|
BrownBoost
BrownBoost is a boosting algorithm that may be robust to noisy datasets. BrownBoost is an adaptive version of the boost by majority algorithm. As is true for all boosting algorithms, BrownBoost is used in conjunction with other machine learning methods. BrownBoost was introduced by Yoav Freund in 2001.Yoav Freund. An adaptive version of the boost by majority algorithm. Machine Learning, 43(3):293--318, June 2001. Motivation AdaBoost performs well on a variety of datasets; however, it can be shown that AdaBoost does not perform well on noisy data sets.Dietterich, T. G., (2000). An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: Bagging, boosting, and randomization. Machine Learning, 40 (2) 139-158. This is a result of AdaBoost's focus on examples that are repeatedly misclassified. In contrast, BrownBoost effectively "gives up" on examples that are repeatedly misclassified. The core assumption of BrownBoost is that noisy examples will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boosting (meta-algorithm)
In machine learning, boosting is an ensemble meta-algorithm for primarily reducing bias, and also variance in supervised learning, and a family of machine learning algorithms that convert weak learners to strong ones. Boosting is based on the question posed by Kearns and Valiant (1988, 1989):Michael Kearns(1988)''Thoughts on Hypothesis Boosting'' Unpublished manuscript (Machine Learning class project, December 1988) "Can a set of weak learners create a single strong learner?" A weak learner is defined to be a classifier that is only slightly correlated with the true classification (it can label examples better than random guessing). In contrast, a strong learner is a classifier that is arbitrarily well-correlated with the true classification. Robert Schapire's affirmative answer in a 1990 paper to the question of Kearns and Valiant has had significant ramifications in machine learning and statistics, most notably leading to the development of boosting. When first introduced, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boosting (machine Learning)
In machine learning, boosting is an ensemble meta-algorithm for primarily reducing bias, and also variance in supervised learning, and a family of machine learning algorithms that convert weak learners to strong ones. Boosting is based on the question posed by Kearns and Valiant (1988, 1989):Michael Kearns(1988)''Thoughts on Hypothesis Boosting'' Unpublished manuscript (Machine Learning class project, December 1988) "Can a set of weak learners create a single strong learner?" A weak learner is defined to be a classifier that is only slightly correlated with the true classification (it can label examples better than random guessing). In contrast, a strong learner is a classifier that is arbitrarily well-correlated with the true classification. Robert Schapire's affirmative answer in a 1990 paper to the question of Kearns and Valiant has had significant ramifications in machine learning and statistics, most notably leading to the development of boosting. When first introduced, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boosting (machine Learning)
In machine learning, boosting is an ensemble meta-algorithm for primarily reducing bias, and also variance in supervised learning, and a family of machine learning algorithms that convert weak learners to strong ones. Boosting is based on the question posed by Kearns and Valiant (1988, 1989):Michael Kearns(1988)''Thoughts on Hypothesis Boosting'' Unpublished manuscript (Machine Learning class project, December 1988) "Can a set of weak learners create a single strong learner?" A weak learner is defined to be a classifier that is only slightly correlated with the true classification (it can label examples better than random guessing). In contrast, a strong learner is a classifier that is arbitrarily well-correlated with the true classification. Robert Schapire's affirmative answer in a 1990 paper to the question of Kearns and Valiant has had significant ramifications in machine learning and statistics, most notably leading to the development of boosting. When first introduced, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AdaBoost
AdaBoost, short for ''Adaptive Boosting'', is a statistical classification meta-algorithm formulated by Yoav Freund and Robert Schapire in 1995, who won the 2003 Gödel Prize for their work. It can be used in conjunction with many other types of learning algorithms to improve performance. The output of the other learning algorithms ('weak learners') is combined into a weighted sum that represents the final output of the boosted classifier. Usually, AdaBoost is presented for binary classification, although it can be generalized to multiple classes or bounded intervals on the real line. AdaBoost is adaptive in the sense that subsequent weak learners are tweaked in favor of those instances misclassified by previous classifiers. In some problems it can be less susceptible to the overfitting problem than other learning algorithms. The individual learners can be weak, but as long as the performance of each one is slightly better than random guessing, the final model can be proven to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boost By Majority
Boost, boosted or boosting may refer to: Science, technology and mathematics * Boost, positive manifold pressure in turbocharged engines * Boost (C++ libraries), a set of free peer-reviewed portable C++ libraries * Boost (material), a material branded and used by Adidas in the midsoles of shoes. * Boost, a loose term for turbo or supercharger * Boost converter, an electrical circuit variation of a DC to DC converter, which increases (boosts) the voltage * Boosted fission weapon, a type of nuclear bomb that uses a small amount of fusion fuel to increase the rate, and thus yield, of a fission reaction * Boosting (machine learning), a supervised learning algorithm * Intel Turbo Boost, a technology that enables a processor to run above its base operating frequency * Jump start (vehicle), to start a vehicle * Lorentz boost, a type of Lorentz transformation Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Boost (''Cars''), a character from the Pixar franchise ''Cars'' * Boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoav Freund
Joab (Hebrew Modern: ''Yōʼav'', Tiberian: ''Yōʼāḇ'') the son of Zeruiah, was the nephew of King David and the commander of his army, according to the Hebrew Bible. Name The name Joab is, like many other Hebrew names, theophoric - derived from YHVH (), the name of the God of Israel, and the Hebrew word 'av' (), meaning 'father'. It therefore means 'YHVH sfather'. Life Joab was the son of Zeruiah, a sister of king David (1 Chronicles 2:15-16). According to Josephus (Antiquities VII, 1, 3) his father was called Suri.Flavius Josephus, ''Antiquities of the Jews''Book VII, Chapter 1, 3 Joab had two brothers, Abishai and Asahel. Asahel was killed by Abner in combat, for which Joab took revenge by murdering Abner against David's wishes and shortly after David and Abner had secured peace between the House of David and the House of Saul (2 Samuel 2:13-3:21; 3:27). While 2 Samuel 3:27 explicitly states that Joab killed Abner "to avenge the blood of his brother Asahel", Jos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
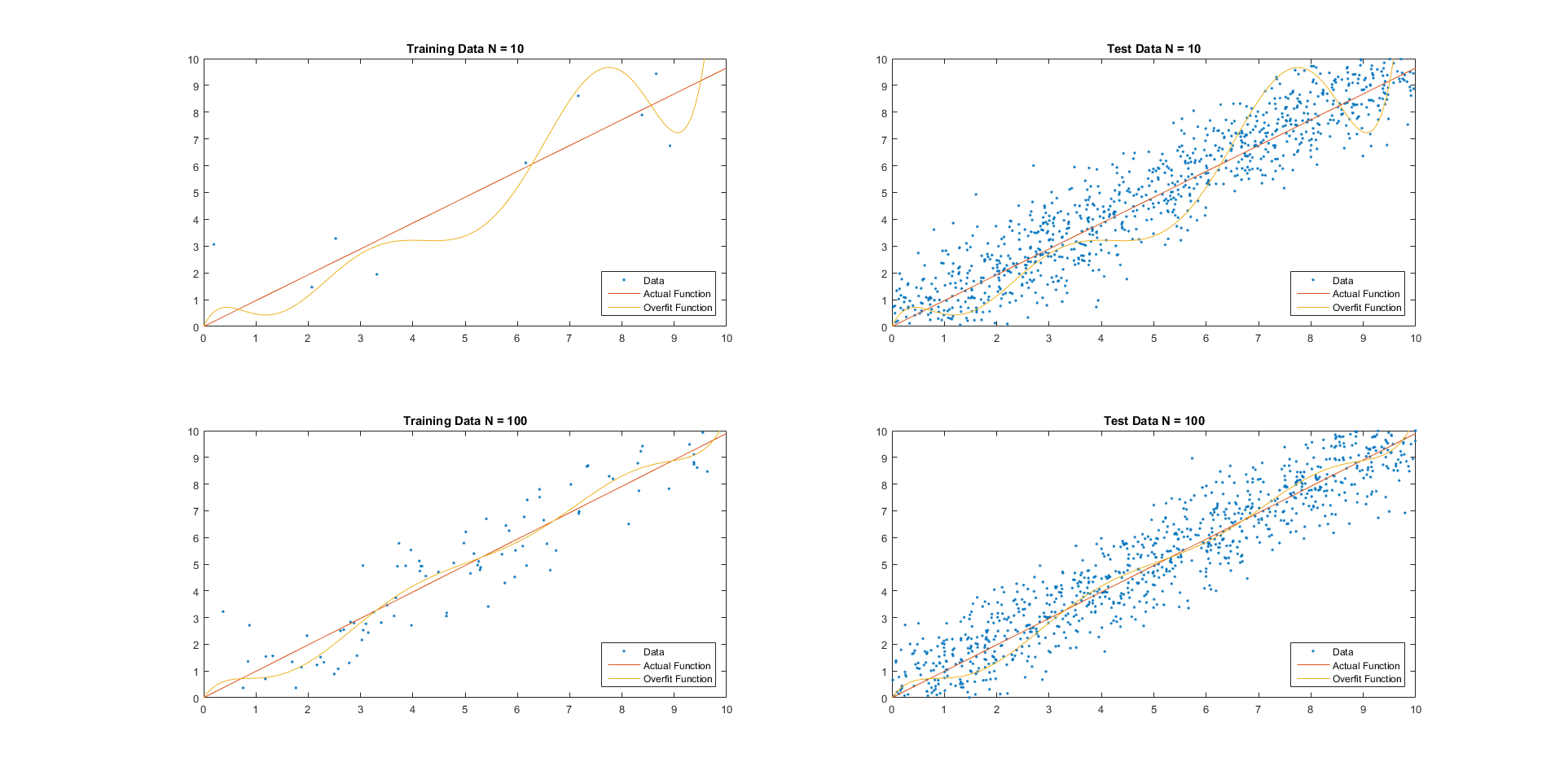
Generalization Error
For supervised learning applications in machine learning and statistical learning theory, generalization error (also known as the out-of-sample error or the risk) is a measure of how accurately an algorithm is able to predict outcome values for previously unseen data. Because learning algorithms are evaluated on finite samples, the evaluation of a learning algorithm may be sensitive to sampling error. As a result, measurements of prediction error on the current data may not provide much information about predictive ability on new data. Generalization error can be minimized by avoiding overfitting in the learning algorithm. The performance of a machine learning algorithm is visualized by plots that show values of ''estimates'' of the generalization error through the learning process, which are called learning curves. Definition In a learning problem, the goal is to develop a function f_n(\vec) that predicts output values y for each input datum \vec. The subscript n indicates tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LogitBoost
In machine learning and computational learning theory, LogitBoost is a boosting algorithm formulated by Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, and Robert Tibshirani. The original paper casts the AdaBoost algorithm into a statistical framework. Specifically, if one considers AdaBoost as a generalized additive model and then applies the cost function of logistic regression, one can derive the LogitBoost algorithm. Minimizing the LogitBoost cost function LogitBoost can be seen as a convex optimization. Specifically, given that we seek an additive model of the form :f = \sum_t \alpha_t h_t the LogitBoost algorithm minimizes the logistic loss: :\sum_i \log\left( 1 + e^\right) See also * Gradient boosting Gradient boosting is a machine learning technique used in regression and classification tasks, among others. It gives a prediction model in the form of an ensemble of weak prediction models, which are typically decision trees. When a decision t ... * Logistic model tree Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The most basic version starts with a single-variable function defined for a real variable , the function's derivative , and an initial guess for a root of . If the function satisfies sufficient assumptions and the initial guess is close, then :x_ = x_0 - \frac is a better approximation of the root than . Geometrically, is the intersection of the -axis and the tangent of the graph of at : that is, the improved guess is the unique root of the linear approximation at the initial point. The process is repeated as :x_ = x_n - \frac until a sufficiently precise value is reached. This algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method. The method can also be extended to complex functions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Decision Tree
An alternating decision tree (ADTree) is a machine learning method for classification. It generalizes decision trees and has connections to boosting. An ADTree consists of an alternation of decision nodes, which specify a predicate condition, and prediction nodes, which contain a single number. An instance is classified by an ADTree by following all paths for which all decision nodes are true, and summing any prediction nodes that are traversed. History ADTrees were introduced by Yoav Freund and Llew Mason. However, the algorithm as presented had several typographical errors. Clarifications and optimizations were later presented by Bernhard Pfahringer, Geoffrey Holmes and Richard Kirkby. Implementations are available in Weka and JBoost. Motivation Original boosting algorithms typically used either decision stumps or decision trees as weak hypotheses. As an example, boosting decision stumps creates a set of T weighted decision stumps (where T is the number of boosting itera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |