaya'' eventually became synonymous to "slave" in these areas. Its maritime supremacy over the Spaniards, at the time, the Spaniards acquired steam-powered ships that began to curb Muslim piracy in the region, the Moro piratical raids began to decrease in number until Governor Narciso Clavería launched the Balanguingui expedition in 1848 to crush the pirate settlements there, effectively ending the Moro pirate raids. By the last quarter of the 19th century, Moro pirates had virtually disappeared and the maritime influence of the sultanate became dependent on the Chinese junk
A junk (Chinese: 船, ''chuán'') is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. There are two types of junk in China: northern junk, which developed from Chinese river boats, and southern junk, which developed from Austronesian ...
trade.
Spanish and British annexations
 In the 18th century, Sulu's dominion covered most of northeastern part of Borneo. However areas like Tempasuk and Abai had never really shown much allegiance to its earlier ruler, Brunei, subsequently similar treatment was given to Sulu. Dalrymple, who made a treaty of allegiance in 1761 with Sulu, had to make a similar agreement with the rulers of Tempasuk and Abai on the north Borneo coast in 1762. The Sultanate of Sulu totally gave up its domain over Palawan to Spain in 1705 and Basilan to Spain in 1762. The territory ceded to Sulu by Brunei initially stretched south to Tapean Durian (now Tanjong Mangkalihat) (another source mentioned the southernmost boundary is at Dumaring), near the Straits of Macassar (now Kalimantan). From 1726 to 1733, the Sulu sultanate restarted their tributary relationship with China, now the
In the 18th century, Sulu's dominion covered most of northeastern part of Borneo. However areas like Tempasuk and Abai had never really shown much allegiance to its earlier ruler, Brunei, subsequently similar treatment was given to Sulu. Dalrymple, who made a treaty of allegiance in 1761 with Sulu, had to make a similar agreement with the rulers of Tempasuk and Abai on the north Borneo coast in 1762. The Sultanate of Sulu totally gave up its domain over Palawan to Spain in 1705 and Basilan to Spain in 1762. The territory ceded to Sulu by Brunei initially stretched south to Tapean Durian (now Tanjong Mangkalihat) (another source mentioned the southernmost boundary is at Dumaring), near the Straits of Macassar (now Kalimantan). From 1726 to 1733, the Sulu sultanate restarted their tributary relationship with China, now the Qing Empire
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, about 300 years since it last ended.
By 1800–1850, the areas gained from Brunei had been effectively controlled by the sultanate of Bulungan
The Sultanate of Bulungan (کسلطانن بولوڠن) was a princely state of Indonesia located in the existing Bulungan Regency in the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia in the east of the island of Borneo. Its territory spanned the ea ...
in Kalimantan, reducing the boundary of Sulu to a cape named Batu Tinagat and Tawau River
Tawau (, Jawi: , ), formerly known as Tawao, is the capital of the Tawau District in Sabah, Malaysia. It is the third-largest city in Sabah, after Kota Kinabalu and Sandakan. It is located on the Semporna Peninsula in the southeast coast of t ...
.
In 1848 and 1851, the Spanish launched attacks on Balanguingui and Jolo respectively. A peace treaty was signed on 30 April 1851 in which the sultan could only regain its capital if Sulu and its dependencies became a part of the Philippine Islands under the sovereignty of Spain. There were different understandings of this treaty, in which although the Spanish interpreted it as the sultan accepted Spanish sovereignty over Sulu and Tawi-Tawi, however the sultan took it as a friendly treaty amongst equals. These areas were only partially controlled by the Spanish, and their power was limited to only military stations and garrisons and pockets of civilian settlements. This lasted until they had to abandon the region as a consequence of their defeat in the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
. On 22 January 1878, an agreement was signed between the Sultanate of Sulu and British commercial syndicate (Alfred Dent
Sir Alfred Dent, (12 December 1844 – 23 November 1927) was a British colonial merchant and entrepreneur. He was a founder of the British North Borneo Company.
Life
Dent was born in London, the son of Thomas Dent. He was educated at Eton Col ...
and Baron de Overbeck), which stipulated that North Borneo was either ceded or leased (depending on translation used) to the British in return for payment of five thousand malayan dollars per year.
:Sulu version
:British version
On 22 April 1903, Sultan Jamalul Kiram signed a document known as "Confirmation of cession of certain islands", in which he granted and ceded additional islands in the neighbourhood of the mainland of North Borneo from Banggi Island to Sibuku Bay to British North Borneo Company. The confirmatory deed of 1903 makes it known and understood between the two parties that the islands mentioned were included in the cession of the districts and islands mentioned on 22 January 1878 agreement. Additional cession money was set at 300 dollars a year with arrears due for past occupation of 3,200 dollars. The originally agreed 5,000 dollars increased to 5,300 dollars per year payable annually.The Confirmatory Deed of 1903 must be viewed in the light of the 1878 Agreement. The British North Borneo Company entered into a Confirmatory Deed with the Sultanate of Sulu in 1903, thereby confirming and ratifying what was done in 1878.
Madrid Protocol
 The Sulu sultanate later came under the control of Spain in Manila. In 1885,
The Sulu sultanate later came under the control of Spain in Manila. In 1885, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
signed the Madrid Protocol #redirect Madrid system
World Intellectual Property Organization treaties
Treaties concluded in 1989
Treaties entered into force in 1995
1989 in Spain
Treaties entered into by the African Intellectual Property Organization
Treaties of Albani ...
to cement Spanish influence over the islands of the Philippines. In the same agreement, Spain relinquished all claim to North Borneo which had belonged to the sultanate in the past to the British government.
Decline
 The sultanate's political power was relinquished in March 1915 after American commanders negotiated with Sultan Jamalul Kiram on behalf of Governor-General
The sultanate's political power was relinquished in March 1915 after American commanders negotiated with Sultan Jamalul Kiram on behalf of Governor-General Francis Burton Harrison
Francis Burton Harrison (December 18, 1873 – November 21, 1957) was an American statesman who served in the United States House of Representatives and was appointed governor-general of the Philippines by President of the United States Woodro ...
. An agreement was subsequently signed, called the "Carpenter Agreement". By this agreement, the sultan relinquished all political power over territory within the Philippines (except for certain specific land granted to Sultan Jamalul Kiram and his heirs), with the religious authority as head of Islam in Sulu.
Legacy
Status within the Philippines
In 1962, the Philippine government under the administration of PresidentDiosdado Macapagal
Diosdado Pangan Macapagal Sr. (; September 28, 1910 – April 21, 1997) was a Filipino lawyer, poet and politician who served as the ninth president of the Philippines, serving from 1961 to 1965, and the sixth vice president, serving from 19 ...
officially recognised the continued existence of the Sultanate of Sulu. It has been asserted that Macapagal was a cousin of the Sulu sultan due to his royal descent tracing to Lakandula of Tondo,Gloria Macapagal Arroyo's Royal Descent and the Value of Genealogical Provenance/ref> Lakandula was the uncle of the Muslim king of Manila, Rajah Sulayman, and they had a grandmother from Sulu in the person of the Tausug princess, Laila Mechanai, wife of Sultan Bolkiah of Brunei and ancestor of
Rajah Matanda
Rajah Ache ( Abecedario: ''Rája Aché'' pronounced ''Aki''), better known by his title Rajah Matanda (1480–1572), was one of the rulers of Maynila, a pre-colonial Indianized and Islamized Tagalog polity along the Pasig River in what is now ...
and Rajah Sulayman
Rajah Sulayman, sometimes referred to as Sulayman III (Sanskrit: स्ललैअह्, Arabic: سليمان, Abecedario: ''Suláimán'') (1558–1575), was the Rajah of Maynila, a fortified Tagalog Muslim polity on the southern half of the ...
of Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
. On 24 May 1974, the reign of Sultan Mohammed Mahakuttah Kiram began and lasted until 1986. He was the last officially recognized Sulu sultan in the Philippines, having been recognized by President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Ferdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
.
Pretenders
After the death of Mahakuttah A. Kiram, the Philippine national government has not formally recognised a new sultan. Mahakutta's crown prince Muedzul Lail Kiram, the heir to the throne according to the line of succession as recognised by the Philippine governments from 1915 to 1986, was 20 years old upon his father's death. Due to his young age, he failed to claim the throne in a time of political instability in the Philippines that led to the peaceful revolution and subsequent removal of President Marcos. The gap in the sultanate leadership was filled by claimants of rival branches. Therefore, the succeeding claimants to the sultanship were not crowned with the support of the Philippine government nor received formal recognition from the national government as their predecessors had until 1986. However, the Philippine national government decided to deal with one or more of the sultan claimants regarding issues concerning the sultanate’s affairs.Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram
Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram (born 28 August 1966) is the head of the Royal House of Sulu, a position which he has held since 16 February 1986. As the eldest son of the former Sultan Mohammad Mahakuttah Abdulla Kiram (who reigned 1974–1986), he i ...
claims that he is the legitimate successor as the 35th sultan of Sulu based on Memorandum Order 427 of 1974, in which former Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
recognised his father, Mahakuttah A. Kiram, as the sultan of Sulu.
North Borneo dispute
 The dispute is based on a territorial claim by the
The dispute is based on a territorial claim by the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
since the era of President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Diosdado Macapagal
Diosdado Pangan Macapagal Sr. (; September 28, 1910 – April 21, 1997) was a Filipino lawyer, poet and politician who served as the ninth president of the Philippines, serving from 1961 to 1965, and the sixth vice president, serving from 19 ...
over much of the eastern part of Sabah in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. Sabah was known as North Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
prior to the formation of the Malaysian federation in 1963. The Eastern Sabah territory was allegedly gifted by the Brunei Sultanate to the Sulu Sultanate due to Sulu intervention in the Brunei Civil War
The Brunei Civil War was a civil war fought in the Bruneian Empire from 1660 to 1673.
Causes
During the reign of the thirteenth Sultan Muhammad Ali, there was a disagreement between the son of the Sultan, ''Pengiran Muda'' ("prince") Bong ...
. However Brunei historian Leigh R. Wright has claimed that Sulu never really provided assistance during the civil war. The Philippines, via the heritage of the Sultanate of Sulu, claim Sabah on the basis that Sabah was only leased to the British North Borneo Company
The North Borneo Chartered Company (NBCC), also known as the British North Borneo Company (BNBC) was a British chartered company formed on 1 November 1881 to administer and exploit the resources of North Borneo (present-day Sabah in Malaysia) ...
with the sultanate's sovereignty never being relinquished. The dispute stems from the difference in the interpretation used on an agreement signed between Sultanate of Sulu and the British commercial syndicate (Alfred Dent and Baron von Overbeck) in 1878, which stipulated that North Borneo was either ceded or leased (depending on translation used) to the British chartered company in return for payment of 5,000 dollars per year. Malaysia views the dispute as a "non-issue", as it not only considers the agreement in 1878 as one of cession, but it also deems that the residents had exercised their act of self-determination when they joined to form the Malaysian federation in 1963. As reported by the Secretary-General of the United Nations, the independence of North Borneo was brought about as the result of the expressed wish of the majority of the people of the territory as supported by the findings of the Cobbold Commission.
Moreover, a later 1903 Confirmation of Cession agreement between the sultan of Sulu and the British government, has provided reaffirmation regarding the understanding of the sultan of Sulu on the treaty in 1878, i.e. it is of the form of a cession. Throughout the British administration of North Borneo, the British government continued to make the annual "cession money" payment to the sultan and its heir and these payments were expressly shown in the receipts as "cession money". In a 1961 conference in London, during which a Philippine and British panel met to discuss on the Philippine claim of North Borneo, the British panel informed the Congressman Salonga that the wording of the receipts has not been challenged by the sultan or its heir. During a meeting of Maphilindo
Maphilindo (for Malaya, the Philippines, and Indonesia), is a proposed, nonpolitical confederation of the three Southeast Asian countries in the Malay Archipelago.
Background
The original plan for a united state based on the concept of ...
between the Philippine, Malayan and Indonesian governments in 1963, the Philippine government said the sultan of Sulu wanted the payment of 5,000 from the Malaysian government. The first Malaysian Prime Minister
The prime minister of Malaysia ( ms, Perdana Menteri Malaysia; ms, ڤردان منتري مليسيا, label= Jawi, script=arab, italic=unset) is the head of government of Malaysia. The prime minister directs the executive branch of the feder ...
at the time, Tunku Abdul Rahman
Tunku Abdul Rahman Putra Al-Haj ibni Almarhum Sultan Abdul Hamid Halim Shah ( ms, تونكو عبد الرحمن ڤوترا الحاج ابن سلطان عبد الحميد حليم شاه, label= Jawi, script=arab, italic=unset; 8 Febru ...
said he would go back to Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = '' Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, su ...
and get on the request. Since then, the Malaysian Embassy in the Philippines issues a cheque in the amount of RM5,300 (approx. ₱77,000 or US$1,710) to the legal counsel of the heirs of the sultan of Sulu. Malaysia considers the settlement an annual "cession payment" for the disputed state, while the sultan's descendants consider it "rent". These payments however have been stopped as of 2013 in light of the attempted invasion of Sabah since Malaysia viewed that as an act of violation of the 1903 Confirmation of Cession agreement and its earlier 1878 agreement.
Republic Act 5446 in the Philippines, which took effect on 18 September 1968, regards Sabah as a territory "over which the Republic of the Philippines has acquired dominion and sovereignty". On 16 July 2011, the Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court ( fil, Kataas-taasang Hukuman; colloquially referred to as the ''Korte Suprema'' lso used in formal writing is the highest court in the Philippines. The Supreme Court was established by the Second Philippine Commission on Ju ...
ruled that the Philippine claim over Sabah is retained and may be pursued in the future. , Malaysia maintains that their Sabah claim is a non-issue and non-negotiable, thereby rejecting any calls from the Philippines to resolve the matter in the International Court of Justice. Sabah authorities sees the claim made by the Philippines' Moro leader Nur Misuari to take Sabah to International Court of Justice as a non-issue and thus dismissed the claim.
In February 2022, an international court ruled that Malaysia had violated a treaty signed in 1878 of annual cession payment and would have to pay at least US$14.92 billion (RM62.59 billion) to the descendants of the Sulu sultan, which Malaysia ceased payment in 2013 as it deemed that the Sulu counterpart had first violated the treaty through 2013 Sabah incursion. The award was reportedly issued in an arbitration court in Paris, France by Spanish arbitrator Gonzalo Stampa. In March 2022, Malaysia filed an application to annul final award over claims by Sulu sultan’s heirs since the appointment of arbitrator Dr Gonzalo Stampa was itself annulled by Madrid High Court in June 2021, rendering any decisions by him to be invalid including the 2022 award. Lawyers for the heirs indicated that they will seek the award’s recognition and execution, citing a 1958 U.N. Convention on Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards. In July 2022, court bailiffs in Luxembourg served Petronas Azerbaijan (Shah Denis) and Petronas South Caucus with a "saiseie-arret," or a size order or behalf of descendants of the Sulu sultan. Petronas said it would defend its legal position.
Other
Outside the North Borneo dispute, the heirs and claimants of the Sulu sultanate have been involved in contemporary Philippine politics such as the lobbying for the creation of a constituent state called Zambasulta within the Philippines under a federal form of government.Economy
Weapons and slave trade
Chinese who lived in Sulu ran guns across a Spanish blockade to supply the Moro datus and sultanates with weapons to fight the Spanish, who were engaging in a campaign to subjugate the Moro sultanates onMindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
. A trade involving the Moros selling slaves and other goods in exchange for guns developed. The Chinese had entered the economy of the sultanate, taking almost total control of the sultanate's economies in Mindanao and dominating the markets. Though the sultans did not like one group of people exercising exclusive control over the economy, they did business with them.
 The Chinese set up a trading network between
The Chinese set up a trading network between Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, Zamboanga, Jolo and Sulu. The Chinese sold small arms like Enfield and Spencer Rifles to the Buayan Datu Uto. They were used to battle the Spanish invasion of Buayan
Buayan is a coastal barangay located at the eastern edge of General Santos in the Philippines. It is bounded by Baluan in the west, Ligaya in the north, Baluntay and Alabel in the east and Sarangani Bay in the south.
Etymology
The baran ...
. The datu paid for the weapons in slaves. The population of Chinese in Mindanao in the 1880s was 1,000. The Chinese ran guns across a Spanish blockade to sell to Mindanao Moros. The purchases of these weapons were paid for by the Moros in slaves in addition to other goods. The main group of people selling guns were the Chinese in Sulu. The Chinese took control of the economy and used steamers to ship goods for exporting and importing. Opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
, textiles, and crockery were among the other goods which the Chinese sold.
The Chinese on Maimbung
Maimbung, officially the Municipality of Maimbung ( Tausūg: كاومن سين ماءيمبوڠ; tl, Bayan ng Maimbung), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 59,59 ...
sent the weapons to the Sulu sultanate, who used them to battle the Spanish and resist their attacks. A Chinese-Mestizo was one of the sultan's brothers-in-law, the sultan was married to his sister. He and the sultan both owned shares in the ship (named the Far East) which helped smuggle the weapons. The Spanish launched a surprise offensive under Colonel Juan Arolas
Juan Arolas (1805–1849) was a Spanish poet and writer.
Biography
The son of well-off traders, he spent his childhood in Valencia where he studied with the Piarists. He joined this order in Peralta de la Sal in the year 1819, according to som ...
in April 1887 by attacking the sultanate's capital at Maimbung in an effort to crush resistance. Weapons were captured and the property of the Chinese were destroyed while the Chinese were deported to Jolo.
Pearling industry
 After the destruction of the pirate haunts of
After the destruction of the pirate haunts of Balanguingui
Banguingui, also known as Sama Banguingui or Samal Banguingui (alternative spellings include Bangingi’, Bangingi, Banguingui, Balanguingui, and Balangingi) is a distinct ethnolinguistic group native to Balanguingui Island but also dispersed ...
effectively ending the centuries of slave raids, which the Sulu sultanate's economy had so depended on, along with the economy of mainland Mindanao, the sultanate's economy experienced a sharp decline as slaves became more inaccessible and the islands' agricultural produce wasn't enough, thus it became dependent on the Mindanao interior even for rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
and produce. The Spaniards thought they had dealt the death blow for the sultanate when they captured Jolo in 1876, rather, the sultanate's capital and economic and trading hub was moved to Maimbung on the other side of the island. Up until the American occupation, this was the residence and economic centre of Sulu. This is where the Sultan Jamalul Kiram II and his adviser Hadji Butu began the Sulu pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
ing industry to increase the sultan's wealth, they organised the Sulu pearling fleet. The sultan's pearling fleet was active way into the early 20th century, when in 1910, the sultan reportedly sold a single giant pearl in London for $100,000.
Culture
Social class system
Among the people of the Sultanate of Sulu, the title of nobility could be acquired only by lineage, a "closed system" whereby the titled persons inherit their offices of powers and prestige. The two main social classes of the sultanete were as follows:
*
The two main social classes of the sultanete were as follows:
* Datu
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, especial ...
(su-sultanun), which is acquired purely by lineage to the sultanate. Whereas, all male members of the royal house of Sulu should hold this hereditary title and should hold the style: His Royal Highness (HRH). Their spouse would automatically hold the title of ''dayang dayang'' (princess of the first degree). Adopted members of the royal house of Sulu hold the style of His Highness (HH) Whereas, their spouse would also hold the title of ''dayang dayang'' (princess of the first degree) and should hold the style: Her Highness according to traditional customs of Sulu.
* Datu sadja
Datu Sadja is a senior titled nobility in the Royal Sultanate of Sulu. It is subordinate to the Datu or Su-sultanun which is acquired purely by inherited lineage or formal relationship to the Sultan. The title of Datu is roughly comparable to Eur ...
, which may be acquired through confirming the titles (gullal) on the middleman of the sultan. The gullal is made if a commoner has achieved outstanding feats or services in line of duty through display of bravery, heroism, etc. Datu sadja is life title of nobility and the title holders should hold the style: His Excellency. Whereas their spouses should hold the title of ''dayang'' and should hold the style: Her Excellency.
The commoners or ''maharlika'' are those who do not trace their descent from royalty. The Wakil Kesultan's, Panglimas, Parkasa's and Laksaman's who are commoners hold responsible positions involving administrative matters.
* ''Wakil Kesultanan'' – region representative outside the Sulu sultanate
* ''Panglima'' – region representative inside the Sulu sultanate
* ''Parkasa'' – aide-de-camp of region representative inside the Sulu sultanate
* ''Laksaman'' – sub region representative inside the Sulu sultanate
The males who hold offices above shall be addressed by the title of nobility ''tuan'' (the title is directly attached to the office), followed by the rank of the office they hold, their given name, surname and region. The females who hold offices above shall be addressed by the title of nobility Sitti (the title is directly attached to the office), followed by the rank of the office they hold, their given name, surname and region.
A very large part of the Sulu society, as well as in the Sultanate of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindana ...
were slaves captured from slave raids or bought from slave markets. They were known as the ''bisaya'', reflecting their most common origin – the Christianized Visayans
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, ...
from Spanish territories in the Philippines – although they also included captured slaves from other ethnic groups throughout Southeast Asia. They were also known as ''banyaga'', ''ipun'', or ''ammas''. It is estimated that as much as 50% of the population of Sulu in the 1850s were ''bisaya'' slaves and they dominated the Sulu economy. For the most part, they were treated like commoners, with their own houses and were responsible for cultivating farms and fisheries of Tausug nobility. But there were harsh punishments for attempts to escape, and a large number of the slaves were sold to European, Chinese, Makassar
Makassar (, mak, ᨆᨀᨔᨑ, Mangkasara’, ) is the capital of the Indonesian province of South Sulawesi. It is the largest city in the region of Eastern Indonesia and the country's fifth-largest urban center after Jakarta, Surabaya, Med ...
, and Bugis
The Bugis people (pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar and Toraja), in the south-western province of Sulawe ...
slavers in the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
.
Visual arts
 The Sultanate of Sulu, along with the rest of Mindanao, has a long tradition of decorative arts known as ''okir'' or ''ukkil''. ''Ukkil'' is the Tausug word for "wood carving" or "engraving". The Tausug and
The Sultanate of Sulu, along with the rest of Mindanao, has a long tradition of decorative arts known as ''okir'' or ''ukkil''. ''Ukkil'' is the Tausug word for "wood carving" or "engraving". The Tausug and Maranao
The Maranao people (Maranao: mәranaw Filipino: ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranao, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is the term used by the Philippine government to refer to the southern indigenous people who are the "people of the lake", a predomi ...
peoples traditionally carved and decorated their boats, houses and even grave markers with ''ukkil'' carvings. Aside from wood carvings, ''ukkil'' motifs were found on various clothing in the Sulu archipelago. ''Ukkil'' motifs tend to emphasise geometric patterns and a flowing design, with floral and leaf patterns as well as folk elements. The Tausug also decorated their weapons with these motifs, and various ''kris'' and ''barong'' blades have finely decorated handles as well as blades covered in floral patterns and the like. Bronze ''lantaka
The ''Lantaka'' (Baybayin: pre virama: ''ᜎᜆᜃ'': post virama: ''ᜎᜈ᜔ᜆᜃ'') also known as ''rentaka'' (In Malay) was a type of bronze portable cannon or swivel gun, sometimes mounted on merchant vessels and warships in Maritime So ...
'' also bear some ''ukkil'' patterns.
Gallery
A flag coloured yellow was used in Sulu by the Chinese.Pierre Sonnerat
Pierre Sonnerat (18 August 1748 – 31 March 1814) was a French naturalist, colonial administrator, writer and explorer. He described numerous species of plants and animals on his travels and is honoured in the genus ''Sonneratia'' and in other ...
File:Merchant flag of the Chinese community in the Sulu Sultanate.svg, Merchant flag of the Chinese community in the Sulu sultanate
File:War Flag of Sulu Sultanate.svg, A war flag
A war flag, also known as a military flag, battle flag, or standard, is a variant of a national flag for use by a country's military forces when on land. The nautical equivalent is a naval ensign. Under the strictest sense of the term, few countri ...
of the Sulu sultanate at the end of the 19th century
File:Bandeira Sulu.svg, The official flag of the Sulu sultanate under the guidance of Ampun Sultan Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram
Muedzul Lail Tan Kiram (born 28 August 1966) is the head of the Royal House of Sulu, a position which he has held since 16 February 1986. As the eldest son of the former Sultan Mohammad Mahakuttah Abdulla Kiram (who reigned 1974–1986), he i ...
of Sulu.
See also
*2013 Lahad Datu standoff
The 2013 Lahad Datu standoff, also known as the Lahad Datu incursion or Operation Daulat ( ms, Operasi Daulat), was a military conflict in Lahad Datu District, Sabah, Malaysia, that started on 11 February 2013, lasting until 24 March 2013. The ...
* List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
*Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
*Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
*Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramaut) ( ...
* Sultanate of Malacca
The Malacca Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Melaka; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Paramesw ...
* Sultanate of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindana ...
* John C. Bates
* Manila Accord
The Manila Accord was signed on 31 July 1963 by the Federation of Malaya, the Republic of Indonesia and the Republic of the Philippines, after a meeting from 7 to 11 June 1963 in Manila.
Initiated by President of the Philippines Diosdado Macapa ...
* Monarchy abolishment
The abolition of monarchy and anti-royalism is a legislative or revolutionary movement to abolish monarchical elements in government, usually hereditary.
Abolition of absolutist monarchy in favor of limited government under constitutional monarc ...
* Hinduism in the Philippines
Recent archaeological and other evidence suggests Hinduism has had some cultural, economic, political and religious influence in the Philippines. Among these is the 9th century Laguna Copperplate Inscription found in 1989, deciphered in 1992 to b ...
* History of the Philippines (Before 1521)
Earliest hominin activity in the Philippine archipelago is dated back to at least 709,000 years ago. ''Homo luzonensis'', a species of archaic humans, was present on the island of Luzon at least 67,000 years ago. The earliest known anatomically ...
* Kiram-Bates Treaty
Notes
References
;General * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Line of succession of the Sultans of Sulu of the Modern Era
as published in the Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines
Philippine Provincial Government of Sulu – The official list of Sultans
on WorldStatesMen.org {{authority control
Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
History of Sulu
Sulu Sea
History of Sabah
Former countries in Borneo
Former countries in Bruneian history
Former countries in Indonesian history
Former countries in Malaysian history
Former countries in Philippine history
Former monarchies of Asia
Moro people
Moro Rebellion
Filipino royalty
States and territories established in 1405
States and territories disestablished in 1915
1405 establishments in Asia
1915 disestablishments in Asia
15th-century establishments in Asia
1915 disestablishments in the Philippines
Maritime Southeast Asia