|
Cao Xiu
Cao Xiu (died 29 September 228?), courtesy name Wenlie, was a Chinese military general of the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period of China. A distant younger relative of the warlord Cao Cao, Cao Xiu started his career in the late Eastern Han dynasty as a military officer under Cao Cao. In the early stages of the Hanzhong Campaign of 217–219, he outwitted Zhang Fei and defeated his subordinate officer Wu Lan (吳蘭). Later in his career, he became a provincial-level military commander and fought in various battles against Wei's rival state, Eastern Wu. He died in 228 shortly after the Wei defeat at the Battle of Shiting. Early life Cao Xiu was a distant younger relative of Cao Cao. When the Yellow Turban Rebellion broke out in the late Eastern Han dynasty, the Cao clan left their ancestral home in Qiao County (譙縣; present-day Bozhou, Anhui) and went in different directions throughout the Han Empire to avoid getting caught up in the chaos. When Cao Xiu was around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Rui
Cao Rui () (204 or 206 – 22 January 239), courtesy name Yuanzhong, was the second emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. His parentage is in dispute: his mother, Lady Zhen, was Yuan Xi's wife, but she later remarried Cao Pi, the first ruler of Wei. Based on conflicting accounts of his age, Pei Songzhi calculated that, in order to be Cao Pi's son, Cao Rui could not have been 33 (by East Asian age reckoning) when he died as recorded, so the recorded age was in error; Lu Bi and Mou Guangsheng argued instead that Cao Rui was Yuan Xi's son. Cao Rui's reign was viewed in many different ways throughout Chinese history. He devoted many resources into building palaces and ancestral temples, and his reign saw the stalemate between his empire, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu become more entrenched. His building projects and his desire to have many concubines (who numbered in the thousands) greatly exhausted the imperial treasury. On his deathbed, he has no biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Shiting
The Battle of Shi'ting (literal meaning "stone pavilion") was fought between the states of Cao Wei and Eastern Wu in 228 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The battle concluded with a Wu victory. Battle The Wu king Sun Quan ordered Zhou Fang to lay a trap for the Wei general Cao Xiu by pretending to defect to Wei. Cao Xiu was deceived into leading his troops straight into Wan (皖; present-day Qianshan County, Anhui). Sun Quan then appointed his general Lu Xun as Grand Chief Controller and ordered him to lead an attack on Cao Xiu. On the way to Wan, Cao Xiu fell into an ambush by Wu forces. He was unable to gain the upper hand in battle so he ordered a retreat to Shiting. In the middle of the night, the Wei soldiers started panicking and many of them deserted and abandoned their weapons, armour, and equipment. After his defeat, Cao Xiu wrote a memorial to the Wei emperor Cao Rui to apologize for his failure and requesting to be punished. After realising that he had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (unit)
''Li'' (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The li has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of a half-kilometer (). This is then divided into 1,500 chi or "Chinese feet". The character 里 combines the characters for "field" ( 田, ''tián'') and "earth" ( 土, ''tǔ''), since it was considered to be about the length of a single village. As late as the 1940s, a "li" did not represent a fixed measure but could be longer or shorter depending on the ''effort'' required to cover the distance. There is also another ''li'' (Traditional: 釐, Simplified: 厘, ''lí'') that indicates a unit of length of a ''chi'', but it is used much less commonly. This ''li'' is used in the People's Republic of China as the equivalent of the ''centi-'' prefix in metric units, thus ''limi'' ( 厘米, límǐ) for centimeter. The tonal difference makes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the Northern Song dynasty. As of 31 December 2018, around 4,465,000 people lived in Kaifeng's Prefecture, of whom 1,652,000 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Xiangfu, Longting, Shunhe Hui, Gulou and Yuwantai Districts. Located along the Yellow River's southern bank, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the west, Xinxiang to the northwest, Shangqiu to the east, Zhoukou to the southeast, Xuchang to the southwest, and Heze of Shandong to the northeast. Kaifeng is also a major city in the world by scientific research outputs as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is home to a campus of Henan University, one of the national key universities in the Double First Class University Plan. Names The postal romanization for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing Province
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in Chinese historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally "chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was from Chu. Chu was conquered by Qin in 223 BCE in the final stages of the Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
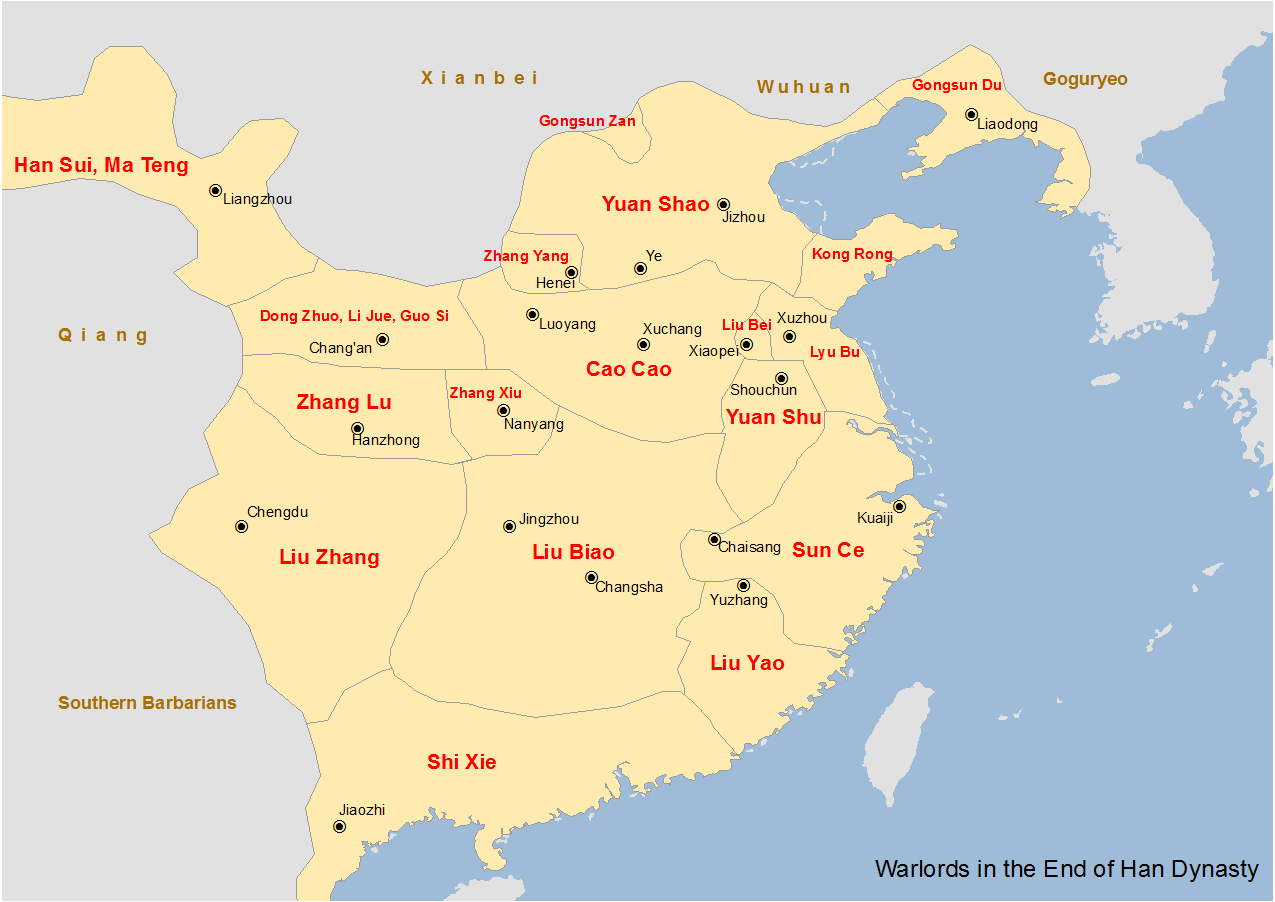
Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (died 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Yet he forced the young Emperor Shao of Han to abdicate and replaced him with his half-brother Emperor Xian of Han while he sought to become the de facto ruler of China in the boy-emperor's name. The Eastern Han dynasty regime survived in name only. Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the eunuch faction by the court officials led by General-in-Chief He Jin. Dong Zhuo subsequently deposed Liu Bian (Emperor Shao) and replaced him with his half-brother, the puppet Emperor Xian of Han. Dong Zhuo's rule was brief and characterized by cruelty and tyranny. In the following year, a coalition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaign Against Dong Zhuo
The Campaign against Dong Zhuo was a punitive expedition initiated by a coalition of regional officials and warlords against the warlord Dong Zhuo in 190 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. The members of the coalition claimed that Dong had the intention of usurping the throne by holding Emperor Xian hostage and by establishing a strong influence in the imperial court. They justified their campaign as to remove Dong from power. The campaign led to the evacuation of the capital Luoyang and the shifting of the imperial court to Chang'an. It was a prelude to the end of the Han dynasty and, subsequently, the Three Kingdoms period. In the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', the campaign is memorable for at least two famous incidents: one is Guan Yu's slaying of Hua Xiong; the other is the three-on-one duel between the three sworn brothers (Liu Bei, Guan Yu, Zhang Fei) and Lü Bu. The two scenes are often reenacted in Chinese opera along with other famous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, Postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an Eastern China, eastern coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third smallest, but the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, fifth most populous and the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population density, most densely populated of the 23 provinces of the People's Republic of China. Jiangsu has the highest GDP per capita of Chinese provinces and second-highest GDP of Chinese provinces, after Guangdong. Jiangsu borders Shandong in the north, Anhui to the west, and Zhejiang and Shanghai to the south. Jiangsu has a coastline of over along the Yellow Sea, and the Yangtze River passes through the southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade and commerce. Administratively, Suzhou is a prefecture-level city with a population of 6,715,559 in the city proper, and a total resident population of 12,748,262 as of the 2020 census in its administrative area. The city jurisdiction area's north waterfront is on a lower reach of the Yangtze whereas it has its more focal south-western waterfront on Lake Tai – crossed by several waterways, its district belongs to the Yangtze River Delta region. Suzhou is now part of the Greater Shanghai metro area, incorporating most of Changzhou, Wuxi and Suzhou urban districts plus Kunshan and Taicang, with a population of more than 38,000,000 residents as of 2020. Its urban population grew at an unprecedented rate of 6.5% between 2000 and 2014, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Commandery
Wu Commandery was a commandery of imperial China. It covers parts of the contemporary Northern Zhejiang and Southern Jiangsu. The capital of Wu commandery was Wu (today's Suzhou). Major counties of Wu commandery include Wu (county), Yuhang county, and Huating county which later became known as Suzhou, Hangzhou and Shanghai. History During its existence, Wu commandery was ruled by various dynasties and regimes. Chronologically, Han dynasty, Eastern Wu, Jin dynasty, Liu Song dynasty, Southern Qi dynasty, Liang dynasty, Chen dynasty, Sui dynasty and Tang dynasty governed Wu commandery in sequence. In the year of 129, Wu commandery was established during the reign of emperor Shun of Han. When Kuaiji Commandery was divided, lands west of Qiantang river in Kuaiji commandery formed the new Wu commandery. After the division of Kuaiji, Wu constitutes one of the commanderies of Yang Province. In 195, local strongman of Fuchun county Sun Ce acquired the entire Wu commandery without the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population. The Yangtze has played a major role in the history, culture, and economy of China. For thousands of years, the river has been used for water, irrigation, sanitation, transportation, industry, boundary-marking, and war. The prosperous Yangtze Delta generates as much as 20% of historical GDP of China, China's GDP. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze is the list of the largest hydroelectric power stations, largest hydro-electric power station in the world that is in use. In mid-2014, the Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River and the Huai River, bordering Jiangsu to the east, Zhejiang to the southeast, Jiangxi to the south, Hubei to the southwest, Henan to the northwest, and Shandong for a short section in the north. With a population of 63.65 million, Anhui is the 8th most populous province in China. It is the 22nd largest Chinese province based on area, and the 12th most densely-populated region of all 34 Chinese provincial regions. Anhui's population is mostly composed of Han Chinese. Languages spoken within the province include Jianghuai Mandarin, Wu, Hui, Gan and small portion of Zhongyuan Mandarin Chinese. The name "Anhui" derives from the names of two cities: Anqing and Huizhou (now Huangshan City). The abbreviation for Anhui is "" after the histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |