|
Drug Checking
Drug checking or pill testing is a way to Harm reduction, reduce the harm from drug consumption by allowing users to find out the content and purity of substances that they intend to consume. This enables users to make safer choices: to avoid more dangerous substances, to use smaller quantities, and to avoid dangerous combinations. Drug checking services have developed over the last twenty-five years in twenty countries and are being considered in more countries, although attempts to implement them in some countries have been hindered by local laws. Drug checking initially focused on MDMA users in electronic dance music events but the services have broadened as drug use has become more complex. These developments have been strongly affected by local laws and culture, resulting in a diverse range of services, both for mobile services that attend events and festivals and fixed sites in town centres and entertainment districts. For instance, staff may or may not be able to handle ille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Drug Information
The Trans-European Drug Information (''TEDI'') project is a European database compiling information from different drug checking services located on the European continent. The non-governmental organizations feeding into the database are referred to as the TEDI network. History The first drug checking service in Europe opened in 1986 in Amsterdam, allowing drug users to analyze the chemical composition of illicit substances that they consume. In the following years, a number of nonprofit organizations present in various other drug scenes in several countries (including in Austria, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Switzerland) set up drug checking services. In 2011, a database was created for to centralize information from these services and allow for the sharing of alerts (for example on new adulterants in illicit substances or circulation of novel psychoactive substance) and the monitoring of drug markets across borders. Between 2008 and 2013, organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harm Reduction
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use and sexual activity without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others. Harm reduction is most commonly applied to approaches that reduce adverse consequences from drug use, and harm reduction programs now operate across a range of services and in different regions of the world. As of 2020, some 86 countries had one or more programs using a harm reduction approach to substance use, primarily aimed at reducing blood-borne infections resulting from use of contaminated injecting equipment. Needle-exchange programmes reduce the likelihood of people who use heroin and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandelin Reagent
The Mandelin reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of ammonium metavanadate and concentrated sulfuric acid. Its primary use is for the detection of ketamine and PMA Unlike the most common reagent test chemicals, it has a deep red colour that changes to yellow if there is no alkaloid, which occurs within about 48 hours of mixing. The United States Department of Justice method for producing the reagent is the addition of 100 mL of concentrated (95–98%) sulfuric acid to 0.5-1 g of ammonium metavanadate. This reagent was invented by the German pharmacologist, Karl Friedrich Mandelin (1854–1906) at the University of Dorpat. See also *Drug checking * Dille–Koppanyi reagent *Folin's reagent Folin's reagent or sodium 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate is a chemical reagent used as a derivatizing agent to measure levels of amines and amino acids. The reagent reacts with them in alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Froehde Reagent
The Froehde reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids, especially opioids, as well as other compounds. It is composed of a mixture of molybdic acid or a molybdate salt dissolved in hot, concentrated sulfuric acid, which is then dripped onto the substance being tested. The United States Department of Justice method for producing the reagent is the addition of 100 ml of hot, concentrated (95–98%) sulfuric acid to 0.5 g of sodium molybdate or molybdic acid. The Virginia Department of Forensic Science method uses 0.5 g ammonium molybdate per 100 ml H2SO4 (conc.) Unheated sulfuric acid can be used to prepare the reagent in a less dangerous manner, but 2–4 hours must be allowed for the molybdate to dissolve. See also *Reagent testing *Drug checking * Dille–Koppanyi reagent *Folin's reagent * Liebermann reagent *Mandelin reagent The Mandelin reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify alkaloids as well as other compounds. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
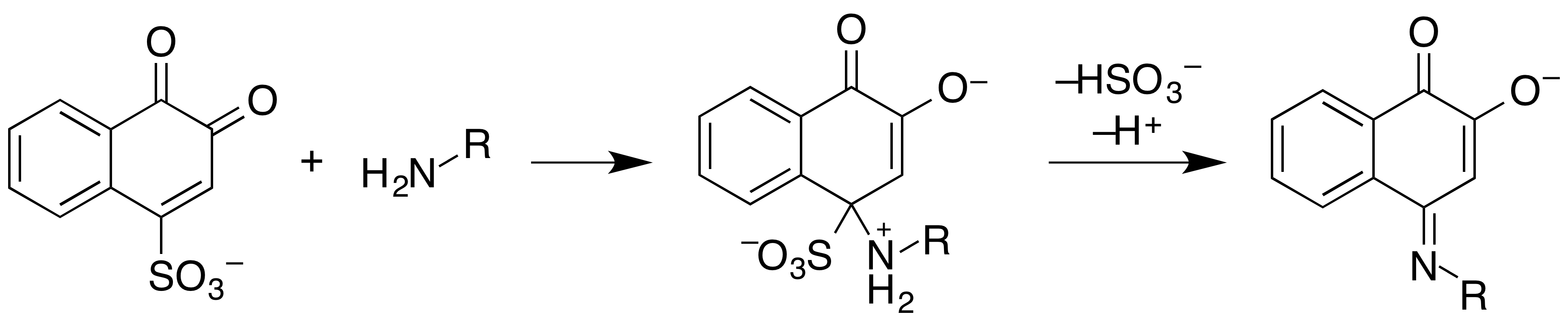
Folin's Reagent
Folin's reagent or sodium 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate is a chemical reagent used as a derivatizing agent to measure levels of amines and amino acids. The reagent reacts with them in alkaline solution to produce a fluorescent material that can be easily detected. This should not be confused with Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, that is used to detect phenolic compounds. The Folin reagent can be used with an acidic secondary reagent to distinguish MDMA and related compounds from PMMA and related compounds. See also * Dille–Koppanyi reagent * Froehde reagent * Liebermann reagent * Mandelin reagent * Marquis reagent * Mecke reagent * Pill testing * Simon's reagent * Sullivan reaction The Sullivan reaction is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of cysteine or cystine in proteins. A red colour appears when a protein with cysteine or cystine is heated with sodium 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate ( Folin's reagent) and so ... * Zwikker reagent References {{reflis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Test
A drug test (also often toxicology screen or tox screen) is a technical analysis of a biological specimen, for example urine, hair, blood, breath, sweat, or saliva, oral fluid/saliva—to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug testing include detection of the presence of Use of performance-enhancing drugs in sport, performance enhancing steroids in sport, employers and parole/probation officers screening for Prohibition (drugs), drugs prohibited by law (such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and heroin) and police officers testing for the presence and concentration of alcoholic drink, alcohol (ethanol) in the blood commonly referred to as Blood alcohol content, BAC (blood alcohol content). BAC tests are typically administered via a breathalyzer while urinalysis is used for the vast majority of drug testing in sports and the workplace. Numerous other methods with varying degrees of accuracy, sensitivity (detection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Education
Drug education is the planned provision of information, guidelines, resources, and skills relevant to living in a world where psychoactive substances are widely available and commonly used for a variety of both medical and non-medical purposes, some of which may lead to harms such as overdose, injury, infectious disease (such as HIV or hepatitis C), or addiction. The two primary approaches to drug education are harm-reduction education and abstinence-based education. Abstinence-based drug education Abstinence-based drug education began with the anti-alcohol " temperance education" programmes of the Woman's Christian Temperance Union in the United States and Canada in the late 19th century. In many respects, the WCTU's progressive education agenda set the template for much of what has been done since in the name of drug education. Abstinence-based education programs aim to inform adolescents of illicit drug use in an effort to prevent illegal drug use while highlighting the dang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dille–Koppanyi Reagent
The Dille–Koppanyi reagent is used as a simple spot-test to presumptively identify barbiturates. It is composed of a mixture of two solutions. Part A is 0.1 g of cobalt(II) acetate dihydrate dissolved in 100 ml of methanol mixed with 0.2 ml of glacial acetic acid. Part B made up of is 5% isopropylamine (v/v) in methanol. Two drops of A are dropped onto the substance followed by one drop of B and any change in colour is observed. The test turns phenobarbital, pentobarbital, amobarbital and secobarbital light purple by complexation of cobalt with the barbiturate nitrogens. The test, in a slightly different formulation, was developed in the 1930s by the Hungarian-American pharmacologist Theodore Koppanyi (1901–1985) and the American Biochemist, James Madison Dille (1928–1986). See also * Drug checking Drug checking or pill testing is a way to Harm reduction, reduce the harm from drug consumption by allowing users to find out the content and purity of substances that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterfeit Drug
A counterfeit medication or a counterfeit drug is a medication or pharmaceutical item which is produced and sold with the intent to deceptively represent its origin, authenticity, or effectiveness. A counterfeit drug may contain inappropriate quantities of active ingredients, or none, may be improperly processed within the body (''e.g.'', absorption by the body), may contain ingredients that are not on the label (which may or may not be harmful), or may be supplied with inaccurate or fake packaging and labeling. Counterfeit drugs are related to pharma fraud. Drug manufacturers and distributors are increasingly investing in countermeasures, such as traceability and authentication technologies, to try to minimise the impact of counterfeit drugs. Antibiotics with insufficient quantities of an active ingredient add to the problem of antimicrobial resistance. Legitimate, correctly labeled, low-cost generic drugs are not counterfeit or fake, although they can be counterfeited much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique based on re-orientation of Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei with non-zero nuclear spins in an external magnetic field. This re-orientation occurs with absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency region from roughly 4 to 900 MHz, which depends on the Isotope, isotopic nature of the nucleus and increases proportionally to the strength of the external magnetic field. Notably, the resonance frequency of each NMR-active nucleus depends on its chemical environment. As a result, NMR spectra provide information about individual functional groups present in the sample, as well as about connections between nearby nuclei in the same molecule. As the NMR spectra are unique or highly characteristic to individual compounds and functional groups, NMR spectroscopy is one of the most important methods to identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Levitation
Magnetic levitation (maglev) or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is levitation (physics), suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Lorentz force, Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces. The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are ''lifting forces'': providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and ''stability'': ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized. Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, levitation melting, contactless melting, magnetic bearings, and for product display purposes. Lift Magnetic materials and systems are able to attract or repel each other with a force dependent on the magnetic field and the area of the magnets. For example, the simplest example of lift would be a simple dipole magnet positioned in the magnetic fields of another dipole magnet, oriented with like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medicine, clinical utility is in pain management for cancer patients and those recovering from painful surgeries. Fentanyl is also used as a sedative. Depending on the method of delivery, fentanyl can be very fast acting and ingesting a relatively small quantity can cause overdose. Fentanyl works by activating μ-opioid receptors. Fentanyl is sold under the brand names Actiq, Duragesic, and Sublimaze, among others. Pharmaceutical fentanyl's adverse effects are similar to those of other opioids and narcotics including addiction, confusion, hypoventilation, respiratory depression (which, if extensive and untreated, may lead to respiratory arrest), drowsiness, nausea, visual disturbances, dyskinesia, hallucinations, delirium, a subset of the latte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |