|
Clifford Holliday
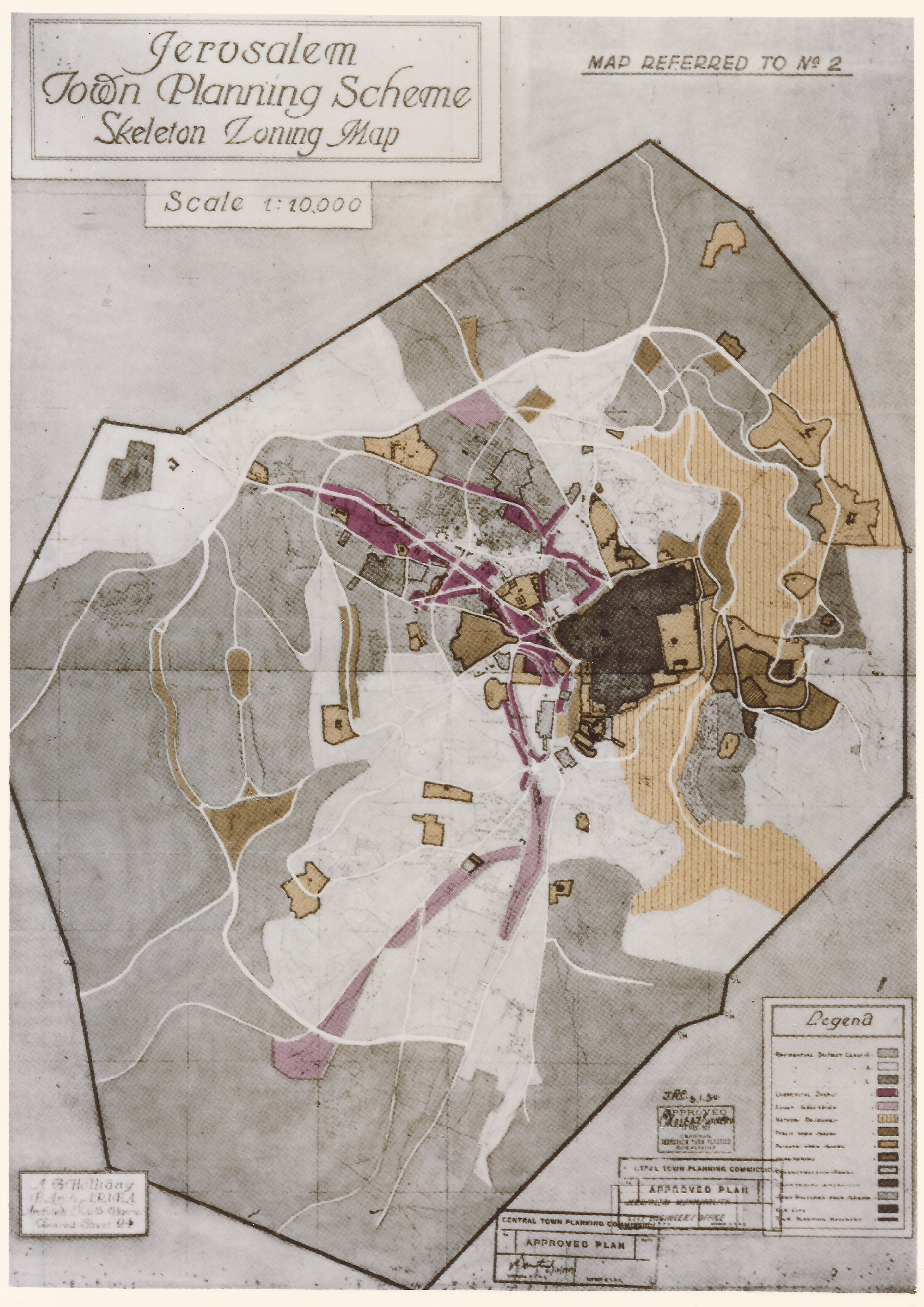
Albert Clifford Holliday (1897–1960) M. Arch, Dip. C.D., F.R.I.B.A., M.T.P., was a British architect and town planner who worked in several places across the British Empire, including Mandatory Palestine, Ceylon and Gibraltar, as well as in the UK. Studies Holliday gained his qualifications at the University of Liverpool where he studied under Sir Charles Reilly and Patrick Abercrombie.'Stevenage Architect', Manchester ''Guardian'', 16 October 1947, p. 6 He later designed the University of Ceylon with Abercrombie.'Prof. C. Holliday' London ''Guardian'', 30 September 1960 p. 15 Career Mandate Palestine Holliday was commissioned as civic adviser to the city of Jerusalem between 1922 and 1926 and town planning advisor to the mandatory government of Palestine between 1928 and 1934. He drew up a master plan for Jerusalem and the restoration of its Old City walls. United Kingdom In 1938, Holliday's design for a satellite town near Kincorth, outside Aberdeen, won an internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gildersome
Gildersome is a village and civil parish in the City of Leeds metropolitan borough 5 miles (7 km) south-west of Leeds city centre in West Yorkshire, England. Glidersome forms part of the Heavy Woollen District. Location Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, it is situated midway between Leeds, Wakefield and Bradford but is in the LS27 (Leeds) postcode area while the village telephone numbers are "0113", the Leeds prefix. Gildersome was an urban district, established in 1894. In 1937 it was absorbed into the Municipal Borough of Morley. In 1974 the borough was abolished and combined with neighbouring authorities in the City of Leeds. Although the village is still classed as part of the Morley urban area in the census, it is technically separate, and is not governed by Morley Town Council. In 2004 a civil parish was established and the village now has a parish council. At the 2011 Census the population of this civil parish was 5,804. Gildersome is sits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and has a population estimate of for the city of Aberdeen, and for the local council area making it the United Kingdom's 39th most populous built-up area. The city is northeast of Edinburgh and north of London, and is the northernmost major city in the United Kingdom. Aberdeen has a long, sandy coastline and features an oceanic climate, with cool summers and mild, rainy winters. During the mid-18th to mid-20th centuries, Aberdeen's buildings incorporated locally quarried grey granite, which may sparkle like silver because of its high mica content. Since the discovery of North Sea oil in 1969, Aberdeen has been known as the offshore oil capital of Europe. Based upon the discovery of prehistoric villages around the mouths of the rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo metropolitan area has a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 in the Municipality. It is the financial centre of the island and a tourist destination. It is located on the west coast of the island and adjacent to the Greater Colombo area which includes Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, and Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia. Colombo is often referred to as the capital since Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is itself within the urban/suburban area of Colombo. It is also the administrative capital of the Western Province and the district capital of Colombo District. Colombo is a busy and vibrant city with a mixture of modern life, colonial buildings and monuments. Due to its large harbour and its strategic position along th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haaretz
''Haaretz'' ( , originally ''Ḥadshot Haaretz'' – , ) is an Israeli newspaper. It was founded in 1918, making it the longest running newspaper currently in print in Israel, and is now published in both Hebrew and English in the Berliner format. The English edition is published and sold together with the ''International New York Times''. Both Hebrew and English editions can be read on the internet. In North America, it is published as a weekly newspaper, combining articles from the Friday edition with a roundup from the rest of the week. It is considered Israel's newspaper of record. It is known for its left-wing and liberal stances on domestic and foreign issues. As of 2022, ''Haaretz'' has the third-largest circulation in Israel. It is widely read by international observers, especially in its English edition, and discussed in the international press. According to the Center for Research Libraries, among Israel's daily newspapers, "''Haaretz'' is considered the most infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Municipality
The Jerusalem Municipality ( he, עיריית ירושלים; Iriyat yerushalayim), the seat of the Israeli municipal administration, consists of a number of buildings located on Jaffa Road in the city of Jerusalem. History British Mandate town hall (1930) Jerusalem's old town hall was built in 1930, during the British Mandate. The construction was financed by Barclays Bank, whose offices were located in the rounded section of the building facing the Old City walls. The building was designed by British architect Clifford Holliday. Stained glass windows designed by Israeli artist Avigdor Arikha were installed in the City Council Chamber in 1972. Israeli municipality compound (1990s) The new complex of the Jerusalem municipality was built in the 1990s in Safra Square. Offices were previously located in 32 different buildings around the city. As the site is at the historic centre of the city, various measures were taken to meet the practical needs of the town hall without d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safra Square
Safra or SAFRA may refer to: People (surname) * Alberto J. Safra (born 1979/1980), Brazilian banker *Edmond Safra (1932–1999), Syrian-Brazilian banker *Jacob Safra (1891–1963), Syrian banker *Jacqui Safra (born 1948), Swiss investor and actor *Joseph Safra (1939–2020), Brazilian banker *Lily Safra (1934–2022), Brazilian philanthropist and socialite *Moise Safra (1934–2014), Brazilian businessman and philanthropist *Rav Safra (280–338), Babylonian Amora *Shmuel Safra, Israeli computer scientist * Vicky Safra (born 1952/1953), Brazilian-born philanthropist People (given name) *Safra Catz (born 1961), American business executive Organizations *Safra Group, an international network of companies controlled by the Joseph Safra family **Banco Safra **Bank Jacob Safra Switzerland **Safra National Bank of New York * SAFRA Radio, a Singaporean broadcasting company *SAFRA National Service Association, Singapore NSmen Recreation Club Places *Safra, Iran, a village in Khuzestan Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Gischala
John of Gischala ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης, ; 70) was a leader of the first Jewish revolt against the Romans. History During the Jewish war with Rome, John of Gischala ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης ἀπὸ Γισχάλων), son of Levi (), vied with Josephus over the control of Galilee and amassed a large band of supporters from Gischala (Gush Halav) and Gabara, including the support of the Sanhedrin in Jerusalem. As part of the Roman campaign to put down the revolt in Judea, Titus marched on Gush Halav, called Giscala by the Romans. Giscala was the last town in Galilee not yet conquered. Outside the walls of the city, he called on them to surrender. John prevailed upon Titus not to enter the city that day, as it was Sabbath, "not so much out of regard to the seventh day as to his own preservation." John fled to Jerusalem that night, and "Titus was greatly displeased that he had not been able to bring this John, who had deluded him, to punishment." When John entered Jerusalem, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Old Town Hall
Jerusalem's old town hall was one of the four public buildings constructed in Jerusalem by the British administration during the British Mandate. History When the town hall at the corner of Jaffa and Mamilla streets became insufficient for the needs of the burgeoning city, the Mandatory government built a new office. It was used by the Municipality of Jerusalem for over 60 years, from 1930 to 1993. Construction of the building was financed by Barclays Bank, whose offices stood in the rounded section which faces the Old City's northwest corner. British architect Clifford Holliday designed the building. In 1972, stained glass windows designed by Israeli artist Avigdor Arikha were installed in the City Council Chamber. Gallery File:Barclays building Jerusalem 1939.JPG, Barclay's bank, 1939 File:JerusalemMunicipalityP4190018.JPG, Entrance File:JerusalemMunicipalityP4190014.JPG, Barclays Bank logo (BB) under a window (southeast facade) File:JerusalemMunicipalityP4190075.JPG, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Andrew's Church, Jerusalem
St Andrew's Church, also known as the Scots Memorial Church, is a church in Jerusalem built as a memorial to the Scottish soldiers who were killed fighting the Turkish Army during the Sinai and Palestine campaign of World War I, bringing to an end Ottoman rule over Palestine. It is a congregation presbyterian of the Church of Scotland. History British Mandate period One of the main campaigners for the memorial church was Ninian Hill, an Edinburgh shipowner and Church elder. The foundation stone was laid by Field Marshal Lord Allenby on 7 May 1927 and the church was opened in 1930 with Ninian Hill as its first minister. The Church was much used by Scots serving in the Mandate administration and soldiers serving with Scottish Regiments stationed in Palestine during the Mandate, including the Second World War.Kernohan, R.D., ''The Road to Zion: Travellers to Palestine and the Land of Israel''. 1994. . pages 138,139. Wars: 1947–1948, 1967 After the outbreak of hostilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arts And Crafts
A handicraft, sometimes more precisely expressed as artisanal handicraft or handmade, is any of a wide variety of types of work where useful and decorative objects are made completely by one’s hand or by using only simple, non-automated related tools like scissors, carving implements, or hooks. It is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid materials, paper, plant fibers,clay etc. One of the oldest handicraft is Dhokra; this is a sort of metal casting that has been used in India for over 4,000 years and is still used. In Iranian Baluchistan, women still make red ware hand-made pottery with dotted ornaments, much similar to the 5000-year-old pottery tradition of Kalpurgan, an archaeological site near the village. Usually, the term is applied to traditional techniques of creating items (whether for per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John Ophthalmic Hospital
The St John of Jerusalem Eye Hospital Group is a charitable foundation which operates an ophthalmic hospital in Jerusalem – one of six hospitals in the East Jerusalem Hospitals Network – and satellite eye care clinics and hospitals in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. It is a wholly owned corporate subsidiary of the Venerable Order of St John. The Hospital Group is based in Jerusalem and is the main provider of eye care in the Palestinian territories. History First site The original Hospital opened by The Order of St John in 1882 on the Bethlehem Road just south of the old city of Jerusalem. Queen Victoria granted the hospital a Royal Charter. Sir Edmund Lechmere, 3rd Baronet was one of the key figures in the establishment of the hospital. Lechmere and his wife were among the founders of Venerable Order of St John and had travelled several times to Jerusalem where they witnessed the need of its residents for eye care. During the First World War, the hospital was closed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent (often abbreviated to Stoke) is a city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Staffordshire, England, with an area of . In 2019, the city had an estimated population of 256,375. It is the largest settlement in Staffordshire and is surrounded by the towns of Newcastle-under-Lyme, Alsager, Kidsgrove, Biddulph and Stone, Staffordshire, Stone, which form a conurbation around the city. Stoke is wikt:polycentric, polycentric, having been formed by Federation of Stoke-on-Trent, the federation of six towns in 1910. It took its name from Stoke-upon-Trent where the main centre of government and the principal Stoke-on-Trent railway station, railway station in the district were located. Hanley, Staffordshire, Hanley is the primary commercial centre; the other four towns which form the city are Burslem, Tunstall, Staffordshire, Tunstall, Longton, Staffordshire, Longton and Fenton, Staffordshire, Fenton. Stoke-on-Trent is the home of the pottery industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_DAILY_OF_THE_EARLY_20S.jpg)



