|
British Logistics In The Siegfried Line Campaign
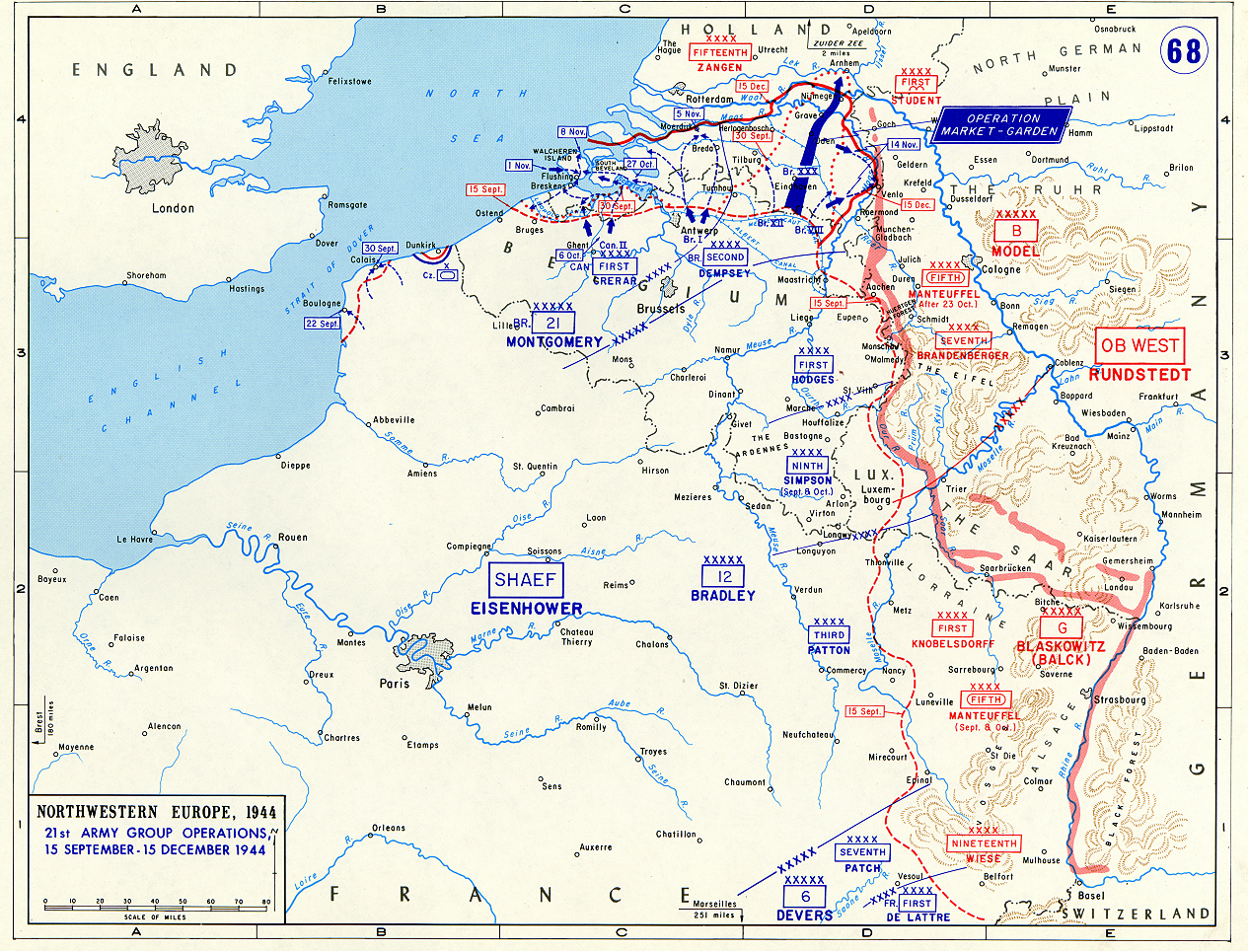
British logistics supported the Anglo-Canadian 21st Army Group operations in the World War II Siegfried Line campaign, which ran from the end of the pursuit of the German armies from Normandy in mid-September 1944 until the end of January 1945. Operation Overlord, the Allied landings in Normandy, commenced on D-Day, 6 June 1944. German resistance was stubborn, and the British and Canadian advance much slower than planned until the German defences were finally breached in July. What followed was a far more rapid advance than anticipated. The British Second Army liberated Brussels on 3 September, but the subsequent effort to cross the Rhine with the aid of airborne forces in Operation Market Garden was unsuccessful. The Canadian First Army had the task of clearing the Channel Coast. Although the port of Antwerp had been captured virtually intact on 4 September, major operations were required to clear the German defenders from the Scheldt estuary, and it was not opened for ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RASC Troops Stacking Ration Boxes In The Harbour At Dieppe, 14 October 1944 is sometimes incorrectly abbreviated RASC. Its correct abbreviation is RASvy.
{{disambig ...
RASC may be: * Reconfigurable Application-Specific Computing, a specialized reconfigurable computer for high-performance computing * Research and Advocacy Standing Committee, part of the Singapore Children's Society * Royal Army Service Corps, a former corps of the British Army * Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, formed in 1903 The former Royal Australian Survey Corps The Royal Australian Survey Corps (RA Svy) was a Corps of the Australian Army, formed on 1 July 1915 and disbanded on 1 July 1996. As one of the principal military survey units in Australia, the role of the Royal Australian Survey Corps was to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-weapon
V-weapons, known in original German as (, German: "retaliatory weapons", "reprisal weapons"), were a particular set of long-range artillery weapons designed for strategic bombing during World War II, particularly strategic bombing and/or aerial bombing of cities. They were the V-1, a pulsejet-powered cruise missile; the V-2, a liquid-fueled ballistic missile (often referred to as V1 and V2); and the V-3 cannon. All of these weapons were intended for use in a military campaign against Britain, though only the V-1 and V-2 were so used in a campaign conducted 1944–45. After the invasion of Europe by the Allies, these weapons were also employed against targets on the mainland of Europe, mainly France and Belgium. Strategic bombing with V-weapons killed approximately 18,000 people, mostly civilians. The cities of London, Antwerp and Liège were the main targets. They were part of the range of the so-called (superweapons, or "wonderweapons") of Nazi Germany. Development As e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal De Caen à La Mer
Canal de Caen à la Mer ( en, Canal from Caen to the sea, also called the "Caen Canal") is a short canal in the department (préfecture) of Calvados, France, connecting the Port of Caen, in the city of Caen, downstream to the town of Ouistreham and the English Channel. Running from north north-east to south south-west, the canal runs parallel to the Orne River which feeds it, it is long, and comprises two locks. Digging began in 1837, and when it was opened on August 23, 1857 it was only deep. It was deepened in 1920. The canal began with the dock at St. Peter's Basin (Bassin Saint-Pierre), in the downtown area of Caen. The canal is made up of a group of quays and docks. The current depth is , and the width can reach in the dock of Calix). The quay at Blainville-sur-Orne measures more than . It acts as the fourth commercial French port for the importation of exotic wood, generally coming from the Gulf of Guinea. It also loads and unloads iron, fertilizer, coal, and construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouistreham
Ouistreham () is a commune in the Calvados department in Normandy region in northwestern France. Ouistreham is a small port with fishing boats, leisure craft and a ferry harbour. It serves as the port of the city of Caen. The town borders the mouth of the Canal de Caen à la Mer. Origin of the place name The name Ouistreham derives from Saxon , meaning 'village'. There is no clear explanation for the first part of the name. A popular etymology is based on Middle French (Old French ), meaning 'oyster'. Actually most linguists agree on a Saxon origin, meaning Western or West (though some other linguists have claimed that it derives from the Saxon word meaning Eastern), because of the presence of Saxon-speaking settlers from England in Viking Normandy. If we follow this theory, 'Ouistreham' is a homonym of 'Westerham' in Kent. History It has been a trading port since the Middle Ages. The harbour is now a part of "Port de Caen-Ouistreham". Since the beginning of the 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,Comparateur de territoire INSEE, retrieved 20 June 2022. making Caen the second largest urban area in and the 19th largest in France. It is also the third largest commune in all of Normandy after and Rouen. It is located inland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine
) , mouth_location = Le Havre/Honfleur , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = Seine basin , basin_size = , tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle , tributaries_right = Ource, Aube, Marne, Oise, Epte The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank). It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy, is negotiable by large barges and most tour boats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in the capital city, Paris. There are 37 bridges in P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodgement
A lodgement is an enclave, taken and defended by force of arms against determined opposition, made by increasing the size of a bridgehead, beachhead, or airhead into a substantial defended area, at least the rear parts of which are out of direct line of fire. An example is Operation Overlord, the establishment of a large-scale lodgement in Normandy during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin .... References Military geography {{mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courseulles
Courseulles-sur-Mer (, ), commonly known as ''Courseulles'', is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Until 1957, the town's name was simply ''Courseulles''. It lies 3 km west of Bernières-sur-Mer and 18 km north of Caen. It is a popular tourist destination not only with locals but also with international visitors who come to tour the Normandy landing beaches. The population of the town can reach 15,000 people in the summer months owing to the numerous summer homes, owned for the most part by Parisians. The town is split in two by the river Seulles. World War Two More than 14,000 Canadians stormed the stretch of a Lower Normandy Beach between Courseulles-sur-Mer and St. Aubin-sur-Mer on 6 June 1944. They were followed by 150,000 additional Canadian troops over the next few months, and throughout the summer of 1944 the Canadian military used the town’s port to unload upwards of 1,000 tons of material a day, for the first two weeks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port-en-Bessin-Huppain
Port-en-Bessin-Huppain () is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. The commune contains the two towns of Port-en-Bessin and Huppain. Population History The name ''Huppain'' stems from Norse/Norwegian ''Oppheim'', reflecting the general Viking history of Normandy. The town was captured by Royal Marines of No. 47 (Royal Marine) Commando in Operation Aubery during the Normandy landings and used as the terminal for PLUTO (Pipe-Lines Under The Ocean). Media Port-en-Bessin was used to represent nearby Ouistreham in the 1962 film '' The Longest Day''. Sister cities * Saint-Pierre, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, (France), since 1976. See also *Communes of the Calvados department Gallery File:Ancien château de Villiers-sur-Port à Huppain.jpg, Château de Villiers-sur-Port File:Ancienne église de Villiers-sur-Port à Huppain.jpg, Église Saint-Nicolas de Villiers-sur-Port Image:Georges Seurat 011.jpg, ''Bridge and port of Port-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
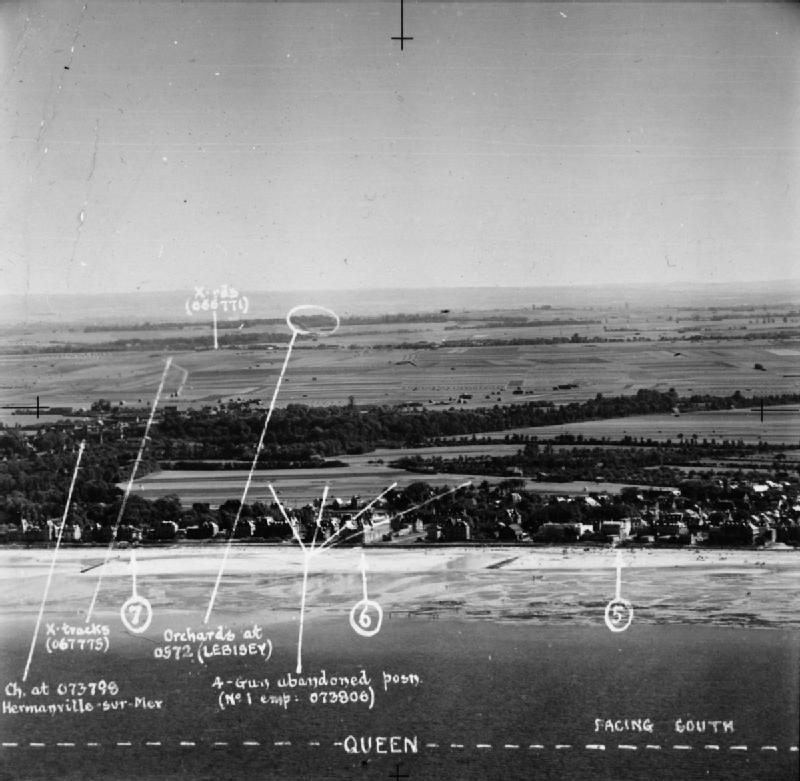
Sword Beach
Sword, commonly known as Sword Beach, was the code name given to one of the five main landing areas along the Normandy coast during the initial assault phase, Operation Neptune, of Operation Overlord. The Allied invasion of German-occupied France commenced on 6 June 1944. Stretching from Ouistreham to Saint-Aubin-sur-Mer, the beach proved to be the easternmost landing site of the invasion after the abortion of an attack on a sixth beach, code-named Band. Taking Sword was to be the responsibility of the British Army with sea transport, mine sweeping and a naval bombardment force provided by the British Royal Navy as well as elements from the Polish, Norwegian and other Allied navies. Among the five beaches of the operation, Sword is the nearest to Caen, about from the goal of the 3rd Infantry Division. The landings were achieved with low Allied casualties but the advance from the beach was slowed by traffic congestion and resistance in defended areas behind the beach. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |