|
Daniel Robertson (British Army Officer)
Colonel Daniel Robertson (''c.'' 1733 – 5 April 1810) was an officer in the British Army in North America, commandant of the British post at Michilimackinac, and a landowner in Chatham Township, Canada. Born in Scotland, he first joined the 42nd Regiment of Foot, also known as the "Black Watch," and was present at the British capture of Montreal in 1760, as well as the invasion of Martinique in 1762. During the American Revolutionary War, he was an officer in the 84th Regiment of Foot, another regiment of Scots known as the Royal Highland Emigrants. In 1779, he was appointed commandant of Fort Osgewatchie and oversaw Native American raids on American settlements on the Mohawk River. From 1782, Robertson served as commandant of Fort Michilimackinac (later known as Fort Mackinac). He freed his black slaves, Jean Bonga and Marie-Jeanne Bonga, before leaving Mackinac Island for Montreal in 1787. "Robinson's Folly" at Mission Point on Mackinac Island was originally called "Robertso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Robertson (Canada)
Daniel Robertson may refer to: * Daniel Robertson (architect) (died 1849), British architect * Daniel Robertson (British Army officer) (1733–1819), British military officer in North America * Daniel Robertson (colonial administrator) (1813–1892), British colonial administrator * Daniel Robertson (infielder) (born 1994), American professional baseball shortstop * Daniel Robertson (outfielder) (born 1985), American professional baseball outfielder * Daniel A. Robertson (1812–1895), American newspaper editor and politician See also * Robertson Daniel (born 1991), American football player {{DEFAULTSORT:Robertson, Daniel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchase Of Commissions In The British Army
The purchase of officer commissions in the British Army was the practice of paying money to the Army to be made an officer of a cavalry or infantry regiment of the English and later British Army. By payment, a commission as an officer could be secured, avoiding the need to wait to be promoted for merit or seniority. This practice was the usual way to obtain a commission in the Army from the 17th to the late 19th century. The practice began in 1683, during the reign of King Charles II, and continued until it was abolished on 1 November 1871, as part of the Cardwell Reforms. Formally, the purchase price of a commission was a cash bond for good behaviour, liable to be forfeited to the Army's cashiers (accountants) if found guilty of cowardice, desertion, or gross misconduct. Great Britain and Ireland Only commissions in cavalry and infantry regiments could be purchased and therefore only those up to the rank of colonel. Commissions in the Royal Engineers and the Royal Artillery wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Du Calvet
Pierre du Calvet (1735 – March 28, 1786) was a Montreal trader, justice of the peace, political prisoner and epistle writer of French Huguenot origin. Biography Family Pierre du Calvet was born in the Summer of 1735 in Caussade in the French province of Guyenne (today the Tarn-et-Garonne ''département''). He was the oldest of a family of five children. His father, Pierre Calvet, of Calvinist confession, had his children baptized as Catholics. He however passed on his Protestant faith to them. His mother was Anne Boudet. His family is said to be of noble origin and owned a domain at Montalzat, north of Toulouse. An ancestor, François Calvet, was hanged on June 23, 1563 for introducing the Reform in Montauban. Education He received a Catholic education without renouncing his Calvinism. Judging from his writings, he certainly studied the Humanities, French law, the Law of Nations and the philosophy of his time, that of the Enlightenment. In the main epistle of his ''Appel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justice Of The Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the same meaning. Depending on the jurisdiction, such justices dispense summary justice or merely deal with local administrative applications in common law jurisdictions. Justices of the peace are appointed or elected from the citizens of the jurisdiction in which they serve, and are (or were) usually not required to have any formal legal education in order to qualify for the office. Some jurisdictions have varying forms of training for JPs. History In 1195, Richard I ("the Lionheart") of England and his Minister Hubert Walter commissioned certain knights to preserve the peace in unruly areas. They were responsible to the King in ensuring that the law was upheld and preserving the " King's peace". Therefore, they were known as "keepers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French people, French colonists who settled in Canada (New France), Canada beginning in the 17th century or to French-speaking or Francophone Canadians of any ethnic origin. During the 17th century, French settlers originating mainly from the west and north of France settled Canada (New France), Canada. It is from them that the French Canadian ethnicity was born. During the 17th to 18th centuries, French Canadians expanded across North America and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. As a result people of French Canadian descent can be found across North America. Between 1840 and 1930, many French Canadians immigrated to New England, an event known as the Grande Hémorragie. Etymology French Canadians get their name from ''Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as ''Fort Ville-Marie, Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a Census Metropolitan Area#Census metropolitan areas, metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest city, and List of cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bouquet
Henry Bouquet (born Henri Louis Bouquet; 1719 – 2 September 1765) was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American force at the Battle of Bushy Run, lifting the siege of Fort Pitt during Pontiac's War. During the conflict Bouquet gained lasting infamy in an exchange of letters with his commanding officer, Jeffery Amherst, who suggested a form of biological warfare in the use of blankets infected with smallpox which were to be distributed to Native Americans. Despite this indictment historians have praised Bouquet for leading British forces in several demanding campaigns on the Western Frontier in which they "protected and rescued" settlers from increasingly frequent attacks. Early life Bouquet was born in Rolle, Switzerland, as the oldest of seven brothers. The son of a Swiss roadhouse owner and his well-to-do wife, he entered military service at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bushy Run
The Battle of Bushy Run was fought on August 5–6, 1763, in western Pennsylvania, between a British column under the command of Colonel Henry Bouquet and a combined force of Delaware, Shawnee, Mingo, and Huron warriors. This action occurred during Pontiac's Rebellion. Though the British suffered serious losses, they routed the tribesmen and successfully relieved the garrison of Fort Pitt. Battle In July 1763, a relief column of 500 British soldiers, including the 42nd Highlanders, 60th Royal Americans, and 77th Highlanders, left Carlisle, Pennsylvania, to relieve Fort Pitt, then under siege. Indian scouts observed Bouquet's force marching west along Forbes Road and reported this to the Indians surrounding Fort Pitt. On August 5, at about 1:00 pm, a part of the force besieging Fort Pitt ambushed the British column one mile east of Bushy Run Station, at Edge Hill. The British managed to hold their ground until after sunset, when the natives withdrew. Bouquet ordered a redou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
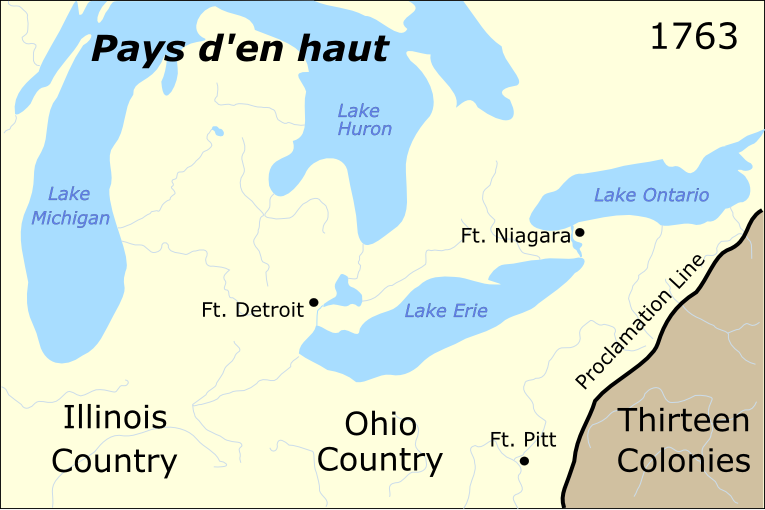
Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–1763). Warriors from numerous nations joined in an effort to drive British soldiers and settlers out of the region. The war is named after Odawa leader Pontiac, the most prominent of many indigenous leaders in the conflict. The war began in May 1763 when Native Americans, alarmed by policies imposed by British General Jeffrey Amherst, attacked a number of British forts and settlements. Eight forts were destroyed, and hundreds of colonists were killed or captured, with many more fleeing the region. Hostilities came to an end after British Army expeditions in 1764 led to peace negotiations over the next two years. The Natives were unable to drive away the British, but the uprising prompted the British government to modify the policies that had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)