Harm reduction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of
 In the case of recreational substance use, harm reduction is put forward as a useful perspective alongside the more conventional approaches of
In the case of recreational substance use, harm reduction is put forward as a useful perspective alongside the more conventional approaches of
HAMS Harm Reduction Network
is a programme which encourages any positive change with regard to the use of alcohol or other mood altering substances. HAMS encourages goals of safer drinking, reduced drinking, moderate drinking, or abstinence and provides some tips on how to achieve these goals. The choice of the goal is up to the individual. Harm reduction in alcohol dependency could be instituted by use of
 Providing medical prescriptions for pharmaceutical heroin (diacetylmorphine) to heroin-dependent people has been employed in some countries to address problems associated with the illicit use of the drug, as potential benefits exist for the individual and broader society. Evidence has indicated that this form of treatment can greatly improve the health and social circumstances of participants, while also reducing costs incurred by criminalisation, incarceration and health interventions.
In Switzerland, heroin assisted treatment is an established programme of the national health system. Several dozen centres exist throughout the country and heroin-dependent people can administer heroin in a controlled environment at these locations. The Swiss heroin maintenance programme is generally regarded as a successful and valuable component of the country's overall approach to minimising the harms caused by illicit drug use. In a 2008
Providing medical prescriptions for pharmaceutical heroin (diacetylmorphine) to heroin-dependent people has been employed in some countries to address problems associated with the illicit use of the drug, as potential benefits exist for the individual and broader society. Evidence has indicated that this form of treatment can greatly improve the health and social circumstances of participants, while also reducing costs incurred by criminalisation, incarceration and health interventions.
In Switzerland, heroin assisted treatment is an established programme of the national health system. Several dozen centres exist throughout the country and heroin-dependent people can administer heroin in a controlled environment at these locations. The Swiss heroin maintenance programme is generally regarded as a successful and valuable component of the country's overall approach to minimising the harms caused by illicit drug use. In a 2008
However, the British government is again moving towards a consideration of heroin prescription as a legitimate component of the National Health Service (NHS). Evidence has shown that methadone maintenance is not appropriate for all people who are dependent on opioids and that heroin is a viable maintenance drug that has shown equal or better rates of success. A committee appointed by the Norwegian government completed an evaluation of research reports on heroin maintenance treatment that were available internationally. In 2011 the committee concluded that the presence of numerous uncertainties and knowledge gaps regarding the effects of heroin treatment meant that it could not recommend the introduction of heroin maintenance treatment in Norway. The first, and only, North American heroin maintenance project is being run in
 Medication assisted treatment (MAT) is the prescription of legal, prescribed opioids or other drugs, often long-acting, to diminish the use of illegal opioids. Many types of MAT exist, including opioid agonist therapy (OAT) where a safer opioid agonist is employed or opioid substitution therapy (OST) which employs partial opioid agonists. However, MAT, OAT, OST are often used synonymously.
Medication assisted treatment (MAT) is the prescription of legal, prescribed opioids or other drugs, often long-acting, to diminish the use of illegal opioids. Many types of MAT exist, including opioid agonist therapy (OAT) where a safer opioid agonist is employed or opioid substitution therapy (OST) which employs partial opioid agonists. However, MAT, OAT, OST are often used synonymously.
National Evaluation of Pharmacotherapies for Opioid Dependence (NEPOD): Report of Results and Recommendation
PillReports.com
invites people who use ecstasy to send samples of substances for laboratory testing and publishes the results online.
/ref> and possession of cannabis is a federal crime in the United States.
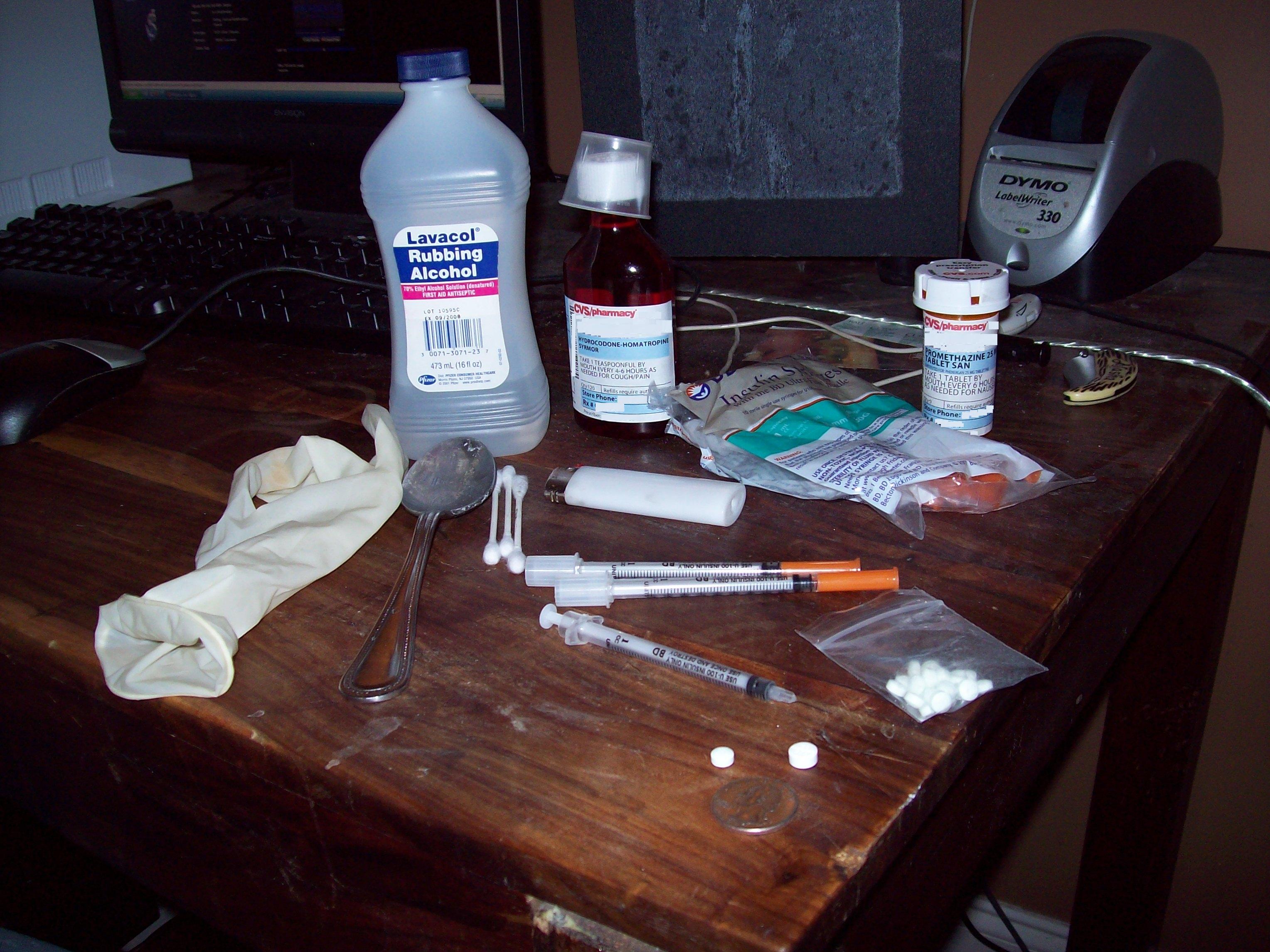
 The use of some illicit drugs can involve hypodermic needles. In some areas (notably in many parts of the US), these are available solely by prescription. Where availability is limited, people who use heroin and other substances frequently share the syringes and use them more than once or participate in unsafe practices such as blood flashing. As a result, infections such as
The use of some illicit drugs can involve hypodermic needles. In some areas (notably in many parts of the US), these are available solely by prescription. Where availability is limited, people who use heroin and other substances frequently share the syringes and use them more than once or participate in unsafe practices such as blood flashing. As a result, infections such as
 ''Supervised injection sites'' (SIS), or ''Drug consumption rooms'' (DCR), are legally sanctioned, medically supervised facilities designed to address public nuisance associated with drug use and provide a hygienic and stress-free environment for drug consumers.
The facilities provide sterile injection equipment, information about drugs and basic health care, treatment referrals, and access to medical staff. Some offer counseling, hygienic and other services of use to itinerant and impoverished individuals. Most programmes prohibit the sale or purchase of illegal drugs. Many require identification cards. Some restrict access to local residents and apply other admission criteria, such as they have to be people who inject substances, but generally in Europe they do not exclude people with substance use disorders who consume their substances through other means.
The Netherlands had the first staffed injection room, although they did not operate under explicit legal support until 1996. Instead, the first center where it was legal to inject drug was in Berne, Switzerland, opened 1986. In 1994, Germany opened its first site. Although, as in the Netherlands they operated in a "gray area", supported by the local authorities and with consent from the police until the Bundestag provided a legal exemption in 2000.
In Europe, Luxembourg, Spain and Norway have opened facilities after year 2000. As did the two existing facilities outside Europe, with Sydney's Medically Supervised Injecting Center (MSIC) established in May 2001 as a trial and
''Supervised injection sites'' (SIS), or ''Drug consumption rooms'' (DCR), are legally sanctioned, medically supervised facilities designed to address public nuisance associated with drug use and provide a hygienic and stress-free environment for drug consumers.
The facilities provide sterile injection equipment, information about drugs and basic health care, treatment referrals, and access to medical staff. Some offer counseling, hygienic and other services of use to itinerant and impoverished individuals. Most programmes prohibit the sale or purchase of illegal drugs. Many require identification cards. Some restrict access to local residents and apply other admission criteria, such as they have to be people who inject substances, but generally in Europe they do not exclude people with substance use disorders who consume their substances through other means.
The Netherlands had the first staffed injection room, although they did not operate under explicit legal support until 1996. Instead, the first center where it was legal to inject drug was in Berne, Switzerland, opened 1986. In 1994, Germany opened its first site. Although, as in the Netherlands they operated in a "gray area", supported by the local authorities and with consent from the police until the Bundestag provided a legal exemption in 2000.
In Europe, Luxembourg, Spain and Norway have opened facilities after year 2000. As did the two existing facilities outside Europe, with Sydney's Medically Supervised Injecting Center (MSIC) established in May 2001 as a trial and
Drugs Policy and Harm Reduction
- Research on the circulation of ideas around harm reduction and urban drug policies by Eugene McCann and Cristina Temenos (Simon Fraser University). * *
TNI on Harm ReductionInternational Harm Reduction AssociationTobacco Harm Reduction
{{DEFAULTSORT:Harm Reduction Alcohol and health Addiction Drug culture Drug policy Public health
 Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
and sexual activity
Human sexual activity, human sexual practice or human sexual behaviour is the manner in which humans experience and express their sexuality. People engage in a variety of sexual acts, ranging from activities done alone (e.g., masturbation) ...
without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others.
Harm reduction is most commonly applied to approaches that reduce adverse consequences from drug use, and harm reduction programs now operate across a range of services and in different regions of the world. As of 2020, some 86 countries had one or more programs using a harm reduction approach to substance use, primarily aimed at reducing blood-borne infections resulting from use of contaminated injecting equipment.
Needle-exchange programmes reduce the likelihood of people who use heroin and other substances sharing the syringes and using them more than once. Syringe-sharing often leads to the spread of infections such as HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
or hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
, which can easily spread from person to person through the reuse of syringes contaminated with infected blood. Needle and syringe programmes (NSP) and Opioid Agonist Therapy (OAT)
Opioid agonist therapy (OAT) is a treatment in which prescribed opioid agonists are given to patients who live with opioid addiction. The benefits of this treatment include a more manageable withdrawal experience, cognitive improvement, and lowe ...
outlets in some settings offer basic primary health care. Supervised injection sites
Supervised injection sites (SIS) are medically supervised facilities designed to provide a hygienic environment in which people are able to consume illicit recreational drugs intravenously and prevent deaths due to drug overdoses. The legality o ...
are legally sanctioned, medically supervised facilities designed to provide a safe, hygienic, and stress-free environment for people who use substances. The facilities provide sterile injection equipment, information about substances and basic health care, treatment referrals, and access to medical staff.
Opioid agonist therapy (OAT) is the medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practi ...
procedure of using a harm-reducing opioid that produces significantly less euphoria, such as methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to hero ...
or buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous and subcutaneous), as a skin patch (transdermal ...
to reduce opioid cravings in people who use illegal opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioi ...
, such as heroin; buprenorphine and methadone are taken under medical supervision. Another approach is Heroin assisted treatment, in which medical prescriptions for pharmaceutical heroin (diacetylmorphine) are provided to people who are dependent on heroin.
Media campaigns inform drivers of the dangers of driving drunk. Most people who recreationally consume alcohol are now aware of these dangers and safe ride techniques like ' designated drivers' and free taxicab programmes are reducing the number of drunk-driving accidents. Many schools now provide safer sex education to teen and pre-teen students, who may engage in sexual activity. Since some adolescents are going to have sex, a harm-reductionist approach supports a sexual education which emphasizes the use of protective devices like condoms
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female con ...
and dental dams to protect against unwanted pregnancy and the transmission of STIs. Since 1999 some countries have legalized prostitution, such as Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
(2002) and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
(2003).
Many street-level harm-reduction strategies have succeeded in reducing HIV transmission in people who inject substances and sex-workers. HIV education, HIV testing, condom use, and safer-sex negotiation greatly decreases the risk of acquiring and transmitting the HIV virus.
Substance use
 In the case of recreational substance use, harm reduction is put forward as a useful perspective alongside the more conventional approaches of
In the case of recreational substance use, harm reduction is put forward as a useful perspective alongside the more conventional approaches of demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ...
and supply reduction. Many advocates argue that prohibitionist laws criminalise people for suffering from a disease and cause harm; for example, by obliging people who use substances to obtain substances of unknown purity from unreliable criminal sources at high prices, thereby increasing the risk of overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
and death. The website Erowid
Erowid, also called Erowid Center, is a non-profit educational organization that provides information about psychoactive plants and chemicals.
Erowid documents legal and illegal substances, including their intended and adverse effects. Informat ...
.org collects and publishes information and first-hand experience reports about all kinds of substances to educate people who use or may use substances.
While the vast majority of harm reduction initiatives are educational campaigns or facilities that aim to reduce substance-related harm, a unique social enterprise was launched in Denmark in September 2013 to reduce the financial burden of illicit substance use for people with a drug dependence. Michael Lodberg Olsen, who was previously involved with the establishment of a substance consumption facility in Denmark, announced the founding of the ''Illegal'' magazine that will be sold by people who use substances in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
and the district of Vesterbro, who will be able to direct the profits from sales towards drug procurement. Olsen explained: "No one has solved the problem of drug addiction, so is it not better that people find the money to buy their drugs this way than through crime and prostitution?"
Substances
Depressants
=Alcohol
= Traditionally,homeless shelter
Homeless shelters are a type of homeless service agency which provide temporary residence for homeless individuals and families. Shelters exist to provide residents with safety and protection from exposure to the weather while simultaneously re ...
s ban alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
. In 1997, as the result of an inquest
An inquest is a judicial inquiry in common law jurisdictions, particularly one held to determine the cause of a person's death. Conducted by a judge, jury, or government official, an inquest may or may not require an autopsy carried out by a co ...
into the deaths of two people experiencing homelessness who recreationally used alcohol two years earlier, Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most pop ...
's Seaton House became the first homeless shelter in Canada to operate a "wet shelter" on a "managed alcohol" principle in which clients are served a glass of wine once an hour unless staff determine that they are too inebriated to continue. Previously, people experiencing homelessness who consumed excessive amounts of alcohol opted to stay on the streets often seeking alcohol from unsafe sources such as mouthwash, rubbing alcohol or industrial products which, in turn, resulted in frequent use of emergency medical facilities. The programme has been duplicated in other Canadian cities, and a study of Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
's "wet shelter" found that emergency room visit and police encounters by clients were cut by half. The study, published in the ''Canadian Medical Association Journal
The ''Canadian Medical Association Journal'' (French ''Journal de l'Association Médicale Canadienne'') is a peer-reviewed general medical journal published by the Canadian Medical Association (CMA). It publishes original clinical research, anal ...
'' in 2006, found that serving people experiencing long-term homelessness and who consume excessive amounts of alcohol controlled doses of alcohol also reduced their overall alcohol consumption. Researchers found that programme participants cut their alcohol use from an average of 46 drinks a day when they entered the programme to an average of 8 drinks and that their visits to emergency rooms dropped from 13.5 to an average of 8 per month, while encounters with the police fall from 18.1 to an average of 8.8.
Downtown Emergency Service Center (DESC), in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
, Washington, operates several Housing First programmes which utilize the harm reduction model. University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seat ...
researchers, partnering with DESC, found that providing housing and support services for homeless alcoholics costs taxpayers less than leaving them on the street, where taxpayer money goes towards police and emergency health care. Results of the study funded by the Substance Abuse Policy Research Program (SAPRP) of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) is an American philanthropic organization. It is the largest one focused solely on health. Based in Princeton, New Jersey, the foundation focuses on access to health care, public health, health equity, ...
appeared in the ''Journal of the American Medical Association
''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (''JAMA'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of bio ...
'' in April 2009. This first controlled assessment in the U.S. of the effectiveness of Housing First, specifically targeting chronically homeless alcoholics, showed that the programme saved taxpayers more than $4 million over the first year of operation. During the first six months, the study reported an average cost-savings of 53 percent (even after considering the cost of administering the housing's 95 residents)—nearly $2,500 per month per person in health and social services, compared to the per month costs of a wait-list control group of 39 homeless people. Further, despite the fact residents are not required to be abstinent or in treatment for alcohol use, stable housing also results in reduced drinking among people experiencing homelessness who recreationally use alcohol.
Alcohol-related programmes A high amount of media coverage exists informing people of the dangers of driving drunk. Most people who recreationally consume alcohol are now aware of these dangers and safe ride techniques like ' designated drivers' and free taxicab programmes are reducing the number of drunk-driving accidents. Many cities have free-ride-home programmes during holidays involving high amounts of alcohol use, and some bars and clubs will provide a visibly drunk patron with a free cab ride. In
New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
groups of licensees have formed local liquor accords and collectively developed, implemented and promoted a range of harm minimisation programmes including the aforementioned 'designated driver' and 'late night patron transport' schemes. Many of the transport schemes are free of charge to patrons, to encourage them to avoid drink-driving and at the same time reduce the impact of noisy patrons loitering around late night venues.
Moderation Management is a programme which helps drinkers to cut back on their consumption of alcohol by encouraging safe drinking behaviour.
ThHAMS Harm Reduction Network
is a programme which encourages any positive change with regard to the use of alcohol or other mood altering substances. HAMS encourages goals of safer drinking, reduced drinking, moderate drinking, or abstinence and provides some tips on how to achieve these goals. The choice of the goal is up to the individual. Harm reduction in alcohol dependency could be instituted by use of
naltrexone
Naltrexone, sold under the brand name Revia among others, is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol or opioid use disorder by reducing cravings and feelings of euphoria associated with substance use disorder. It has also been found to ...
.
=Opioids
=Heroin maintenance programmes (HAT)
 Providing medical prescriptions for pharmaceutical heroin (diacetylmorphine) to heroin-dependent people has been employed in some countries to address problems associated with the illicit use of the drug, as potential benefits exist for the individual and broader society. Evidence has indicated that this form of treatment can greatly improve the health and social circumstances of participants, while also reducing costs incurred by criminalisation, incarceration and health interventions.
In Switzerland, heroin assisted treatment is an established programme of the national health system. Several dozen centres exist throughout the country and heroin-dependent people can administer heroin in a controlled environment at these locations. The Swiss heroin maintenance programme is generally regarded as a successful and valuable component of the country's overall approach to minimising the harms caused by illicit drug use. In a 2008
Providing medical prescriptions for pharmaceutical heroin (diacetylmorphine) to heroin-dependent people has been employed in some countries to address problems associated with the illicit use of the drug, as potential benefits exist for the individual and broader society. Evidence has indicated that this form of treatment can greatly improve the health and social circumstances of participants, while also reducing costs incurred by criminalisation, incarceration and health interventions.
In Switzerland, heroin assisted treatment is an established programme of the national health system. Several dozen centres exist throughout the country and heroin-dependent people can administer heroin in a controlled environment at these locations. The Swiss heroin maintenance programme is generally regarded as a successful and valuable component of the country's overall approach to minimising the harms caused by illicit drug use. In a 2008 national referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
, a majority of 68 per cent voted in favour of continuing the Swiss programme.
The Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
has studied medically supervised heroin maintenance. A German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
study of long-term heroin addicts demonstrated that diamorphine was significantly more effective than methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to hero ...
in keeping patients in treatment and in improving their health and social situation. Many participants were able to find employment, some even started a family after years of homelessness and delinquency. Since then, treatment had continued in the cities that participated in the pilot study, until heroin maintenance was permanently included into the national health system in May 2009.
A heroin maintenance programme has existed in the United Kingdom (UK) since the 1920s, as drug addiction was seen as an individual health problem. Addiction to opiates was rare in the 1920s and was mostly limited to either middle-class people who had easy access due to their profession, or people who had become addicted as a side effect of medical treatment. In the 1950s and 1960s a small number of doctors contributed to an alarming increase in the number of people who are experiencing addiction in the U.K. through excessive prescribing—the U.K. switched to more restrictive drug legislation as a result.Rachel Lart BRITISH MEDICAL PERCEPTION FROM ROLLESTON TO BRAIN, CHANGING IMAGES OF THE ADDICT AND ADDICTIONHowever, the British government is again moving towards a consideration of heroin prescription as a legitimate component of the National Health Service (NHS). Evidence has shown that methadone maintenance is not appropriate for all people who are dependent on opioids and that heroin is a viable maintenance drug that has shown equal or better rates of success. A committee appointed by the Norwegian government completed an evaluation of research reports on heroin maintenance treatment that were available internationally. In 2011 the committee concluded that the presence of numerous uncertainties and knowledge gaps regarding the effects of heroin treatment meant that it could not recommend the introduction of heroin maintenance treatment in Norway. The first, and only, North American heroin maintenance project is being run in
Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. Th ...
, B.C. and Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
. Currently, over 80 long-term heroin addicts who have not been helped by available treatment options are taking part in the North American Opiate Medication Initiative (NAOMI) trials. However, critics have alleged that the control group gets unsustainably low doses of methadone, making them prone to fail and thus rigging the results in favor of heroin maintenance.
Critics of heroin maintenance programmes object to the high costs of providing heroin to people who use it. The British heroin study cost the British government £15,000 per participant per year, roughly equivalent to average person who uses heroin's expense of £15,600 per year. Drug Free AustraliaDrug Free Australia p 3 contrast these ongoing maintenance costs with Sweden's investment in, and commitment to, a drug-free society where a policy of compulsory rehabilitation of people who are experiencing drug addiction is integral, which has yielded the one of the lowest reported illicit drug use levels in the developed world, a model in which successfully rehabilitated people who use substances present no further maintenance costs to their community, as well as reduced ongoing health care costs.
King's Health Partners notes that the cost of providing free heroin for a year is about one-third of the cost of placing the person in prison for a year.
Naloxone distribution
Naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
is a drug used to counter an overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
from the effect of opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioi ...
s; for example, a heroin or morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. Ther ...
overdose. Naloxone displaces the opioid molecules from the brain's receptors and reverses the respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide ( hypercapn ...
caused by an overdose within two to eight minutes. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) includes naloxone on their " List of Essential Medicines", and recommends its availability and utilization for the reversal of opioid overdoses.
Formal programs in which the opioid inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse ag ...
drug naloxone is distributed have been trialled and implemented. Established programs distribute naloxone, as per WHO's minimum standards, to people who use substances and their peers, family members, police, prisons, and others. These treatment programs and harm reduction centres operate in Afghanistan, Australia, Canada, China, Germany, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Norway, Russia, Spain, Tajikistan, the United Kingdom (UK), the United States (US), Vietnam, India, Thailand, Kyrgyzstan, Denmark and Estonia. Many reviews of the literature support the effectiveness of naloxone based interventions in reducing overdose deaths where it is available at the time of the overdose event. This effectiveness has been explained in a Realist Evaluation which explained the effectiveness through bystander effect, social identity theory
Social identity is the portion of an individual's self-concept derived from perceived membership in a relevant social group.
As originally formulated by social psychologists Henri Tajfel and John Turner in the 1970s and the 1980s, social ...
, and skills training such that universal access to training supports social identity and in-group norms (of people who use drugs), which supports the conditions for the success of a peer-to-peer distribution model of naloxone based interventions. Stigma and stigmatising attitudes reduced the effectiveness of naloxone based interventions.
Medication assisted treatment (MAT): Opioid agonist therapy (OAT) and Opioid substitution therapy (OST)
 Medication assisted treatment (MAT) is the prescription of legal, prescribed opioids or other drugs, often long-acting, to diminish the use of illegal opioids. Many types of MAT exist, including opioid agonist therapy (OAT) where a safer opioid agonist is employed or opioid substitution therapy (OST) which employs partial opioid agonists. However, MAT, OAT, OST are often used synonymously.
Medication assisted treatment (MAT) is the prescription of legal, prescribed opioids or other drugs, often long-acting, to diminish the use of illegal opioids. Many types of MAT exist, including opioid agonist therapy (OAT) where a safer opioid agonist is employed or opioid substitution therapy (OST) which employs partial opioid agonists. However, MAT, OAT, OST are often used synonymously.
Opioid agonist therapy (OAT)
Opioid agonist therapy (OAT) is a treatment in which prescribed opioid agonists are given to patients who live with opioid addiction. The benefits of this treatment include a more manageable withdrawal experience, cognitive improvement, and lowe ...
involves the use of a full opioid agonist treatment like methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid agonist used for chronic pain and also for opioid dependence. It is used to treat chronic pain, and it is also used to treat addiction to hero ...
and is generally taken daily at a clinic
A clinic (or outpatient clinic or ambulatory care clinic) is a health facility that is primarily focused on the care of outpatients. Clinics can be privately operated or publicly managed and funded. They typically cover the primary care nee ...
.Richard P. Mattick et al.National Evaluation of Pharmacotherapies for Opioid Dependence (NEPOD): Report of Results and Recommendation
Opioid substitution therapy (OST)
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a substance use disorder characterized by cravings for opioids, continued use despite physical and/or psychological deterioration, increased tolerance with use, and withdrawal symptoms after discontinuing opioids. Op ...
involves the use of the partial agonist buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous and subcutaneous), as a skin patch (transdermal ...
or a combination of buprenorphine naloxone (brand name Suboxone). Oral/sublingual formulations of buprenorphine incorporate the opioid antagonist naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
to prevent people from crushing the tablets and injecting them. Unlike methadone treatment, buprenorphine therapy can be prescribed month-to-month and obtained at a traditional pharmacy
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medication, medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it ...
rather than a clinic.
The driving principle behind OAT/OST is the program's capacity to facilitate a resumption of stability in the person's life, while they experience reduced symptoms of withdrawal
Withdrawal means "an act of taking out" and may refer to:
* Anchoresis (withdrawal from the world for religious or ethical reasons)
* '' Coitus interruptus'' (the withdrawal method)
* Drug withdrawal
* Social withdrawal
* Taking of money from ...
symptoms and less intense drug cravings; however, a strong euphoric effect is not experienced as a result of the treatment drug.
In some countries, such as Switzerland, Austria, and Slovenia, patients are treated with slow-release morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. Ther ...
when methadone is deemed inappropriate due to the individual's circumstances. In Germany, dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) (as in co-dydramol) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 ...
has been used off-label in OAT for many years, however it is no longer frequently prescribed for this purpose. Extended-release dihydrocodeine is again in current use in Austria for this reason. Research into the usefulness of piritramide
Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic (narcotic painkiller) that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the ...
, extended-release hydromorphone
Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by m ...
(including polymer implants lasting up to 90 days), dihydroetorphine
Dihydroetorphine was developed by K. W. Bentley at McFarlan-Smith in the 1960s and is a potent opioid analgesic used mainly in China. It is a derivative of the better-known opioid etorphine, a very potent veterinary painkiller and anesthetic m ...
and other substances for OAT is at various stages in a number of countries. In 2020 in Vancouver, Canada, health authorities began vending machine dispensing of hydromorphone tablets as a response to elevated rates of fatal overdose from street drugs contaminated with fentanyl and fentanyl analogues.
In some countries (not the US, UK, Canada, or Australia), regulations enforce a limited time period for people on OAT/OST programs that conclude when a stable economic and psychosocial situation is achieved. (Patients with HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
or Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
are usually excluded from this requirement.) In practice, 40–65% of patients maintain complete abstinence from opioids while receiving opioid agonist therapy, and 70–95% are able to reduce their use significantly, while experiencing a concurrent elimination or reduction in medical (improper diluent
A diluent (also referred to as a filler, dilutant or thinner) is a diluting agent. Certain fluids are too viscous to be pumped easily or too dense to flow from one particular point to the other. This can be problematic, because it might not be e ...
s, non- sterile injecting equipment), psychosocial (mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental hea ...
, relationships), and legal ( arrest and imprisonment
Imprisonment is the restraint of a person's liberty, for any cause whatsoever, whether by authority of the government, or by a person acting without such authority. In the latter case it is "false imprisonment". Imprisonment does not necessari ...
) issues that can arise from the use of illicit opioids.
OAT/OST outlets in some settings also offer basic primary health care. These are known as 'targeted primary health care outlet'- as these outlets primarily target people who inject drugs and/or 'low-threshold health care outlet'- as these reduce common barriers clients often face when they try to access health care from the conventional health care outlets. For accessing sterile injecting equipment clients frequently visit NSP outlets, and for receiving pharmacotherapy (e.g. methadone, buprenorphine) they visit OST clinics; these frequent visits are used opportunistically to offer much needed health care. These targeted outlets have the potential to mitigate clients' perceived barriers to access to healthcare delivered in traditional settings. The provision of accessible, acceptable and opportunistic services which are responsive to the needs of this population is valuable, facilitating a reduced reliance on inappropriate and cost-ineffective emergency department care.
Psychedelics The Zendo Project conducted by the
Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies
The Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) is an American nonprofit organization working to raise awareness and understanding of psychedelic substances. MAPS was founded in 1986 by Rick Doblin and is now based in San Jose, C ...
uses principles from psychedelic therapy to provide safe places and emotional support for people having difficult experiences on psychedelic drugs at select festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival co ...
s such as Burning Man, Boom Festival, and Lightning in a Bottle without medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practi ...
or law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term ...
intervention.
Substances such as MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desired ...
(commonly sold by the slang names "ecstasy" and "molly") are often adulterated. One harm reduction approach is drug checking, where people intending to use drugs can have their substances tested for content and purity so that they can then make more informed decisions about safer consumption. European organisations have offered drug checking services since 1992 and these services now operate in over twenty countries. As an example, the nonprofit organization DanceSafe offers on-site testing of the contents of pills and powders at various electronic music
Electronic music is a Music genre, genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or electronics, circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromech ...
events around the US. They also sell kits for people who use substances to test the contents of the substances themselvesPillReports.com
invites people who use ecstasy to send samples of substances for laboratory testing and publishes the results online.
=Cannabis
= Specific harms associated with cannabis include increased accident-rate while driving under intoxication, dependence,psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
, detrimental psychosocial outcomes for adolescents who use substances, and respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, ...
. Some safer cannabis usage campaigns including the UKCIA (United Kingdom Cannabis Internet Activists) encourage methods of consumption shown to cause less physical damage to a person's body, including oral (eating) consumption, vaporization, the usage of bongs which cool and to some extent filters the smoke, and smoking the cannabis without mixing it with tobacco.
The fact that cannabis possession carries prison sentences in most developed countries is also pointed out as a problem by European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) is an agency of the European Union located in Lisbon, Portugal, and established in 1993. In June 2022, the Council of the European Union approved a reform of the organization ...
(EMCDDA), as the consequences of a conviction for otherwise law-abiding people who use substances arguably is more harmful than any harm from the substance itself. For example, by adversely affecting employment opportunities, impacting civil rights, and straining personal relationships. Some people like Ethan Nadelmann of the Drug Policy Alliance
The Drug Policy Alliance (DPA) is a New York City–based nonprofit organization that seeks to advance policies that “reduce the harms of both drug use and drug prohibition, and to promote the sovereignty of individuals over their minds and b ...
have suggested that organized marijuana legalization would encourage safe use and reveal the factual adverse effects from exposure to this herb's individual chemicals.
The way the laws concerning cannabis are enforced is also very selective, even discriminatory. Statistics show that the socially disadvantaged, immigrants and ethnic minorities have significantly higher arrest rates. Drug decriminalisation
Decriminalization or decriminalisation is the reclassification in law relating to certain acts or aspects of such to the effect that they are no longer considered a crime, including the removal of criminal penalties in relation to them. This refor ...
, such as allowing the possession of small amounts of cannabis and possibly its cultivation for personal use, would alleviate these harms. Where decriminalisation has been implemented, such as in several states in Australia and United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, as well as in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
no, or only very small adverse effects have been shown on population cannabis usage rate. The lack of evidence of increased use indicates that such a policy shift does not have adverse effects on cannabis-related harm while, at the same time, decreasing enforcement costs.
In the last few years certain strains of the cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternativel ...
plant with higher concentrations of THC and drug tourism
Recreational drug tourism is travel for the purpose of obtaining or using drugs for recreational use that are unavailable, illegal or very expensive in one's home jurisdiction. A drug tourist may cross a national border to obtain a drug that is not ...
have challenged the former policy in the Netherlands and led to a more restrictive approach; for example, a ban on selling cannabis to tourists in coffeeshops suggested to start late 2011. Sale and possession of cannabis is still illegal in PortugalEMCDDA:Drug policy profiles, Portugal, June 2011/ref> and possession of cannabis is a federal crime in the United States.
Stimulants
=Tobacco
= Tobacco harm reduction describes actions taken to lower the health risks associated with using tobacco, especially combustible forms, without abstaining completely from tobacco and nicotine. Some of these measures include switching to safer (lower tar) cigarettes, switching tosnus
Snus ( , ) is a tobacco product, originating from a variant of dry snuff in early 18th-century Sweden. It is placed between the upper lip and gum for extended periods, as a form of sublabial administration. Snus is not fermented. Although use ...
or dipping tobacco
Dipping tobacco is a type of finely ground or shredded, moistened smokeless tobacco product. It is commonly and idiomatically known as "dip". Dipping tobacco is used by placing a pinch, or "dip", of tobacco between the lip and the gum ( sublab ...
, or using a non-tobacco nicotine delivery systems. In recent years, the growing use of electronic cigarette
An electronic cigarette is an electronic device that simulates tobacco smoking. It consists of an atomizer, a power source such as a battery, and a container such as a cartridge or tank. Instead of smoke, the user inhales vapor. As such ...
s (or vaping) for smoking cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often m ...
, whose long-term safety remains uncertain, has sparked an ongoing controversy among medical and public health between those who seek to restrict and discourage all use until more is known and those who see them as a useful approach for harm reduction, whose risks are most unlikely to equal those of smoking tobacco. "Their usefulness in tobacco harm reduction as a substitute for tobacco products is unclear, but in an effort to decrease tobacco related death and disease, they have a potential to be part of the strategy.
It is widely acknowledged that discontinuation of all tobacco products confers the greatest lowering of risk. However, there is a considerable population of inveterate smokers who are unable or unwilling to achieve abstinence. Harm reduction may be of substantial benefit to these individuals.
Routes of administration
Needle exchange programmes (NEP)
 The use of some illicit drugs can involve hypodermic needles. In some areas (notably in many parts of the US), these are available solely by prescription. Where availability is limited, people who use heroin and other substances frequently share the syringes and use them more than once or participate in unsafe practices such as blood flashing. As a result, infections such as
The use of some illicit drugs can involve hypodermic needles. In some areas (notably in many parts of the US), these are available solely by prescription. Where availability is limited, people who use heroin and other substances frequently share the syringes and use them more than once or participate in unsafe practices such as blood flashing. As a result, infections such as HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
or hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
can spread from person to person through the reuse of syringes contaminated with infected blood. The principles of harm reduction propose that syringes should be easily available or at least available through a needle and syringe programmes (NSP). Where syringes are provided in sufficient quantities, rates of HIV are much lower than in places where supply is restricted. In many countries people who use substances are supplied equipment free of charge, others require payment or an exchange of dirty needles for clean ones, hence the name.
A 2010 review found insufficient evidence that NSP prevents transmission of the hepatitis C virus, tentative evidence that it prevents transmission of HIV and sufficient evidence that it reduces self-reported injecting risk behaviour. It has been shown in the many evaluations of needle-exchange programmes that in areas where clean syringes are more available, illegal drug use is no higher than in other areas. Needle exchange programmes have reduced HIV incidence by 33% in New Haven
New Haven is a city in the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in New Haven County, Connecticut and is part of the New York City metropolitan area. With a population of 134,023 ...
and 70% in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
.
The Melbourne, Australia inner-city suburbs of Richmond and Abbotsford are locations in which the use and dealing of heroin has been concentrated for a protracted time period. Research organisation the Burnet Institute completed the 2013 'North Richmond Public Injecting Impact Study' in collaboration with the Yarra Drug and Health Forum, City of Yarra and North Richmond Community Health Centre and recommended 24-hour access to sterile injecting equipment due to the ongoing "widespread, frequent and highly visible" nature of illicit drug use in the areas. During the period between 2010 and 2012 a four-fold increase in the levels of inappropriately discarded injecting equipment was documented for the two suburbs. In the local government area the City of Yarra, of which Richmond and Abbotsford are parts of, 1550 syringes were collected each month from public syringe disposal bins in 2012. Furthermore, ambulance callouts for heroin overdoses were 1.5 times higher than for other Melbourne areas in the period between 2011 and 2012 (a total of 336 overdoses), and drug-related arrests in North Richmond were also three times higher than the state average. The Burnet Institute's researchers interviewed health workers, residents and local traders, in addition to observing the drug scene in the most frequented North Richmond public injecting locations.
On 28 May 2013, the Burnet Institute stated in the media that it recommends 24-hour access to sterile injecting equipment in the Melbourne suburb of Footscray after the area's drug culture continues to grow after more than ten years of intense law enforcement efforts. The institute's research concluded that public injecting behaviour is frequent in the area and inappropriately discarding injecting paraphernalia has been found in carparks, parks, footpaths and drives. Furthermore, people who inject drugs have broken open syringe disposal bins to reuse discarded injecting equipment.
The British public body, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE), introduced a new recommendation in early April 2014 due to an increase in the presentation of the number of young people who inject steroids at UK needle exchanges. NICE previously published needle exchange guidelines in 2009, in which needle and syringe services are not advised for people under the age of 18 years, but the organisation's director Professor Mike Kelly explained that a "completely different group" of people were presenting at programs. In the updated guidance, NICE recommended the provision of specialist services for "rapidly increasing numbers of steroid users", and that needles should be provided to people under the age of 18—a first for NICE—following reports of 15-year-old steroid injectors seeking to develop their muscles.
=Supervised injection sites (SIS)
=Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. Th ...
's Insite, opened in September 2003. In 2010, after a nine-year trial, the Sydney site was confirmed as a permanent public health facility. As of late 2009 there were a total of 92 professionally supervised injection facilities in 61 cities.
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) is an agency of the European Union located in Lisbon, Portugal, and established in 1993. In June 2022, the Council of the European Union approved a reform of the organization ...
's latest systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on t ...
from April 2010 did not find any evidence to support concerns that DCR might "encourage drug use, delay treatment entry or aggravate problems of local drug markets." Jürgen Rehm and Benedikt Fischer explained that while evidence show that DCR are successful, that "interpretation is limited by the weak designs applied in many evaluations, often represented by the lack of adequate control groups." Concluding that this "leaves the door open for alternative interpretations of data produced and subsequent ideological debate."
The EMCDDA review noted that research into the effects of the facilities "faces methodological challenges in taking account of the effects of broader local policy or ecological changes", still they concluded "that the facilities reach their target population and provide immediate improvements through better hygiene and safety conditions for injectors." Further that "the availability of safer injecting facilities does not increase levels of drug use or risky patterns of consumption, nor does it result in higher rates of local drug acquisition crime." While its usage is "associated with self-reported reductions in injecting risk behaviour such as syringe sharing, and in public drug use" and "with increased uptake of detoxification
Detoxification or detoxication (detox for short) is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. Additionally, it can refer to the period of ...
and treatment services." However, "a lack of studies, as well as methodological problems such as isolating the effect from other interventions or low coverage of the risk population, evidence regarding DCRs—while encouraging—is insufficient for drawing conclusions with regard to their effectiveness in reducing HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
or hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
virus (HCV) incidence." Concluding with that "there is suggestive evidence from modelling studies that they may contribute to reducing drug-related deaths at a city level where coverage is adequate, the review-level evidence of this effect is still insufficient."
Critics of this intervention, such as drug prevention advocacy organisations, Drug Free Australia and Real Women of Canada point to the most rigorous evaluations, those of Sydney and Vancouver. Two of the centers, in Sydney, Australia and Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada cost $2.7 million and $3 million per annum to operate respectively, yet Canadian mathematical modeling, where there was caution about validity, indicated just one life saved from fatal overdose per annum for Vancouver,see Executive Summary of 2008 while the Drug Free Australia analysis demonstrates the Sydney facility statistically takes more than a year to save one life. The Expert Advisory Committee of the Canadian Government studied claims by journal studies for reduced HIV transmission by Insite but "were not convinced that these assumptions were entirely valid." The Sydney facility showed no improvement in public injecting and discarded needles beyond improvements caused by a coinciding heroin drought, while the Vancouver facility had an observable impact. Drug dealing and loitering around the facilities were evident in the Sydney evaluation, but not evident for the Vancouver facility.
Sex
Safer sex programmes
Many schools now provide safer sex education to teen and pre-teen students, who may engage in sexual activity. Since some adolescents are going to have sex, a harm-reductionist approach supports a sexual education which emphasizes the use of protective devices likecondoms
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female con ...
and dental dams to protect against unwanted pregnancy and the transmission of STIs. This runs contrary to abstinence
Abstinence is a self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol, drugs, food, etc.
...
-only sex education, which teaches that educating children about sex can encourage them to engage in it.
These programmes have been found to decrease risky sexual behaviour and prevent sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especi ...
. They also reduce rates of unwanted pregnancies. Abstinence only
Abstinence-only sex education is a form of sex education that teaches not having sex outside of marriage. It often excludes other types of sexual and reproductive health education, such as birth control and safe sex. Comprehensive sex educatio ...
programmes do not appear to affect HIV risks in developed countries with no evidence available for other areas.
Legalized prostitution
Since 1999 some countries have legalized prostitution, such asGermany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
(2002) and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
(2003). However, in most countries the practice is prohibited. Gathering accurate statistics on prostitution and human trafficking is extremely difficult. This has resulted in proponents of legalization claiming that it reduces organized crime rates while opponents claim exactly the converse. The Dutch prostitution policy, which is one of the most liberal in the world, has gone back and forth on the issue several times. In the period leading up to 2015 up to a third of officially sanctioned work places had been closed down again after reports of human trafficking. Prostitutes themselves are generally opposed to what they see as "theft of their livelihood".
Legal prostitution means prostitutes can contact police in instances of abuse or violence without fear of arrest or prosecution because of what they are doing being illegal. A legal and regulated system can also provide licensed brothels as opposed to prostitutes working on the streets, in which the owners or staff of the premises can call the police in instances of violence against sex workers without fear of workers or the business facing criminal charges or being shut down. Legal and regulated prostitution can require prostitutes to undergo regular health checks for sexually transmitted diseases and infections (STDs and STIs) by law. Sex workers in Nevada for instance have to get monthly tests for syphilis and HIV and weekly tests for gonorrhea and chlamydia. "Researchers at a public research institute in the Netherlands discovered that when major cities in that country opened tippelzones, or areas where street prostitutes could work legally, reports of rape and sexual abuse declined by as much as 30 to 40 percent in the first two years after the zones were opened. In cities that licensed the prostitutes permitted to work in these tippelzones, rapes and sexual abuse dropped by as much as 40 percent, while the reductions in sexual violence were slightly lower in zones that did not enforce the licensing of sex workers." Dutch researchers also found significant reductions in drug-related crime in these areas with licensed prostitution. In cities with both a tippelzone and a licensing requirement, for instance, they found a 25 percent reduction in drug-related crimes within two years.
Sex-work and HIV
Despite the depth of knowledge of HIV/AIDS, rapid transmission has occurred globally in sex workers. The relationship between these two variables greatly increases the risk of transmission among these populations, and also to anyone associated with them, such as their sexual partners, their children, and eventually the population at large. Many street-level harm-reduction strategies have succeeded in reducing HIV transmission ininjecting drug user
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or subcutaneous location). Intravenous t ...
s and sex-workers. HIV education, HIV testing, condom use, and safer-sex negotiation greatly decreases the risk to the disease. Peer education as a harm reduction strategy has especially reduced the risk of HIV infection, such as in Chad, where this method was the most cost-effective per infection prevented.
The threat of criminal repercussions marginalizes sex-workers and people who inject substances, often resulting in high-risk behaviour, increasing the rate of overdose, infectious disease transmission, and violence.
Decriminalisation as a harm-reduction strategy gives the ability to treat substance use disorder solely as a public health issue rather than a criminal activity. This enables other harm-reduction strategies to be employed, which results in a lower incidence of HIV infection.
One of the first harm reduction models was called the "Mersey Harm Reduction Model" in 1980s Liverpool, and the success of utilizing outreach workers, distribution of education, and providing clean equipment to drug users was shown in the fact that an HIV epidemic did not happen in Mersey. This catapulted the model into International conferences on drug related harm in the midst of the AIDS epidemic, making it an internationally recognized model of preventing HIV/AIDS specifically within injecting drug user populations. There was much connection between San Francisco (an epicenter of HIV/AIDS advocacy in the US) and Liverpool. Harm reduction slowly began to transform the action around drug use from an individualistic approach that mainstream US healthcare often relies on, towards a more holistic population-based approach.
The AIDS epidemic, which began in the 80s and peaked in 1995, further complicated the politicization of drug users and drug use in the US. The implementation of harm reduction faced much resistance within the US due to the demonization of particular drugs associated with stigmatized groups, such as sex workers and drug-injecting users.
Decriminalisation
Decriminalisation as a harm-reduction strategy gives the ability to treat substance use disorder solely as a public health issue rather than a criminal activity. This enables other harm-reduction strategies to be employed, which results in a lower incidence of HIV infection.Psychiatric medications
With the growing concern about psychiatric medication adverse effects and long-term dependency, peer-run mental health groups Freedom Center andThe Icarus Project
The Icarus Project (2002-2020) was a network of peer-support groups and media projects with the stated aim of changing the language and culture of what gets called mental health and mental illness. The name is derived from Icarus, a hero in Greek ...
published the ''Harm Reduction Guide to Coming Off Psychiatric Drugs''. The self-help guide provides patients with information to help assess risks and benefits, and to prepare to come off, reduce, or continue medications when their physicians are unfamiliar with or unable to provide this guidance. The guide is in circulation among mental health consumer groups and has been translated into ten languages.
Criticism
Critics, such asDrug Free America Foundation
The Drug Free America Foundation (DFAF) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization founded in 1976 by former US Ambassador Mel Sembler, his wife Betty Sembler (), and Joseph Zappala as Straight, Inc., renamed The Straight Foundation, Inc. in 1985 and ...
and other members of network ''International Task Force on Strategic Drug Policy'', state that a risk posed by harm reduction is by creating the perception that certain behaviours can be partaken of safely, such as illicit drug use, that it may lead to an increase in that behaviour by people who would otherwise be deterred. The signatories of the drug prohibitionist network International Task Force on Strategic Drug Policy stated that they oppose drug use harm reduction "...strategies as endpoints that promote the false notion that there are safe or responsible ways to use drugs. That is, strategies in which the primary goal is to enable drug users to maintain addictive, destructive, and compulsive behavior by misleading users about some drug risks while ignoring others."
In 2008, the World Federation Against Drugs stated that while "...some organizations and local governments actively advocate the legalization of drugs and promote policies such as "harm reduction" that accept drug use and do not help people who use substances to become free from substance use. This undermines the international efforts to limit the supply of and demand for drugs." The Federation states that harm reduction efforts often end up being "drug legalization or other inappropriate relaxation efforts, a policy approach that violates the UN Conventions."
Critics furthermore reject harm reduction measures for allegedly trying to establish certain forms of drug use as acceptable in society. The Drug Prevention Network of Canada states that harm reduction has "...come to represent a philosophy in which illicit substance use is seen as largely unpreventable, and increasingly, as a feasible and acceptable lifestyle as long as use is not 'problematic'", an approach which can increase "acceptance of drug use into the mainstream of society". They say harm reduction "...sends the wrong message to...children and youth" about drug use. In 2008, the Declaration of World Forum Against Drugs criticized harm reduction policies that "...accept drug use and do not help drug users to become free from drug abuse", which the group say undermines "...efforts to limit the supply of and demand for drugs." They state that harm reduction should not lead to less efforts to reduce drug demand.
Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereig ...
criticised harm reduction policies with regards to HIV/AIDS, saying that it was "a tragedy that cannot be overcome by money alone, that cannot be overcome through the distribution of condoms, which even aggravates the problems". This position was in turn widely criticised for misrepresenting and oversimplifying the role of condoms in preventing infections.
Neil Hunt's article entitled "A review of the evidence-base for harm reduction approaches to drug use" examines the criticisms of harm reduction, which include claims that it is not effective; that it prevents addicts from "hitting a rock bottom" thus trapping them in addiction; that it encourages drug use; that harm reduction is a Trojan horse
The Trojan Horse was a wooden horse said to have been used by the Greeks during the Trojan War to enter the city of Troy and win the war. The Trojan Horse is not mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'', with the poem ending before the war is concluded, ...
strategy for " drug law reform", such as drug legalization.
See also
*Low-threshold treatment programs Low-threshold treatment programs are harm reduction-based Community health center, health care centers targeted towards Recreational drug use, people who use substances. "Low-threshold" programs are programs that make minimal demands on the patient, ...
* Mitigation
References
External links
*Drugs Policy and Harm Reduction
- Research on the circulation of ideas around harm reduction and urban drug policies by Eugene McCann and Cristina Temenos (Simon Fraser University). * *
TNI on Harm Reduction
{{DEFAULTSORT:Harm Reduction Alcohol and health Addiction Drug culture Drug policy Public health