|
Bunsen Reaction
The Bunsen reaction is a chemical reaction that describes water, sulfur dioxide, and iodine reacting to form sulfuric acid and hydrogen iodide: : 2H2O + SO2 + I2 → H2SO4 + 2HI This reaction is the first step in the sulfur-iodine cycle to produce hydrogen. The products separate into two aqueous layers, with the sulfuric acid floating on top, and a mixture of hydrogen iodide and unreacted iodine on the bottom. While the two layers are generally considered immiscible, small amounts of sulfuric acid may still remain in the hydrogen iodide layer and vice versa. This can lead to unwanted side reactions, one of which precipitates out sulfur, a potential obstruction to the reaction vessel. The reaction is named after Robert Bunsen, who discovered it in 1853. A similar reaction is the basis for Karl Fischer titration. Note that at sufficiently high temperatures, concentrated H2SO4 may react with HI, giving I2, SO2 and H2O, which reverses the reaction. Many chemical processes are rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (; 30 March 1811 – 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bunsen–Kirchhoff Award for spectroscopy is named after Bunsen and Kirchhoff. Bunsen also developed several gas-analytical methods, was a pioneer in photochemistry, and did early work in the field of organic arsenic chemistry. With his laboratory assistant Peter Desaga, he developed the Bunsen burner, an improvement on the laboratory burners then in use. Early life and education Bunsen was born in Göttingen, Germany in 1811, in what is now the state of Lower Saxony in Germany. Bunsen was the youngest of four sons of the University of Göttingen's chief librarian and professor of modern philology, Christian Bunsen (1770–1837). After attending school in Holzminden, Bunsen matriculated at Göttingen in 1828 and studied chemistry with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances transition between the reactants and products at equal rates, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the concentration of neither changes. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. In physics, concerning thermodynamics, a closed system is in thermodynamic equilibrium when reactions occur at such rates that the composition of the mixture does not change with time. Reactions do in fact occur, sometimes vigorously, but to such an extent that changes in composition cannot be observed. Equilibrium constants can be expressed in terms of the rate constants for reversible reactions. Examples In a new bottle of soda, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever-decreasing rate, and the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Chatelier Principle
Le Chatelier's principle (pronounced or ), also called Chatelier's principle (or the Equilibrium Law), is a principle of chemistry used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on chemical equilibria. The principle is named after French chemist Henry Louis Le Chatelier, and sometimes also credited to Karl Ferdinand Braun, who discovered it independently. It can be stated as: Phenomena in apparent contradiction to Le Chatelier's principle can also arise in systems of simultaneous equilibrium (see response reactions). Le Chatelier's principle is sometimes alluded to in discussions of topics other than thermodynamics. Thermodynamic statement The Le Chatelier–Braun principle analyzes the qualitative behaviour of a thermodynamic system when a designated one of its externally controlled state variables, say L, changes by an amount \Delta L, the 'driving change', causing a change \delta_ M, the 'response of prime interest', in its conjugate state variable M, all other ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia Production
Ammonia is one of the most highly produced inorganic chemicals. There are numerous large-scale ammonia plants worldwide, producing a grand total of 144 million tonnes of nitrogen (equivalent to 175 million tonnes of ammonia) in 2016. This has increased to 235 million tonnes of ammonia in 2021. China produced 31.9% of the worldwide production, followed by Russia with 8.7%, India with 7.5%, and the United States with 7.1%. 80% or more of the ammonia produced is used for fertilizing agricultural crops. Ammonia is also used for the production of plastics, fibres, explosives, nitric acid (via the Ostwald process), and intermediates for dyes and pharmaceuticals. History Dry distillation Before the start of World War I, most ammonia was obtained by the dry distillation of nitrogenous vegetable and animal products; by the reduction of nitrous acid and nitrites with hydrogen; and also by the decomposition of ammonium salts by alkaline hydroxides or by quicklime, the salt most generally use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Reaction
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously. : \mathit aA + \mathit bB \mathit cC + \mathit dD A and B can react to form C and D or, in the reverse reaction, C and D can react to form A and B. This is distinct from a reversible process in thermodynamics. Weak acids and bases undergo reversible reactions. For example, carbonic acid: : H2CO3 (l) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq). The concentrations of reactants and products in an equilibrium mixture are determined by the analytical concentrations of the reagents (A and B or C and D) and the equilibrium constant, ''K''. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant depends on the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction. So, when the free energy change is large (more than about 30 kJ mol−1), the equilibrium constant is large (log K > 3) and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium are very small. Such a reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Process
In a scientific sense, a chemical process is a method or means of somehow changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds. Such a chemical process can occur by itself or be caused by an outside force, and involves a chemical reaction of some sort. In an "engineering" sense, a chemical process is a method intended to be used in manufacturing or on an industrial scale (see Industrial process) to change the composition of chemical(s) or material(s), usually using technology similar or related to that used in chemical plants or the chemical industry. Neither of these definitions are exact in the sense that one can always tell definitively what is a chemical process and what is not; they are practical definitions. There is also significant overlap in these two definition variations. Because of the inexactness of the definition, chemists and other scientists use the term "chemical process" only in a general sense or in the engineering sense. However, in the "process (engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Fischer Titration
Karl Fischer titration is a classic titration method in chemical analysis that uses coulometric or volumetric titration to determine trace amounts of water in a sample. It was invented in 1935 by the German chemist Karl Fischer. Today, the titration is done with an automated Karl Fischer titrator. Chemical principle The elementary reaction responsible for water quantification in the Karl Fischer titration is oxidation of sulfur dioxide with iodine: : 2 H2O + SO2 + I2 → H2SO4 + 2 HI This elementary reaction consumes exactly one molar equivalent of water vs. iodine. Iodine is added to the solution until it is present in excess, marking the end point of the titration, which can be detected by potentiometry. The reaction is run in an alcohol solution containing a base, which consumes the sulfur trioxide and hydroiodic acid produced. Coulometric titration The main compartment of the titration cell contains the anode solution plus the analyte. The anode solution consists of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immiscible
Miscibility () is the property of two chemical substance, substances to mix in all mixing ratio, proportions (that is, to fully dissolution (chemistry), dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneity and heterogeneity, homogeneous mixture (a Solution (chemistry), solution). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies to solids and gases. For example, water and ethanol are miscible because they mix in all proportions. By contrast, substances are said to be immiscible if there are certain proportions in which the mixture does not form a solution. For one example, oil is not soluble in water, so these two solvents are immiscible. As another example, butanone (methyl ethyl ketone) is significantly soluble in water, but these two solvents are also immiscible because in some proportions the mixture will separate into two Phase (matter), phases. Organic compounds In organic compounds, the Concentration#Mass percentage (fraction), weight percent of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
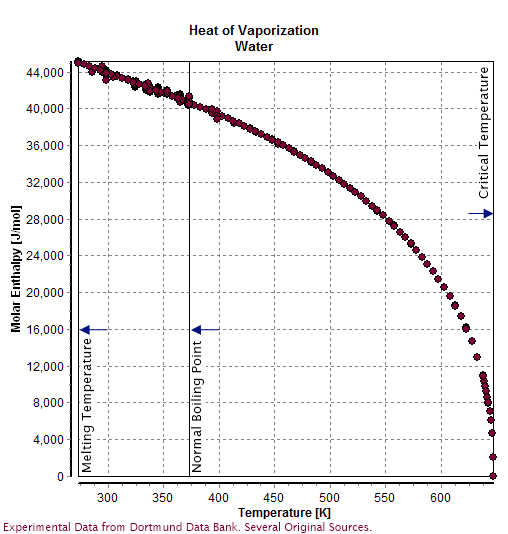
Properties Of Water
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric, meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiphasic Liquid
A multiphasic liquid is a mixture consisting of more than two immiscible liquid phases. Biphasic mixtures consisting of two immiscible phases are very common and usually consist of an organic solvent and an aqueous phase ("oil and water"). Multiphasic liquids can be used for selective liquid-liquid extractions or for decorative purposes, e.g. in cosmetics. While it is possible to get multilayered phases by layering nonpolar and aqueous phases of decreasing densities on top of each other, these phases will not separate after mixing like true multiphasic liquids. Compositions The following types of multiphasic liquids exist: Triphasic systems * Nonpolar solvent / aqueous biphasic mixture *: ''e.g. using hexane, heptane, cyclohexane, or mineral oil as the nonpolar solvent'' ** Nonpolar solvent / polar solvent / salt / water **: ''e.g. 100 ml mineral oil, 100 ml isopropanol, 75 ml water, 35 g calcium chloride'' ** Nonpolar solvent / water-soluble polymer A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |