|
Qadiriyya
The Qadiriyya (), also transliterated Qādirīyah, ''Qadri'', ''Qadriya'', ''Kadri'', ''Elkadri'', ''Elkadry'', ''Aladray'', ''Alkadrie'', ''Adray'', ''Kadray'', ''Kadiri'', ''Qadiri'', ''Quadri'' or ''Qadri'' are members of the Sunni Qadiri tariqa (Sufi order). The tariqa got its name from Abdul Qadir Gilani (1077–1166, also transliterated ''Jilani''), who was a Hanbali scholar from Gilan, Iran. The order relies strongly upon adherence to the fundamentals of Sunni Islamic law. The order, with its many offshoots, is widespread, particularly in the non-Arabic-speaking world, and can also be found in Turkey, Indonesia, Afghanistan, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, the Balkans, Russia, Palestine, China, Gladney, Dru "Muslim Tombs and Ethnic Folklore: Charters for Hui Identity"''Journal of Asian Studies'', August 1987, Vol. 46 (3): 495-532; pp. 48-49 in the PDF file. and East and West Africa. History The founder of the Qadiriyya, Abdul Qadir Gilani, was a scholar and preacher. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadri
The Qadiriyya (), also transliterated Qādirīyah, ''Qadri'', ''Qadriya'', ''Kadri'', ''Elkadri'', ''Elkadry'', ''Aladray'', ''Alkadrie'', ''Adray'', ''Kadray'', ''Kadiri'', ''Qadiri'', ''Quadri'' or ''Qadri'' are members of the Sunni Qadiri tariqa ( Sufi order). The tariqa got its name from Abdul Qadir Gilani (1077–1166, also transliterated ''Jilani''), who was a Hanbali scholar from Gilan, Iran. The order relies strongly upon adherence to the fundamentals of Sunni Islamic law. The order, with its many offshoots, is widespread, particularly in the non-Arabic-speaking world, and can also be found in Turkey, Indonesia, Afghanistan, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, the Balkans, Russia, Palestine, China, Gladney, Dru "Muslim Tombs and Ethnic Folklore: Charters for Hui Identity"''Journal of Asian Studies'', August 1987, Vol. 46 (3): 495-532; pp. 48-49 in the PDF file. and East and West Africa. History The founder of the Qadiriyya, Abdul Qadir Gilani, was a scholar and preacher. Hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Razzaq Gilani
ʿAbd al-Razzāq b. ʿAbd al-Qādir al-Jīlānī (c. Dhu al-Qi'dah 528 AH – 6 Shawwal 603 AH/9 September 1134 – 7 May 1207),''The works of Shaykh Umar Eli of Somalia of al-Tariqat al-Qadiriyyah.'' also known as Abū Bakr al-Jīlī or ʿAbd al-Razzāq al-Jīlānī (often simplified as Abdul-Razzaq Gilani) for short, or reverentially as Shaykh ʿAbd al-Razzāq al-Jīlānī by Sunni Muslims, was a Persian Sunni Muslim Hanbali theologian, jurist, traditionalist and Sufi mystic based in Baghdad. He received his initial training in the traditional Islamic sciences from his father, Abdul-Qadir Gilani (d. 1166), the founder of the Qadiriyya order of Sunni mysticism, prior to setting out "on his own to attend the lectures of other prominent Hanbali scholars" in his region. Ohlander, Erik S., “ʿAbd al-Razzāq b. ʿAbd al-Qādir al-Jīlānī”, in: ''Encyclopaedia of Islam, THREE'', Edited by: Kate Fleet, Gudrun Krämer, Denis Matringe, John Nawas, Everett Rowson. He is som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ritualism, asceticism and esotericism. It has been variously defined as "Islamic mysticism",Martin Lings, ''What is Sufism?'' (Lahore: Suhail Academy, 2005; first imp. 1983, second imp. 1999), p.15 "the mystical expression of Islamic faith", "the inward dimension of Islam", "the phenomenon of mysticism within Islam", the "main manifestation and the most important and central crystallization" of mystical practice in Islam, and "the interiorization and intensification of Islamic faith and practice". Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) – congregations formed around a grand who would be the last in a chain of successive teachers linking back to Muh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
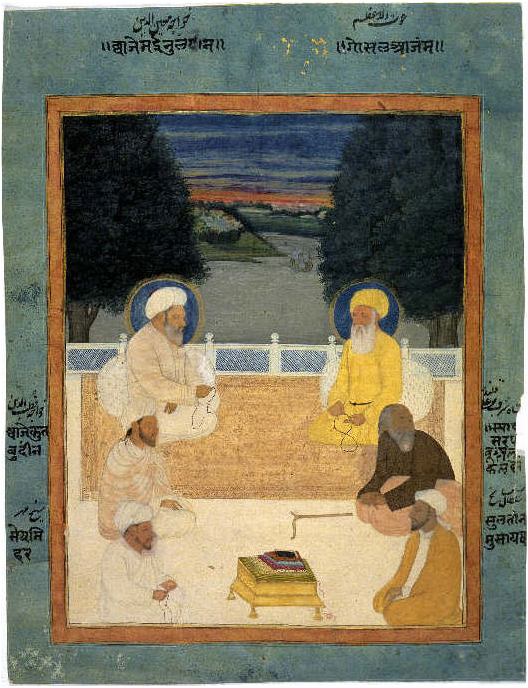
Abdul Qadir Gilani
ʿAbdul Qādir Gīlānī, ( ar, عبدالقادر الجيلاني, ʿAbd al-Qādir al-Jīlānī; fa, ) known by admirers as Muḥyī l-Dīn Abū Muḥammad b. Abū Sāliḥ ʿAbd al-Qādir al-Jīlānī al-Baḡdādī al-Ḥasanī al-Ḥusaynī (March 23, 1078February 21, 1166), was a Sunni Muslim preacher, ascetic, mystic, jurist, and theologian belonging to the Hanbali school, and the eponymous founder of the Qadiriyya tariqa (Sufi order) of Sufism.W. Braune, ''Abd al-Kadir al-Djilani, The Encyclopaedia of Islam'', Vol. I, ed. H.A.R Gibb, J.H.Kramers, E. Levi-Provencal, J. Schacht, (Brill, 1986), 69;"authorities are unanimous in stating that he was a Persian from Nayf (Nif) in Djilan, south of the Caspian Sea."John Renard, The A to Z of Sufism. p 142. Juan Eduardo Campo, Encyclopedia of Islam, p. 288. The Qadiriyya tariqa is named after him. He was born on March 23, 1078 (1 Ramdhan 470 AH) in the town of Na'if, Rezvanshahr in Gilan, Iran, and died on February 21, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum Of Abdul-Qadir Gilani
fa, مزار غوث, , native_name_lang = ara / fa , image = الحضرة القادرية منظر عام.jpg , image_upright = 1.4 , alt = , caption = The mausoleum complex in 2016 , map_type = Iraq Baghdad#Iraq#Middle East#Asia , map_size = 240 , map_alt = , map_relief = 1 , map_caption = Location in Baghdad , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , religious_affiliation = Sunni Islam , locale = , location = , deity = , rite = Qadiriyya Sufi , sect = , tradition = , festival = , cercle = , sector = , municipality = , district = , territory = , prefecture = , state = , province = , region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Saeed Mubarak Makhzoomi
Abu Saeed Mubarak Makhzoomi ( ar, ابوسعیدمبارک مخزومی), known also as Mubarak bin Ali Makhzoomi and Abu Saeed and Abu Sa'd al-Mubarak (rarely known as Qazi Abu Sa'd al-Mubarak al-Mukharrimi) was a Sufi saint as well as a Muslim mystic and traditionalist. He was an Islamic theologian and a Hanbali jurist based in Baghdad, Iraq. Abu Saeed was his patronym. Biography Abu Saeed Mubarak Makhzoomi was born in Hankar (the land of his Murshid) on 12th Rajab 403 Hijri but spent most of his life in Makhzum, a small town in Baghdad. He established Baab-ul-Azj, the famous madrasa of Baghdad whom he later handed over to his disciple and khalifah, Shaikh Abdul Qadir Jilani. Abu Saeed Mubarak Makhzoomi was also appointed as the chief justice but he preferred to renounce the worldly life. Thereafter he led his life as a mystic and devoted his time to the dhikr of Allah. He died on 11th Rabī’ al-Thānī 513 Hijri and was buried in Baab-ul-Azj, Baghdad. Sufi tradition Abu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools ('' madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal (d. 855), and was institutionalized by his students. The Hanbali madhhab is the smallest of four major Sunni schools, the others being the Hanafi, Maliki and Shafi`i. The Hanbali school derives ''sharia'' primarily from the '' Qur'an'', the '' Hadiths'' (sayings and customs of Muhammad), and the views of Sahabah (Muhammad's companions). In cases where there is no clear answer in sacred texts of Islam, the Hanbali school does not accept '' istihsan'' (jurist discretion) or '''urf'' (customs of a community) as a sound basis to derive Islamic law, a method that Hanafi and Maliki Sunni '' madh'habs'' accept. Hanbali school is the strict traditionalist school of jurisprudence in Sunni Islam. It is found primarily in the countries of Saudi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
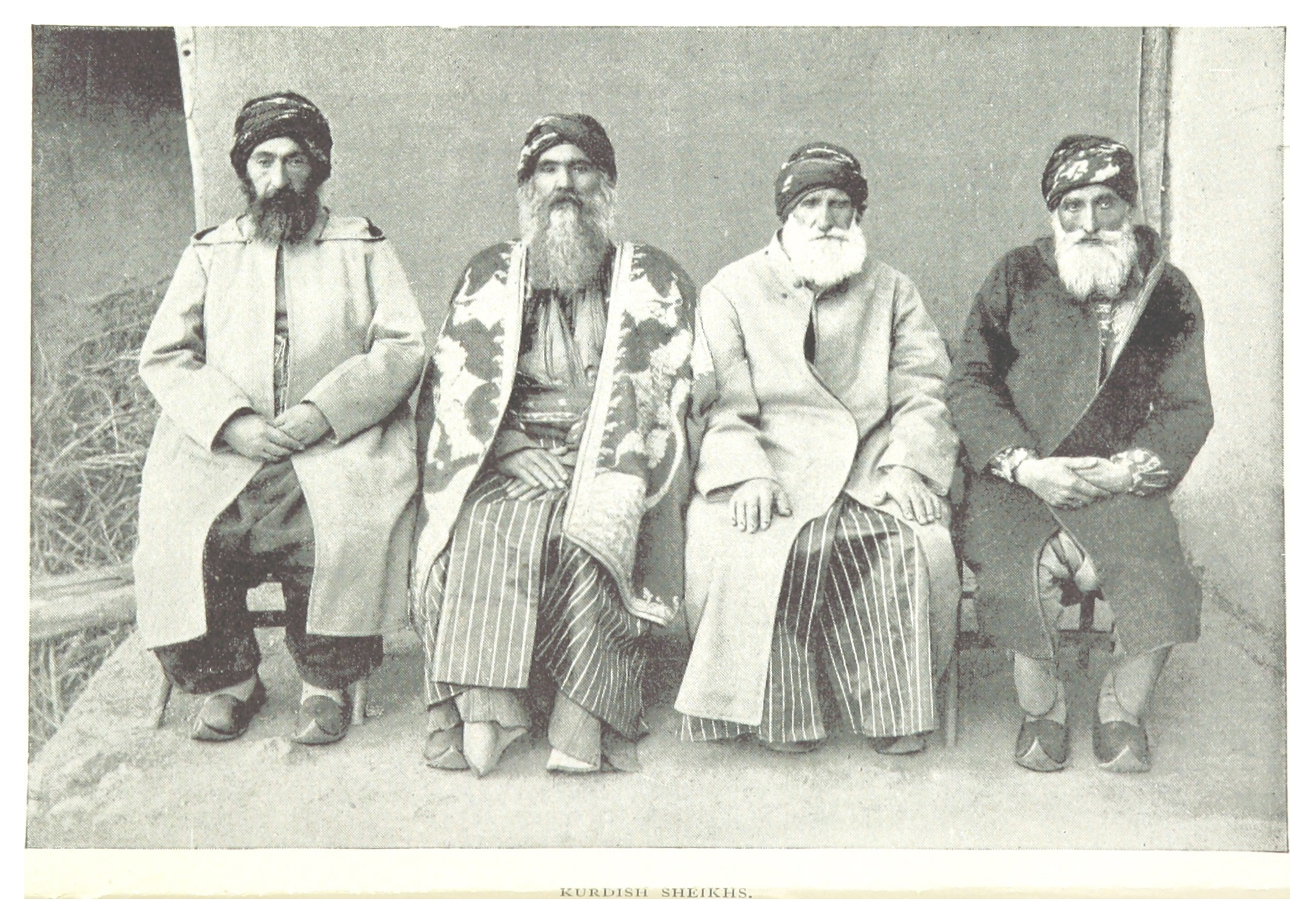
Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a tribe or a royal family member in Arabian countries, in some countries it is also given to those of great knowledge in religious affairs as a surname by a prestige religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. It is also commonly used to refer to a Muslim religious scholar. It is also used as an honorary title by people claiming to be descended from Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali both patrilineal and matrilineal who are grandsons of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The term is literally translated to "Elder" (is also translated to " Lord/ Master" in a monarchical context). The word 'sheikh' is mentioned in the 23rd verse of Surah Al-Qasas in the Quran. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions. According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad left no successor and the participants of the Saqifah event appointed Abu Bakr as the next-in-line (the first caliph). This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor. The adherents of Sunni Islam are referred to in Arabic as ("the people of the Sunnah and the community") or for short. In English, its doctrines and practices are sometimes called ''Sunnism'', while adherents are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, Sunnites and Ahlus Sunnah. Sunni Islam is sometimes referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadariyah
Qadariyyah ( ar, قدرية, Qadariyya), also Qadarites or Kadarites, from (), meaning "power"); was originally a derogatory term designating early Islamic theologians who rejected the concept of predestination in Islam, ''qadr'', and asserted that humans possess absolute free will, making them responsible for their actions, justifying divine punishment and absolving God of responsibility for evil in the world. Some of their doctrines were later adopted by the Mu'tazilis and rejected by the Ash'aris. They argued that evil actions of human beings could not be decreed by God, as they would have to be if there was no free will and all events in the universe were determined by God. Qadariyyah was one of the first philosophical schools in Islam. The earliest document associated with the movement is the pseudoepigraphical text ''Risala'' attributed to Hasan al-Basri, which was composed between 75 AH/694 CE and 80/699, though debates about free will in Islam probably predate this text. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of Southeast Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. The term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia in the 19th century, the European provinces of the Ottoman Empire. It had a geop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




.jpg)