|
Chalcis Decree
The Chalcis Decree was an oath of loyalty that the people of the city of Chalcis on the island of Euboea were forced to swear after the failure of a revolt from the Athenian Empire in 446/5 BC. The decree is difficult to date but it followed the revolt of the cities of Euboea in 446. The islanders were angered by the increasingly harsh imperialism of Athens and attempted to take advantage of the defeat of Athens in the Battle of Coronea in neighbouring Boeotia (c. 447 BC) which resulted in the loss of the Athenian “land empire”. The revolt was crushed by the Athenians led by Pericles. Other cities on Euboea, such as Eretria, had decrees with exactly the same provisions passed. The decree is considered a point at which there was no longer any doubt of the imperial power held by Athens over its allies in the Delian League. ''I will not revolt from the people of Athens by any means or device whatsoever, neither in word or in deed, nor will I obey anyone who does revolt, and if a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
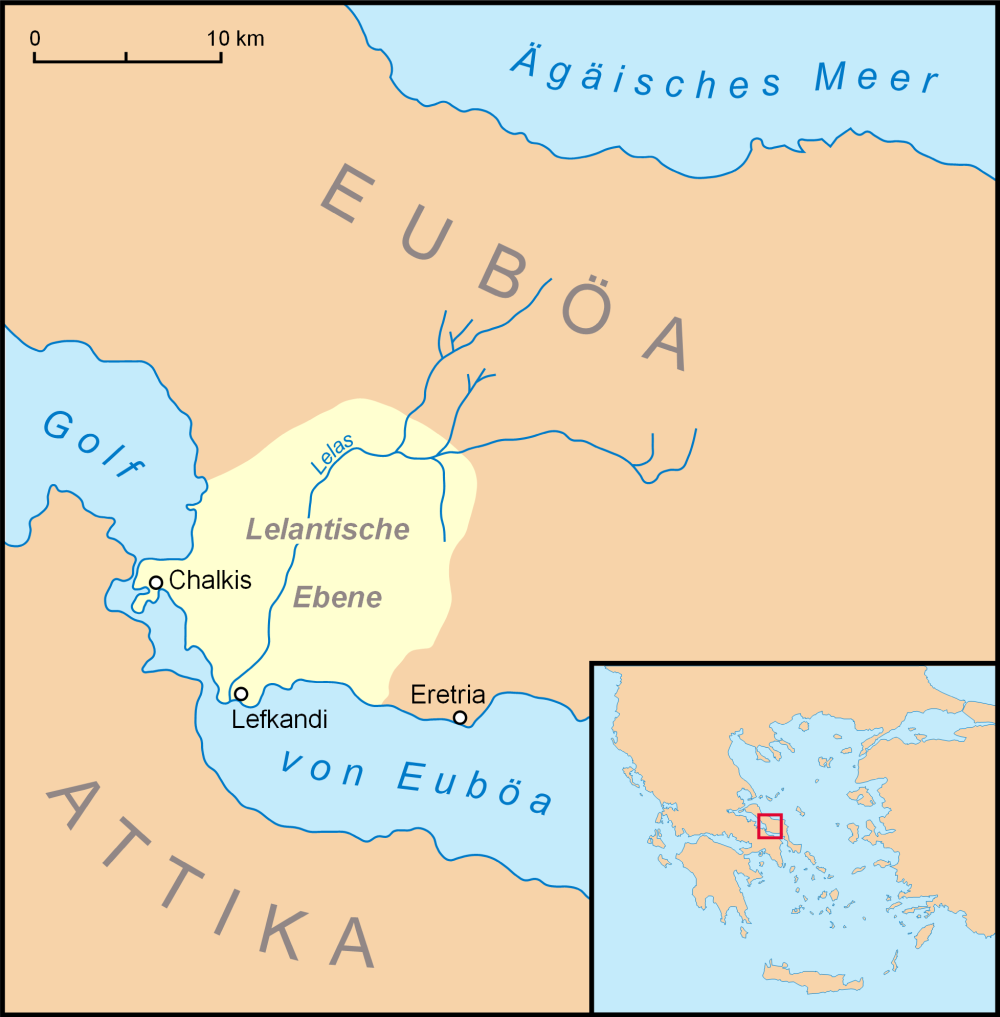
Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from antiquity and is derived from the Greek χαλκός (copper, bronze), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea. History Ancient Greece The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty townships on the peninsula of Chalcidice and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
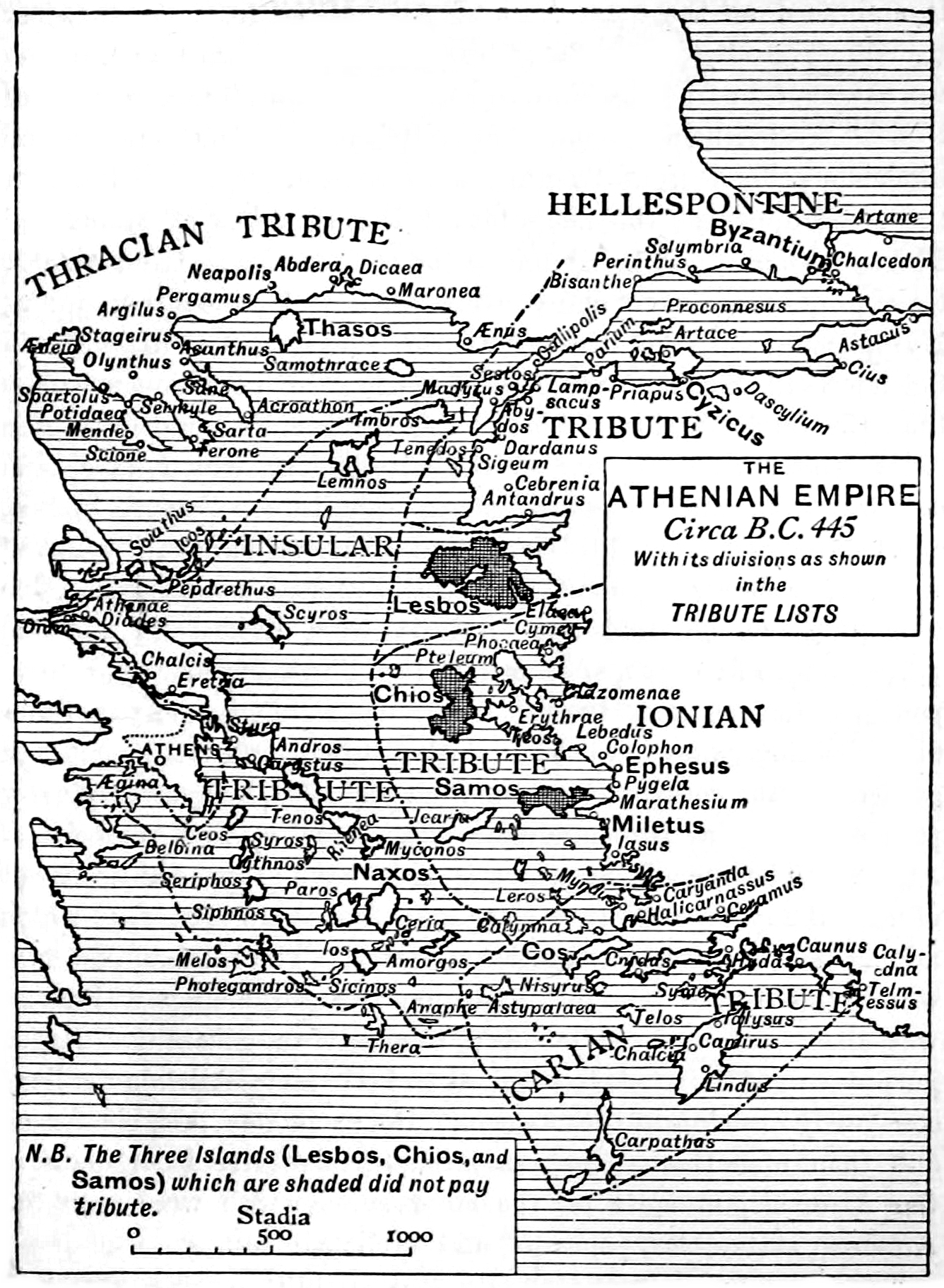
Athenian Empire
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held in the temple and where the treasury stood until, in a symbolic gesture, Pericles moved it to Athens in 454 BC. Shortly after its inception, Athens began to use the League's funds for its own purposes, which led to conflicts between Athens and the less powerful members of the League. By 431 BC, the threat the League presented to Spartan hegemony combined with Athens's heavy-handed control of the Delian League prompted the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War; the League was dissolved upon the war's conclusion in 404 BC under the direction of Lysander, the Spartan commander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Coronea (447 BC)
The Battle of Coronea (also known as the First Battle of Coronea) took place between the Athenian-led Delian League and the Boeotian League in 447 BC during the First Peloponnesian War. In 457 BC the Athenians had taken control of Boeotia at the Battle of Oenophyta, and spent the next ten years attempting to consolidate the League's power. In 454 BC Athens lost a fleet attempting to aid an Egyptian revolt against Persia; fearing revolts by the other members of the Delian League, Athens moved the treasury to their city from Delos in 453 BC, and signed the Peace of Callias with Persia around 450 BC. The Delian League was essentially an Athenian empire, and while Athens was usually successful at holding their possessions in the Aegean Sea, they were less successful on land. By 447 BC some of the men exiled from Boeotia after the Athenian victory there in 457 BC had returned home and began to take back some of the Boeotian towns. The Athenians under Tolmides, with 1,000 hoplit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center of Boeotia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, Περικλῆς; c. 495 – 429 BC) was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed by Thucydides, a contemporary historian, as "the first citizen of Athens".Thucydides, 2.65 Pericles turned the Delian League into an Athenian empire and led his countrymen during the first two years of the Peloponnesian War. The period during which he led Athens, roughly from 461 to 429 BC, is sometimes known as the "Age of Pericles", but the period thus denoted can include times as early as the Persian Wars or as late as the following century. Pericles promoted the arts and literature, and it is principally through his efforts that Athens acquired the reputation of being the educational and cultural center of the ancient Greek world. He started an ambitious project that generated most of the surviving stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held in the temple and where the treasury stood until, in a symbolic gesture, Pericles moved it to Athens in 454 BC. Shortly after its inception, Athens began to use the League's funds for its own purposes, which led to conflicts between Athens and the less powerful members of the League. By 431 BC, the threat the League presented to Spartan hegemony combined with Athens's heavy-handed control of the Delian League prompted the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War; the League was dissolved upon the war's conclusion in 404 BC under the direction of Lysander, the Spartan comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliaia
Heliaia or Heliaea ( grc, Ἡλιαία; Doric: Ἁλία ''Halia'') was the supreme court of ancient Athens. The view generally held among scholars is that the court drew its name from the ancient Greek verb , which means ''congregate''. Another version is that the court took its name from the fact that the hearings were taking place outdoors, under the sun. Initially, this was the name of the place where the hearings were convoked, but later this appellation included the court as well.''The Helios'' The judges were called ''heliasts'' () or ''dikastes'' (, = those who have sworn, namely the jurors). The operation of judging was called (). Institution and composition of Heliaia It is not clear whether Heliaia was instituted by Cleisthenes or Solon, but it seems that the latter initiated a function of the Assembly to sit as an appeals court. The court had 6,000 members, chosen annually by lot among all the male citizens over 30 years old, unless they were disfranchised.AristotleC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |