|
Dunduka
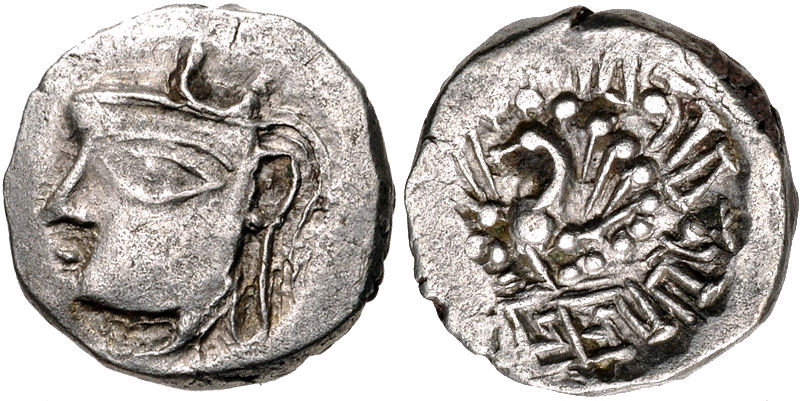
Dunduka was a ruler of the state of Kannauj in North India during the early 8th century CE. Early life Dunduka was the son and successor of Āma, the king of Kannauj and surrounding areas during the late 8th century CE. Āma, his father, had lost control of Kannauj, and moved to Gopagiri (modern Gwalior).Shyam Manohar Mishra (1977). Yaśovarman of Kanauj. Abhinav. pp. 120–121 OCLC 5782454 Being under Jain influence, Āma abdicated the throne in favour of Dunduka. Reign Dunduka was an immoral and cruel person, who was the ruler of a small and reduced territory. He did not take any interest in his royal duties and neglected his queen Padma.Shyam Manohar Mishra (1977). Yaśovarman of Kanauj. Abhinav. pp. 120–121 OCLC 5782454 He indulged in debauchery and was pleasure-loving. He is described as "immoral" in the Gaudavaho, ''Gaudavaho'' as well.Shyam Manohar Mishra (1977). Yaśovarman of Kanauj. Abhinav. pp. 120–121 OCLC 5782454 He even made several futile attempts to kill his o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhoja Of Kannauj
Bhoja was a medieval Indian king who ruled Kannauj in the late 8th century CE His parents were Dunduka and Padma, Dunduka's queen. Dunduka made several futile attempts to kill Bhoja. Later, Bhoja killed Dunduka for the throne in his royal court. After killing his father, Bhoja ascended the throne with the favour and support of Dunduka's subjects and high officials. Bhoja, like his father Dunduka and grandfather Āma, became a ''parama'' Jaina. He fought off an invasion by an invading Muslim army. He either retired as a king after a short rule, or his kingdom was annexed by the Ayudhas, who established a new dynasty, or he was deposed by the Pratiharas The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj. The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the .... References {{Reflist Indian rulers Kannauj Year of birth missing Yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Āma
Āma was a medieval Indian king who ruled Kannauj and surrounding areas during the 8th and the 9th centuries. According to the Jain chronicles, he was the son and successor of Yashovarman. Jain account The Jain chronicle ''Bappabhatti-Suri-Charita'' states Yashovarman's chief queen Suyasha gave birth to Āma during her exile at Ramasainya. Also called Yashodevi, the queen was exiled because of a conspiracy by another queen. Āma was brought up by the Jain monk Siddhasena at Modherakapura, but he and his mother were later restored to their royal positions. As a prince, Āma was a spendthrift, so Yashovarman asked him to be frugal. This annoyed Āma, who returned to Modherakapura. According to the ''Prabandha Kosha'', when Yashovarman fell ill towards the end of his life, he recalled Āma to Kannauj and appointed him as the new king. The '' Prabhavaka Charita'' and ''Prabandha Kosha'' suggest that Āma ascended the throne during 749-753 CE (807-811 VS). According to ''Prabha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja Kannauj is an ancient city. It is said that the Kanyakubja Brahmins who included Shandilya (teacher of Rishi Bharadwaja) were held one of the three prominent families originally from Kannauj. In Classical India, it served as the center of imperial Indian dynasties. The earliest of these was the Maukhari dynasty, and later, Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana dynasty.Tripathi, ''History of Kanauj'', p. 192 The city later came under the Gahadavala dynasty, and under the rule of Govindachandra, the city reached "unprecedented glory". Kannauj was also the main place of war in the Tripartite struggle between the Gurjara-Pratihara, the Palas and the Rashtra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja Kannauj is an ancient city. It is said that the Kanyakubja Brahmins who included Shandilya (teacher of Rishi Bharadwaja) were held one of the three prominent families originally from Kannauj. In Classical India, it served as the center of imperial Indian dynasties. The earliest of these was the Maukhari dynasty, and later, Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana dynasty.Tripathi, ''History of Kanauj'', p. 192 The city later came under the Gahadavala dynasty, and under the rule of Govindachandra, the city reached "unprecedented glory". Kannauj was also the main place of war in the Tripartite struggle between the Gurjara-Pratihara, the Palas and the Rashtra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
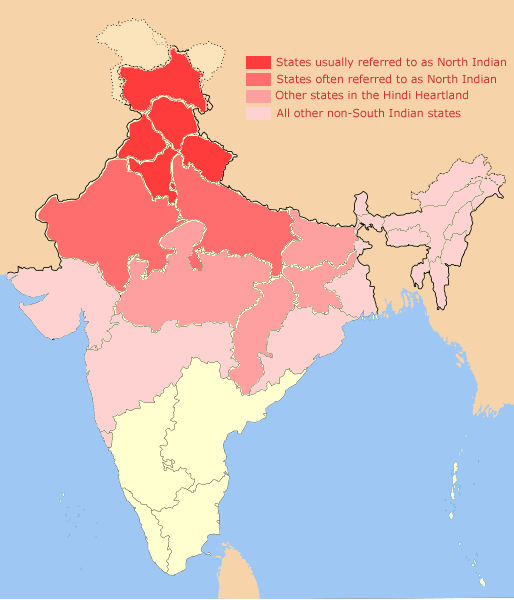
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the state capital, Gwalior occupies a strategic location in the Gird region of India. The historic city and its fortress have been ruled by several historic Indian kingdoms. From the Kachchhapaghatas in the 10th century, Tomars in the 13th century, it was passed on to the Mughal Empire, then to the Maratha in 1754, and the Scindia dynasty of Maratha Empire in the 18th century. In April 2021, It was found that Gwalior had the best air quality index (AQI 152) amongst the 4 major cities in Madhya Pradesh. Besides being the administrative headquarters of Gwalior district and Gwalior division, Gwalior has many administrative offices of the Chambal division of northern Madhya Pradesh. Several administrative and judicial organisations, commission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and '' aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), '' satya'' (truth), '' asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and '' aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaudavaho
''Gaudavaho'' ("Slaying of the Gauda king") is an 8th-century Prakrit-language epic poem by Vakpati-raja. It narrates the exploits of the poet's patron, king Yashovarman, who ruled in northern India. The poem deifies the king as an incarnation of the god Vishnu, and credits him with several military achievements, including slaying of the Gauda king. A little over 1200 verses of the text are known from several manuscripts. According to some scholars such as Georg Bühler, the surviving text is only a prelude to the larger poem that Vakpati intended to write, but possibly never finished. Authorship Gaudavaho was composed by Vakpati-raja (Prakrit: "Bappai-rāa"), a court poet of king Yashovarman. He wrote in the first half of the 8th century. He states that he was known as ''Kavi-raja'' (Prakrit: "Kairāa", "king of poets"), an epithet possibly awarded to him by his patron Yashovarman. Kalhana's ''Rajatarangini'' suggests that both Vakpati and Bhavabhuti were court poets of Lalita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihira Bhoja
Mihira Bhoja (c. 836–885 CE) or Bhoja I was a king belonging to the Gurjara-Pratihara Dynasty. He succeeded his father Ramabhadra. Bhoja was a devotee of Vishnu and adopted the title of ''Ādivarāha'' which is inscribed on some of his coins. One of the outstanding political figures of India in ninth century, he ranks with Dhruva Dharavarsha and Dharmapala as a great general and empire builder. At its height, Bhoja's empire extended to Narmada River in the South, Sutlej River in the northwest, and up to Bengal in the east. It extended over a large area from the foot of the Himalayas up to the river Narmada and included the present district of Etawah in Uttar Pradesh. Reign During his reign, the capital was in Kannauj (present-day Uttar Pradesh), during his period Kannauj was referred as Panchala. He was a bitter enemy of the Arab invaders who, according to an Arab chronicler, Sulaiman, maintained a large army and had a fine cavalry. He was succeeded by his son Mah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Rulers
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |