|
Carnobacterium Viridans
''Carnobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria within the family Carnobacteriaceae. ''C. divergens'' and ''C. maltaromaticum'' are found in the wild and in food products and can grow anaerobically. These species are not known to be pathogenic in humans, but may cause disease in fish. A species of ''Carnobacterium'', ''C. maltaromaticum'' strain CB1, has been evaluated under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999, as a food additive for vacuum- or modified atmosphere-packaged ready-to-eat meat and fresh comminuted, processed meat. Based on the hazard and exposure considerations, the risk assessment conducted by Health Canada concluded that ''C. maltaromaticum'' strain CB1 is not considered to be toxic to the Canadian environment or human health as described in Section 64 of CEPA 1999. ''Carnobacterium'' sp. has also been found in the gut of stingles carrion-eating vulture bees, besides other acidophilic (acid-loving) ''Lactobacillus ''Lactobacillus'' is a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
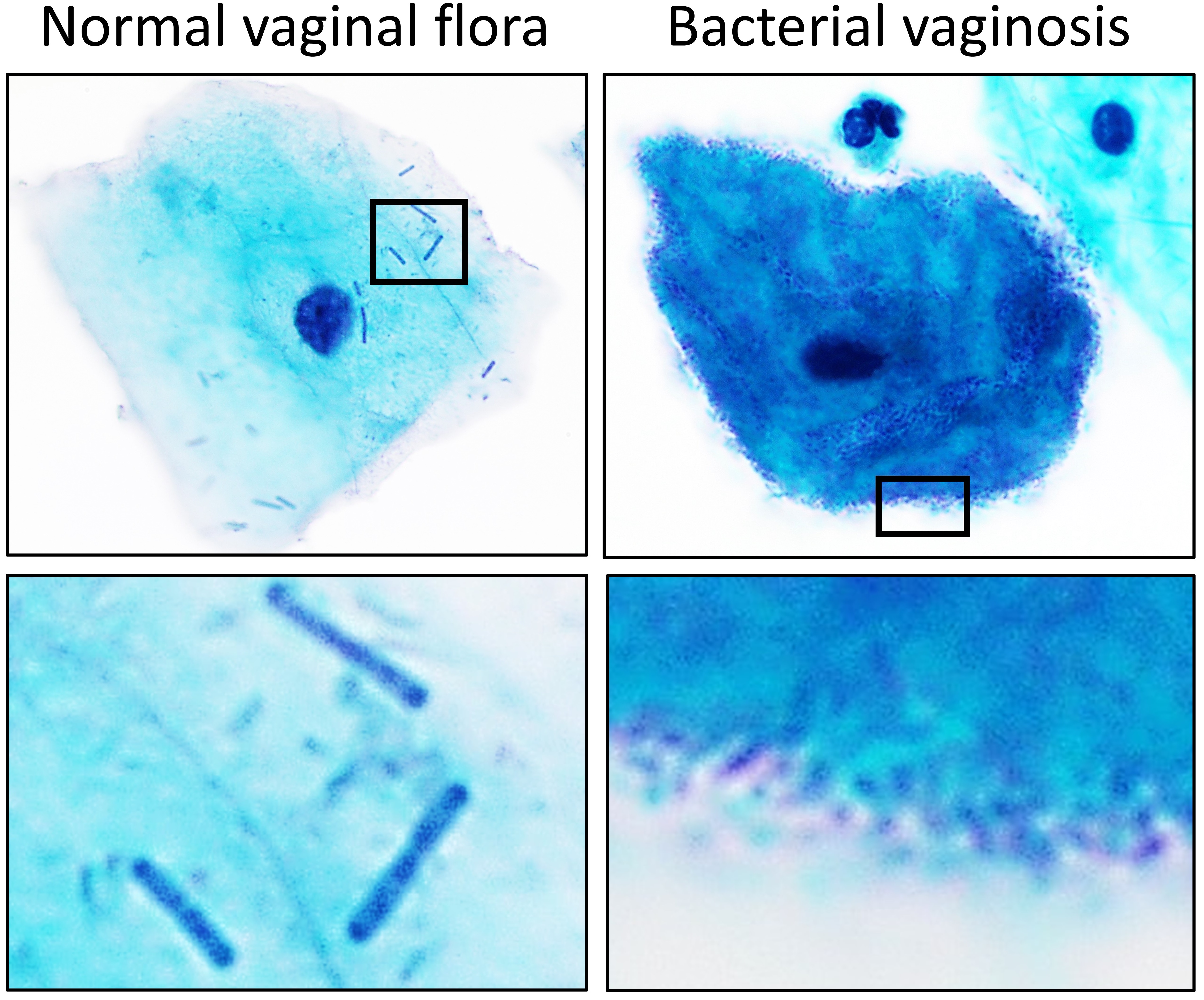
Lactobacillales
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, GC-content, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, Aerotolerant anaerobe, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped (bacillus (shape), bacilli) or spherical (cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation (food), fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Production of lactic acid has linked LAB with Fermentation (food), food fermentations, as acidification inhibits the growth of spoilage agents. Proteinaceous bacteriocins are produced by several LAB strains and provide an additional hurdle for spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, lactic acid and other metabolic products contribute to the organoleptic and textural profile of a food item. The industrial importance of the LAB is further evidenced by their gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidophilic
Acidophiles or acidophilic organisms are those that thrive under highly acidic conditions (usually at pH 5.0 or below). These organisms can be found in different branches of the tree of life, including Archaea, Bacteria,Becker, A.Types of Bacteria Living in Acidic pH" Retrieved 10 May 2017. and Eukarya. Examples A list of these organisms includes: Archaea :* Sulfolobales, an order in the Thermoproteota branch of Archaea :* Thermoplasmatales, an order in the Euryarchaeota branch of Archaea :* ARMAN, in the Euryarchaeota branch of Archaea :* ''Acidianus brierleyi, A. infernus'', facultatively anaerobic thermoacidophilic archaebacteria :* '' Halarchaeum acidiphilum'', acidophilic member of the Halobacteriacaeae :* ''Metallosphaera sedula'', thermoacidophilic Bacteria :* Acidobacteriota, a phylum of Bacteria :* Acidithiobacillales, an order of Pseudomonadota e.g. ''A. ferrooxidans, A. thiooxidans'' :*''Thiobacillus prosperus, T. acidophilus, T. organovorus, T. cuprinus'' :*''Acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulture Bee
Vulture bees, also known as carrion bees, are a small group of three closely related South American stingless bee species in the genus ''Trigona'' which feed on rotting meat. Vulture bees produce a honey-like substance which is not derived from nectar, but rather from protein-rich secretions of the bees' hypopharyngeal glands. These secretions are likely derived from the bees' diet, which consists of carrion eaten outside the nest.Laura L. Figueroa, Jessica J. Maccaro, Erin Krichilsky, Douglas Yanega, Quinn S. McFrederickWhy Did the Bee Eat the Chicken? Symbiont Gain, Loss, and Retention in the Vulture Bee Microbiome In: ASM mBio, vol. 12, no. 6, e02317-12, 23 November 2021, doi:10.1128/mBio.02317-21 This unusual behavior was only discovered in 1982, nearly two centuries after the bees were first classified.Roubik, D.W. (1982)"Obligate Necrophagy in a Social Bee" ''Science'' 217 (4564): 1059–60. Taxonomy The three species in this group are: * ''Trigona crassipes'' (Fabricius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; french: Santé Canada, SC)Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Government of Canada responsible for national health policy. The department itself is also responsible for numerous federal health-related agencies, including the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) and the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), among others. These organizations help to ensure compliance with federal law in a variety of Healthcare in Canada, healthcare, Agriculture in Canada, agricultural, and Pharmaceutics, pharmaceutical activities. This responsibility also involves extensive collaboration with various other federal- and provincial-level organizations in order to ensure the safety of food, health, and Medication, pharmaceutical products—including the regulation of health research and pharmaceutic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Environmental Protection Act
The ''Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999'' (''CEPA, 1999''; french: Loi canadienne sur la protection de l'environnement (1999)) is an act of the 36th Parliament of Canada, whose goal is to contribute to sustainable development through pollution prevention and to protect the environment, human life and health from the risks associated with toxic substances. It covers a diversity of activities that can affect human health and the environment, and acts to address any pollution issues not covered by other federal laws. As such, the act is a "catch all" piece of legislation that ensures potentially toxic substances are not inadvertently exempt from federal oversight as a result of unforeseen legislative loopholes. The act also recognizes the contribution of pollution prevention and the management and control of toxic substances and hazardous waste to reducing threats to Canada's ecosystems and biological diversity. It acknowledges, for the first time, the need to virtually e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flame an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnobacteriaceae
The Carnobacteriaceae are a family of Gram-positive lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bact .... References Lactobacillales Gram-positive bacteria {{lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnobacterium Viridans
''Carnobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria within the family Carnobacteriaceae. ''C. divergens'' and ''C. maltaromaticum'' are found in the wild and in food products and can grow anaerobically. These species are not known to be pathogenic in humans, but may cause disease in fish. A species of ''Carnobacterium'', ''C. maltaromaticum'' strain CB1, has been evaluated under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999, as a food additive for vacuum- or modified atmosphere-packaged ready-to-eat meat and fresh comminuted, processed meat. Based on the hazard and exposure considerations, the risk assessment conducted by Health Canada concluded that ''C. maltaromaticum'' strain CB1 is not considered to be toxic to the Canadian environment or human health as described in Section 64 of CEPA 1999. ''Carnobacterium'' sp. has also been found in the gut of stingles carrion-eating vulture bees, besides other acidophilic (acid-loving) ''Lactobacillus ''Lactobacillus'' is a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |