|
Byzas
Byzas (Ancient Greek: Βύζας, ''Býzas'') was the legendary founder of Byzantium (Ancient Greek: Βυζάντιον, ''Byzántion''), the city later known as Constantinople and then Istanbul. Background The legendary history of the founding of Byzantium as recorded by later Byzantine authors is most fully preserved in the ''Patria of Constantinople'' by 6th century writer Hesychius of Miletus. The ''Patria'' recorded multiple versions of the city's founding myth. Hesychius' preferred account says the city received its name from Io, daughter of the Argive king, who was raped by Inachus and then transformed into a cow. Zeus had fallen in love with Io, and in a jealous fit, Hera sent a gadfly to drive Io from one place to another in torment until she arrived in Thrace, giving birth to Ceroessa, the mother of Byzas by Poseidon, for whom the Golden Horn was named ''Ceras''. One tradition holds that the city was founded by the Argives who received an oracle at Delphi with referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a name of Constantinople sporadically and to varying degrees during the thousand year existence of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantium was colonized by Greeks from Megara in the 7th century BC and remained primarily Greek-speaking until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire in AD 1453. Etymology The etymology of ''Byzantium'' is unknown. It has been suggested that the name is of Thracian origin. It may be derived from the Thracian personal name Byzas which means "he-goat". Ancient Greek legend refers to the Greek king Byzas, the leader of the Megarian colonists and founder of the city. The name ''Lygos'' for the city, which likely corresponds to an earlier Thracian settlement, is mentioned by Pliny the Elder in his '' Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
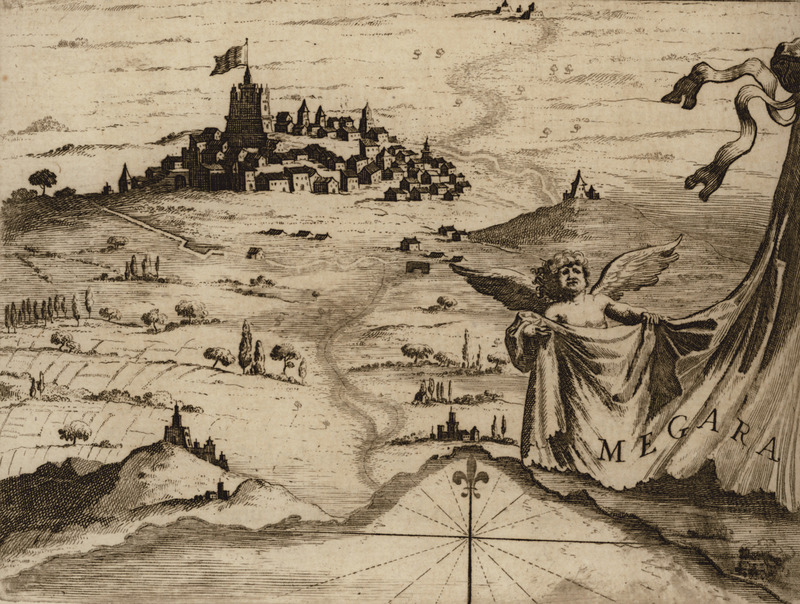
Megarians
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King Pandion II, of whom Nisos was the ruler of Megara. Megara was also a trade port, its people using their ships and wealth as a way to gain leverage on armies of neighboring poleis. Megara specialized in the exportation of wool and other animal products including livestock such as horses. It possessed two harbors, Pagae to the west on the Corinthian Gulf, and Nisaea to the east on the Saronic Gulf of the Aegean Sea. It is part of Athens metropolitan area. Early history According to Pausanias, the Megarians said that their town owed its origin to Car, the son of Phoroneus, who built the citadel called 'Caria' and the temples of Deme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King Pandion II, of whom Nisos was the ruler of Megara. Megara was also a trade port, its people using their ships and wealth as a way to gain leverage on armies of neighboring poleis. Megara specialized in the exportation of wool and other animal products including livestock such as horses. It possessed two harbors, Pagae to the west on the Corinthian Gulf, and Nisaea to the east on the Saronic Gulf of the Aegean Sea. It is part of Athens metropolitan area. Early history According to Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias, the Megarians said that their town owed its origin to Car (Greek mythology), Car, the son of Phoroneus, who bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keroessa
In Greek mythology, Ceroessa (Ancient Greek: Κερόεσσα ''Keroessa'' means "the horned") was a heroine of the foundational myth of Byzantium. She was the daughter of Io and Zeus; elder sister of Epaphus; and mother of Byzas, founder of Byzantium, with her uncle, Poseidon. Story According to the historian Hesychius of Miletus, as Io, changed into a heifer and being chased by a gadfly on behalf of the jealous Hera, was passing through Thrace, she gave birth to a girl, Keroessa, on the banks of the Golden Horn, by the altar of the nymph Semystra. According to legend, Keroessa's birthplace is called Semystra (today Eyüp district), where the rivers Kydaros (today Alibeyköy Stream) and Barbyses (today Kağıthane Stream) flow into the sea at the end of Chrysokeras (Golden Horn or Haliç). Semystra takes its name from the Semystra Altar, where today Eyüp Ensari's tomb is located, and its water is believed to have healing powers. Keroessa was reared by Semystra and grew up surpass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceroessa
In Greek mythology, Ceroessa (Ancient Greek: Κερόεσσα ''Keroessa'' means "the horned") was a heroine of the foundational myth of Byzantium. She was the daughter of Io and Zeus; elder sister of Epaphus; and mother of Byzas, founder of Byzantium, with her uncle, Poseidon. Story According to the historian Hesychius of Miletus, as Io, changed into a heifer and being chased by a gadfly on behalf of the jealous Hera, was passing through Thrace, she gave birth to a girl, Keroessa, on the banks of the Golden Horn, by the altar of the nymph Semystra. According to legend, Keroessa's birthplace is called Semystra (today Eyüp district), where the rivers Kydaros (today Alibeyköy Stream) and Barbyses (today Kağıthane Stream) flow into the sea at the end of Chrysokeras (Golden Horn or Haliç). Semystra takes its name from the Semystra Altar, where today Eyüp Ensari's tomb is located, and its water is believed to have healing powers. Keroessa was reared by Semystra and grew up surpassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semystra (nymph)
Semystra ( grc, Σημύστρα) or Semestra was a nymph, in Greek mythology. Mythology Semystra nurtured Keroessa, daughter of Io and Zeus. Keroessa's mother gave birth at Semystra's altar and left the baby there in order to protect her from Hera. Semystra found the infant and raised her. According to a legend, Semystra was also the mother of Byzas, who was the founder of Byzantium Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont .... The city of Semystra was named after her and there was an altar of her there. References Nymphs {{Greek-deity-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, cultural and historic hub. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, lying in both Europe and Asia, and has a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the list of European cities by population within city limits, most populous European city, and the world's List of largest cities, 15th-largest city. The city was founded as Byzantium ( grc-gre, Βυζάντιον, ) in the 7th century BCE by Ancient Greece, Greek settlers from Megara. In 330 CE, the Roman emperor Constantine the Great made it his imperial capital, renaming it first as New Rome ( grc-gre, Νέα Ῥώμη, ; la, Nova Roma) and then as Constantinople () after himself. The city grew in size and influence, eventually becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes. He also had the cult title "earth shaker". In the myths of isolated Arcadia he is related with Demeter and Persephone and he was venerated as a horse, however, it seems that he was originally a god of the waters.Seneca quaest. Nat. VI 6 :Nilsson Vol I p.450 He is often regarded as the tamer or father of horses, and with a strike of his trident, he created springs which are related to the word horse.Nilsson Vol I p.450 His Roman equivalent is Neptune. Poseidon was the protector of seafarers, and of many Hellenic cities and colonies. Homer and Hesiod suggest that Poseidon became lord of the sea when, following the overthrow of his father Cronus, the world was divided by lot among Cronus' three sons; Zeus w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisos
In Greek mythology, Nisos or Nisus (Ancient Greek: Νῖσος) was a King of Megara. Family Nisos was one of the four sons of Pandion II, King of Athens, and Pylia, daughter of King Pylas of Megara. He was the brother of Aegeas, Pallas, Lykos and the wife of Sciron. According to Hyginus, Nisus's father was the god Ares while other authors affirmed that he was the offspring of Deion.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'198/ref> Nisos was married to Abrota, sister of Megareus, and when she died, Nisos commanded that the Megarian women should wear clothes like she had. His daughter Eurynome, with Poseidon, had the famous son Bellerophon. The second daughter Iphinoe married Megareus, her maternal uncle. Lastly, the third princess Scylla was responsible for Nisos' death. Mythology Early days Metion, the uncle of Nisos, had seized the throne from Pandion II. However, upon their father's death, Nisos and his brothers returned to Athens and took back control. They drove out the sons of Metion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |