|
Religion In Kurdistan
The main religions that exist or existed in Kurdistan are as follows: Sunni Islam, Shia Islam, Christianity, Zoroastrianism, Yarsanism, Yazidism, Kurdish Alevism, Alevism and Judaism. Sunni Islam is the most adhered religion in Kurdistan. Islam The majority of Kurdish people are Muslim by religion. While the relationship between religion and nationalism has usually been strained and ambivalent with the strong hold of the Islamic leaders in Kurdish society, it has generally been the conservative Muslim Kurds who formed the backbone of the Kurdish movements. Sunni Islam The majority of Kurds are Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims. The exact proportion is uncertain but McDowall gives the percentage as 'approximately 75%', while Martin van Bruinessen estimates around two thirds or three quarters at least. Most Sunni Kurds follow the Shafi‘i madhhab, which distinguishes them from Arab and Turkish neighbors who in general are Hanafi. This difference is identified by some Kurds as being ess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish languages, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros Mountains, Zagros and the eastern Taurus Mountains, Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey (Turkish Kurdistan, Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan, Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Iranian Kurdistan, Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Syrian Kurdistan, Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern South Caucasus, Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Ubeydullah
}) also known as ''Sayyid Ubeydullah'', was the leader of the first modern Kurdish nationalist struggle. Ubeydullah demanded recognition from Ottoman Empire and Qajar dynasty authorities for an independent Kurdish state, or Kurdistan, which he would govern without interference from Ottoman or Qajar authorities.Ozoglu, Hakan. ''Kurdish Notables and the Ottoman State: Evolving Identities, Competing Loyalties, and Shifting Boundaries''. Feb 2004. . pp. 74-75. Sheikh Ubeydullah was an influential landowner in the 19th century and a member of the powerful Kurdish Şemdinan family from Nehri. He was the son of Sheikh Taha and a nephew to Sheikh Salih, from whom he inherited the leadership of the Naqshbandi order in Şemdinan. After his rebellion was suppressed, he was exiled first to Istanbul, then to Hijaz where he died. Rise to power The emergence of Islamic scholars and leaders, or Sheikhs, as national leaders among the Kurds was the result of the elimination of hereditary semi-aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Said
Sheikh Said of Palu ( ku, شێخ سەعید, translit=Şêx Seîd, 1865 – June 29, 1925) was a Kurdish sheikh, the main leader of the Sheikh Said rebellion and a Sheikh of the Naqshbandi order. He was born in 1865 in Palu to an influential family from the Naqshbandi order. He had five brothers. Still in his childhood, the family settled to Hınıs, Erzurum, where his grandfather was an influential Sheikh. Sheikh Said studied religious sciences at the madrasa led by his father Sheikh Mahmud Fevzi as well from several Islamic scholars in the region. Later he was involved in the local tekke set up by his grandfather Sheikh Ali. His grandfather was a respected leader of the religious community and his grave was visited by thousands of pilgrims. He became the head of the religious community after his father Sheikh Mahmud died. In 1907 he toured the neighboring provinces in the east and he established contacts with officers from the Hamidiye cavalry. Civata Xweseriya Kurd (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadiriyyah
The Qadiriyya (), also transliterated Qādirīyah, ''Qadri'', ''Qadriya'', ''Kadri'', ''Elkadri'', ''Elkadry'', ''Aladray'', ''Alkadrie'', ''Adray'', ''Kadray'', ''Kadiri'', ''Qadiri'', ''Quadri'' or ''Qadri'' are members of the Sunni Qadiri tariqa (Sufi order). The tariqa got its name from Abdul Qadir Gilani (1077–1166, also transliterated ''Jilani''), who was a Hanbali scholar from Gilan, Iran. The order relies strongly upon adherence to the fundamentals of Sunni Islamic law. The order, with its many offshoots, is widespread, particularly in the non-Arabic-speaking world, and can also be found in Turkey, Indonesia, Afghanistan, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, the Balkans, Russia, Palestine, China, Gladney, Dru "Muslim Tombs and Ethnic Folklore: Charters for Hui Identity"''Journal of Asian Studies'', August 1987, Vol. 46 (3): 495-532; pp. 48-49 in the PDF file. and East and West Africa. History The founder of the Qadiriyya, Abdul Qadir Gilani, was a scholar and preacher. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud Barzanji
Sheikh Mahmud Barzanji ( ku, شێخ مهحموود بەرزنجی) or Mahmud Hafid Zadeh (1878 – October 9, 1956) was a Kurdish leader of a series of Kurdish uprisings against the British Mandate of Iraq. He was sheikh of a Qadiriyah Sufi family of the Barzanji clan from the city of Sulaymaniyah, which is now in Iraqi Kurdistan. He was named King of Kurdistan during several of these uprisings. Background After World War I, the British and other Western powers occupied parts of the Ottoman Empire. Plans made with the French in the Sykes–Picot Agreement designated Britain as the mandate power. The British were able to form their own borders to their pleasure to gain an advantage in this region. The British had firm control of Baghdad and Basra and the regions around these cities mostly consisted of Shiite and Sunni Arabs. In 1921, the British appointed Faisal I the King of Iraq. It was an interesting choice because Faisal had no local connections, as he was part of the Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadiriyya
The Qadiriyya (), also transliterated Qādirīyah, ''Qadri'', ''Qadriya'', ''Kadri'', ''Elkadri'', ''Elkadry'', ''Aladray'', ''Alkadrie'', ''Adray'', ''Kadray'', ''Kadiri'', ''Qadiri'', ''Quadri'' or ''Qadri'' are members of the Sunni Qadiri tariqa (Sufi order). The tariqa got its name from Abdul Qadir Gilani (1077–1166, also transliterated ''Jilani''), who was a Hanbali scholar from Gilan, Iran. The order relies strongly upon adherence to the fundamentals of Sunni Islamic law. The order, with its many offshoots, is widespread, particularly in the non-Arabic-speaking world, and can also be found in Turkey, Indonesia, Afghanistan, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, the Balkans, Russia, Palestine, China, Gladney, Dru "Muslim Tombs and Ethnic Folklore: Charters for Hui Identity"''Journal of Asian Studies'', August 1987, Vol. 46 (3): 495-532; pp. 48-49 in the PDF file. and East and West Africa. History The founder of the Qadiriyya, Abdul Qadir Gilani, was a scholar and preacher. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
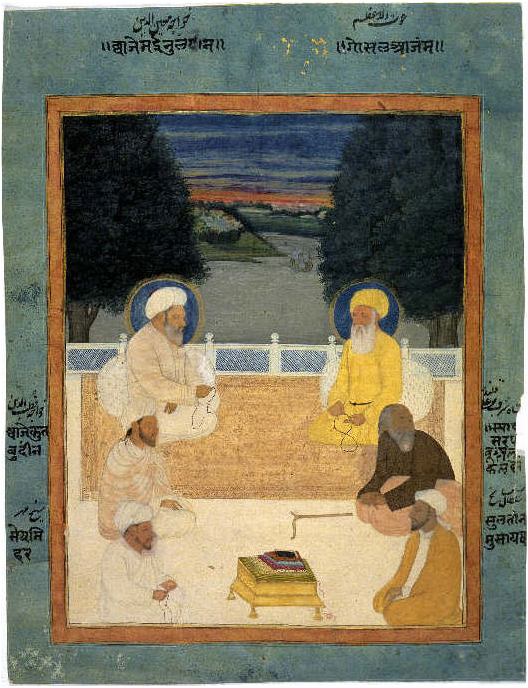
Naqshbandi
The Naqshbandi ( fa, نقشبندی)), Neqshebendi ( ku, نهقشهبهندی), and Nakşibendi (in Turkish) is a major Sunni order of Sufism. Its name is derived from Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari. Naqshbandi masters trace their lineage to the Islamic prophet Muhammad through Abu Bakr, the first Caliph of Sunni Islam and Ali, the fourth Caliph of Sunni Islam. It is because of this dual lineage through Ali and Abu Bakr through the 6th Imam Jafar al Sadiq that the order is also known as the "convergence of the two oceans" or "Sufi Order of Jafar al Sadiq". History The Naqshbandi order owes many insights to Yusuf Hamdani and Abdul Khaliq Gajadwani in the 12th century, the latter of whom is regarded as the organizer of the practices and is responsible for placing stress upon the purely silent ''invocation''. It was later associated with Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari in the 14th century, hence the name of the order. The name can be interpreted as "engraver (of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
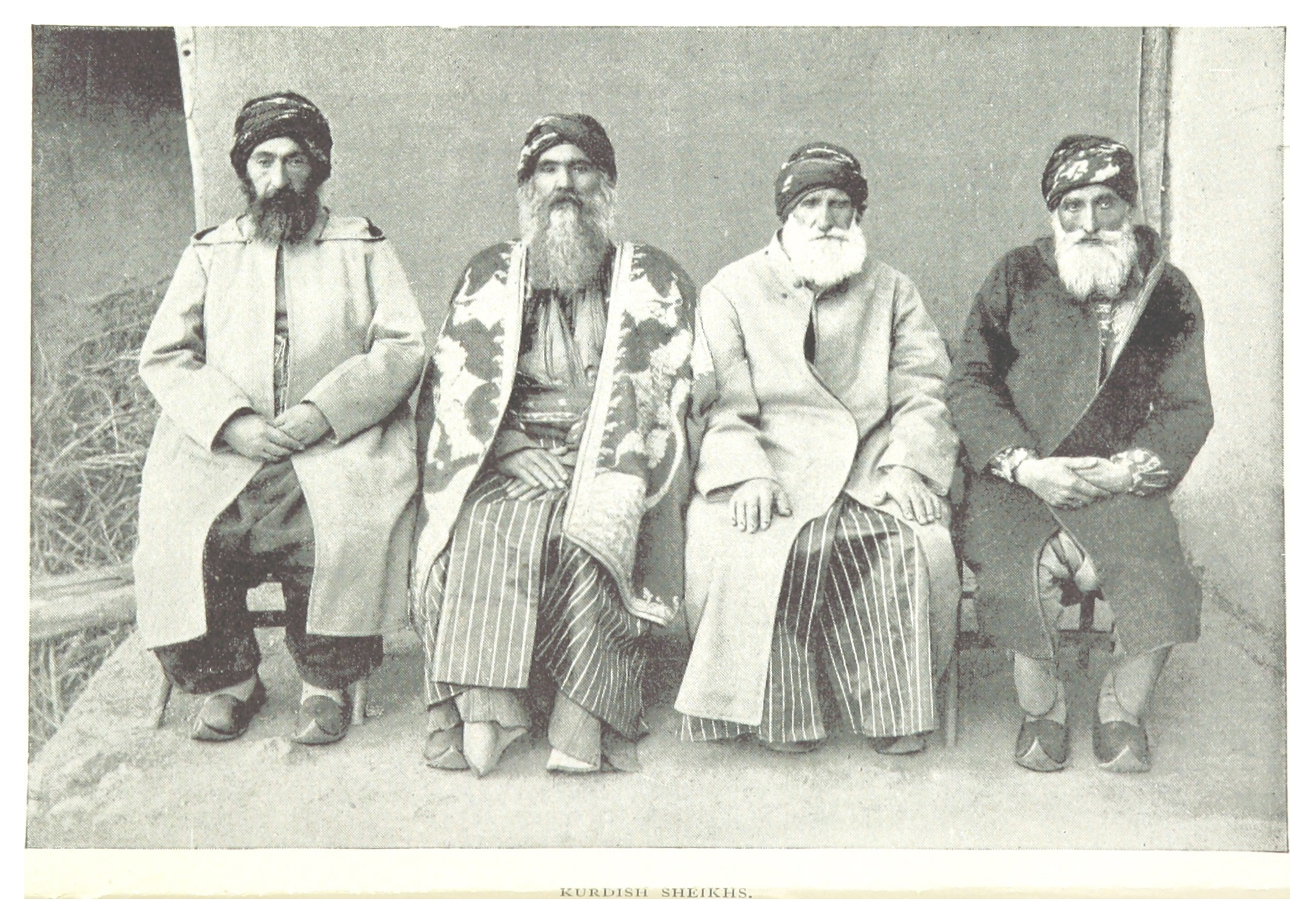
Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a tribe or a royal family member in Arabian countries, in some countries it is also given to those of great knowledge in religious affairs as a surname by a prestige religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. It is also commonly used to refer to a Muslim religious scholar. It is also used as an honorary title by people claiming to be descended from Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali both patrilineal and matrilineal who are grandsons of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The term is literally translated to " Elder" (is also translated to "Lord/Master" in a monarchical context). The word 'sheikh' is mentioned in the 23rd verse of Surah Al-Qasas in the Quran. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ritualism, asceticism and esotericism. It has been variously defined as "Islamic mysticism",Martin Lings, ''What is Sufism?'' (Lahore: Suhail Academy, 2005; first imp. 1983, second imp. 1999), p.15 "the mystical expression of Islamic faith", "the inward dimension of Islam", "the phenomenon of mysticism within Islam", the "main manifestation and the most important and central crystallization" of mystical practice in Islam, and "the interiorization and intensification of Islamic faith and practice". Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) – congregations formed around a grand who would be the last in a chain of successive teachers linking back to Muham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |