|
Dynamic Equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances initially transition between the reactants and products at different rates until the forward and backward reaction rates eventually equalize, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the concentration of neither changes. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. Examples In a new bottle of soda, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever-decreasing rate, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the gas phase will increase until equilibrium is reached. At that point, due to thermal motion, a molecule of CO2 may leave the liquid phase, but within a very short time another molecule of CO2 will pass from the gas to the liquid, and vice versa. At equilibrium, the rate of tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrium Chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is concerned with systems in '' chemical equilibrium''. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid–base, host–guest, metal–complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria. Thermodynamic equilibrium A chemical system is said to be in equilibrium when the quantities of the chemical entities involved do not and ''cannot'' change in time without the application of an external influence. In this sense a system in chemical equilibrium is in a stable state. The system at chemical equilibrium will be at a constant temperature, pressure or volume and a composition. It will be insulated from exchange of heat with the surroundings, that is, it is a closed system. A change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances initially transition between the reactants and products at different rates until the forward and backward reaction rates eventually equalize, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the concentration of neither changes. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. Examples In a new bottle of soda, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever-decreasing rate, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the gas phase will increase until equilibrium is reached. At that point, due to thermal motion, a molecule of CO2 may leave the liquid phase, but within a very short time another molecule of CO2 will pass from the gas to the liquid, and vice versa. At equilibrium, the rate of tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Constant
In chemical kinetics, a reaction rate constant or reaction rate coefficient () is a proportionality constant which quantifies the rate and direction of a chemical reaction by relating it with the concentration of reactants. For a reaction between reactants A and B to form a product C, where :A and B are reactants :C is a product :''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are stoichiometric coefficients, the reaction rate is often found to have the form: r = k mathrmm mathrm Here is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature, and and are the molar concentrations of substances A and B in moles per unit volume of solution, assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution. (For a reaction taking place at a boundary, one would use moles of A or B per unit area instead.) The exponents ''m'' and ''n'' are called partial orders of reaction and are ''not'' generally equal to the stoichiometric coefficients ''a'' and ''b''. Instead they depend on the reactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Reaction
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time. Reaction rates can vary dramatically. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many years, but the combustion of cellulose in a fire is a reaction that takes place in fractions of a second. For most reactions, the rate decreases as the reaction proceeds. A reaction's rate can be determined by measuring the changes in concentration over time. Chemical kinetics is the part of physical chemistry that concerns how rates of chemical reactions are measured and predicted, and how reaction-rate data can be used to deduce probable reaction mechanisms. The concepts of chemical kinetics are applied in many disciplines, such as chemical engineering, enzymology and environmental en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Reaction
An elementary reaction is a chemical reaction in which one or more chemical species react directly to form Product (chemistry), products in a single reaction step and with a single transition state. In practice, a reaction is assumed to be elementary if no reaction intermediates have been detected or need to be postulated to describe the reaction on a molecular scale. An apparently elementary reaction may be in fact a stepwise reaction, i.e. a complicated sequence of chemical reactions, with reaction intermediates of variable lifetimes. In a unimolecular elementary reaction, a molecule Dissociation (chemistry), dissociates or Isomerisation, isomerises to form the products(s) :\mbox \rightarrow \mbox At constant temperature, the reaction rate, rate of such a reaction is proportional to the concentration of the species :\frac=-k[\mbox]. In a bimolecular elementary reaction, two atoms, molecules, ions or Radical (chemistry), radicals, and , react together to form the product(s) :\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization. When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers can often be observed and the equilibrium ratio will shift in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, \Delta G^\circ, have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data. Examples and applications Alkanes Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry to convert straight chain alkanes to isoparaffins as exemplified in the conversion of normal octane to 2,5-dimethylhexane (an "isoparaffin"): : Fuels containing branched hydrocarbons are favored for internal combustion engines for their higher octan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year, primarily for the production of fertilizers. Nitrogen dioxide is poisonous and can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Cooking with a gas stove produces nitrogen dioxide which causes poorer indoor air quality. Combustion of gas can lead to increased concentrations of nitrogen dioxide throughout the home environment which is linked to respiratory issues and diseases. The LC50 ( median lethal dose) for humans has been estimated to be 174 ppm for a 1-hour exposure. It is also included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above and becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
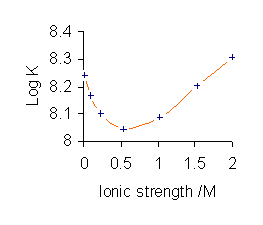
Stability Constants Of Complexes
In coordination chemistry, a stability constant (also called formation constant or binding constant) is an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the reagents that come together to form the Complex (chemistry), complex. There are two main kinds of complex: compounds formed by the interaction of a metal ion with a ligand and supramolecular complexes, such as host–guest complexes and complexes of anions. The stability constant(s) provide(s) the information required to calculate the concentration(s) of the complex(es) in solution. There are many areas of application in chemistry, biology and medicine. History Jannik Bjerrum (son of Niels Bjerrum) developed the first general method for the determination of stability constants of Metal ammine complex, metal-ammine complexes in 1941. The reasons why this occurred at such a late date, nearly 50 years after Alfred Werner had proposed the correct structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |