|
CGS-12066A
CGS-12066A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT1B receptor Receptor may refer to: * Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse *Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a ... with lower affinity for the three 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. It is used for studying the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in various processes including perception of pain and the sleep-wake cycle. References Serotonin receptor agonists Trifluoromethyl compounds Piperazines Quinoxalines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT1B Receptor
5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR1B'' gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype. Tissue distribution and function 5-HT1B receptors are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system with the highest concentrations found in the frontal cortex, basal ganglia, striatum, and the hippocampus. The function of the 5-HT1B receptor differs depending upon its location. In the frontal cortex, it is believed to act as a postsynaptic receptor inhibiting the release of dopamine. In the basal ganglia and the striatum, evidence suggests 5-HT signaling acts on an autoreceptor, inhibiting the release of serotonin and decreasing glutamatergic transmission by reducing miniature excitatory postsynaptic potential (mEPSP) frequency, respectively. In the hippocampus, a recent study has demonstrated that activation of postsynaptic 5-HT1B heteroreceptors produces a facilitation in excitatory synap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug injection, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption (skin), absorption via a dermal patch, patch on the skin, suppository, or sublingual administration, dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to pharmacotherapy, treat, cure, preventive healthcare, prevent, or medical diagnosis, diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In the field of pharmacology, potency is a measure of drug activity expressed in terms of the amount required to produce an effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, alprazolam, risperidone, bumetanide, bisoprolol) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (meperidine, diazepam, ziprasidone, furosemide, metoprolol) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness or more side effects. The IUPHAR The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) is a voluntary, non-profit association representing the interests of scientists in pharmacology-related fields to facilitate ''Better Medicines through Global Education and Resear ... has stated that 'potency' is ''"an imprecise term that should always be further defined"'', for instance as EC_, IC_, ED_, LD_ and so on. See also * Reaction inhibitor § Potency References Further readin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Selectivity
Functional selectivity (or “agonist trafficking”, “biased agonism”, “biased signaling”, "ligand bias" and “differential engagement”) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a reference ligand (often the endogenous hormone or peptide) at the same receptor. Functional selectivity can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways. To which degree each pathway is activated thus depends on which ligand binds to the receptor. Functional selectivity, or biased signaling, is most extensively characterized at G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). A number of biased agonists, such as those at muscarinic M2 receptors tested as analgesics or antiproliferative drugs, or those at opioid receptors that mediate pain, show potential at various receptor families to increase beneficial properties while reducing side effects. For example, pre-clinical studies with G protein biased agonists at the μ-opioid re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2 Receptor
The 5-HT2 receptors are a subfamily of 5-HT receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT2 subfamily consists of three G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) which are coupled to Gq/G11 and mediate excitatory neurotransmission Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), ..., including 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C. For more information, please see the respective main articles of the individual subtypes: * 5-HT2A receptor * 5-HT2B receptor * 5-HT2C receptor See also * 5-HT1 receptor * 5-HT3 receptor * 5-HT4 receptor * 5-HT5 receptor * 5-HT6 receptor * 5-HT7 receptor * 5-HT2 antagonists References {{Serotonergics Serotonin receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
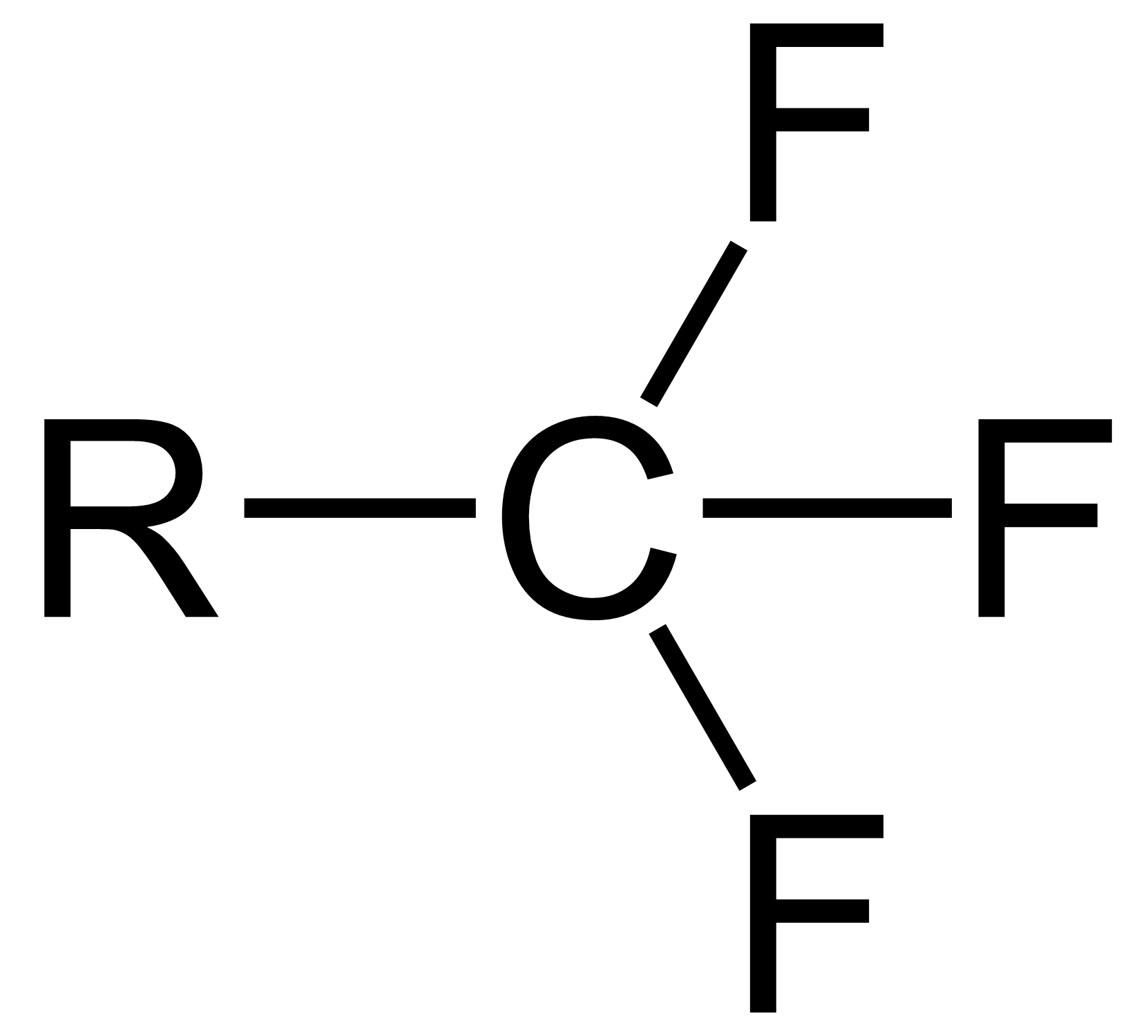
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperazines
Substituted piperazines are a class of chemical compounds based on a piperazine core. Some are used as recreational drugs and some are used in scientific research. List of substituted piperazines Benzylpiperazines File:Benzylpiperazine.svg, 1-Benzylpiperazine File:MBZP.svg, 1-Methyl-4-benzylpiperazine File:DBZP.svg, 1,4-Dibenzylpiperazine File:MDBZP.svg, 3,4-Methylenedioxy-1-benzylpiperazine File:2C-B-BZP.svg, 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine File:Methoxypiperamide.png, Methoxypiperamide File:Sunifiram.svg , Sunifiram File:3-Methylbenzylpiperazine structure.png, 3-Methylbenzylpiperazine * 1-Benzylpiperazine (BZP) * 1-Methyl-4-benzylpiperazine (MBZP) * 1,4-Dibenzylpiperazine (DBZP) * 3,4-Methylenedioxy-1-benzylpiperazine (MDBZP) * 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) * Methoxypiperamide (MeOP, MEXP) ((4-methoxyphenyl)(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methanone) * Sunifiram (1-benzoyl-4-propanoylpiperazine) * 3-Methylbenzylpiperazine (3-MeBZP) Befuraline, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |