|
Bosnian–Dalmatian Dialect
Younger Ikavian (), also called Western Ikavian/Western Neoshtokavian Ikavian (), or Bosnian–Dalmatian dialect (), is a subdialect of Shtokavian Serbo-Croatian spoken primarily by Croats in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, and Italy. It is spoken to a lesser extent by Bosniaks and rarely by Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Most speakers use the Latin alphabet. Area of use In Croatia, it is spoken in pockets of Gorski kotar, south of Novi Vinodolski in the Lika hinterland, Kordun, central Slavonia, Dalmatia, and in small pockets on the Dalmatian islands of Šolta, Brač, Hvar, and Korčula. In Bosnia and Herzegovina, it is spoken west of the rivers of Bosna and Neretva, in the Bačka region of Serbia and Hungary (inc. Budapest), and in Italy, in Molise. Characteristics This dialect is a sub-dialect of the Shtokavian dialect group, specifically the western sub-group. It is a descendant of Western Shtokavian, which was spoken in parts of Dalmatia, Western Bosnia and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest, with a coast on the Adriatic Sea in the south. Bosnia (region), Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Its geography is largely mountainous, particularly in the central and eastern regions, which are dominated by the Dinaric Alps. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city. The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, with permanent human settlement traced to the Neolithic cultures of Butmir culture, Butmir, Kakanj culture, Kakanj, and Vučedol culture, Vučedol. After the arrival of the first Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-Europeans, the area was populated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novi Vinodolski
Novi Vinodolski (, often also called Novi or ''Novi del Vinodol'' o ''Novi in Valdivino'' in Italian) is a town on the Adriatic Sea coast in Croatia, located south of Crikvenica, Selce and Bribir and north of Senj. The population of Novi is 3,988, with a total of 5,131 people in the city administered area. The city area became a Frankopan property in the 13th century, marking the period to which the most valuable heritage is dated, including the Law codex of Vinodol. City hinterland is dominated by the Vinodol Valley, used for agriculture and winemaking. The city's economy is dominated by tourism, as Novi Vinodolski is well known tourist centre situated in an area largely unaffected by other types of industry and it offers a wide variety of tourist amenities. The Vinodol Valley is also the site of a hydroelectric power plant utilizing water collected in Gorski Kotar reservoirs. Transport links of the city are substantially dependent on the nearby city of Rijeka. History and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
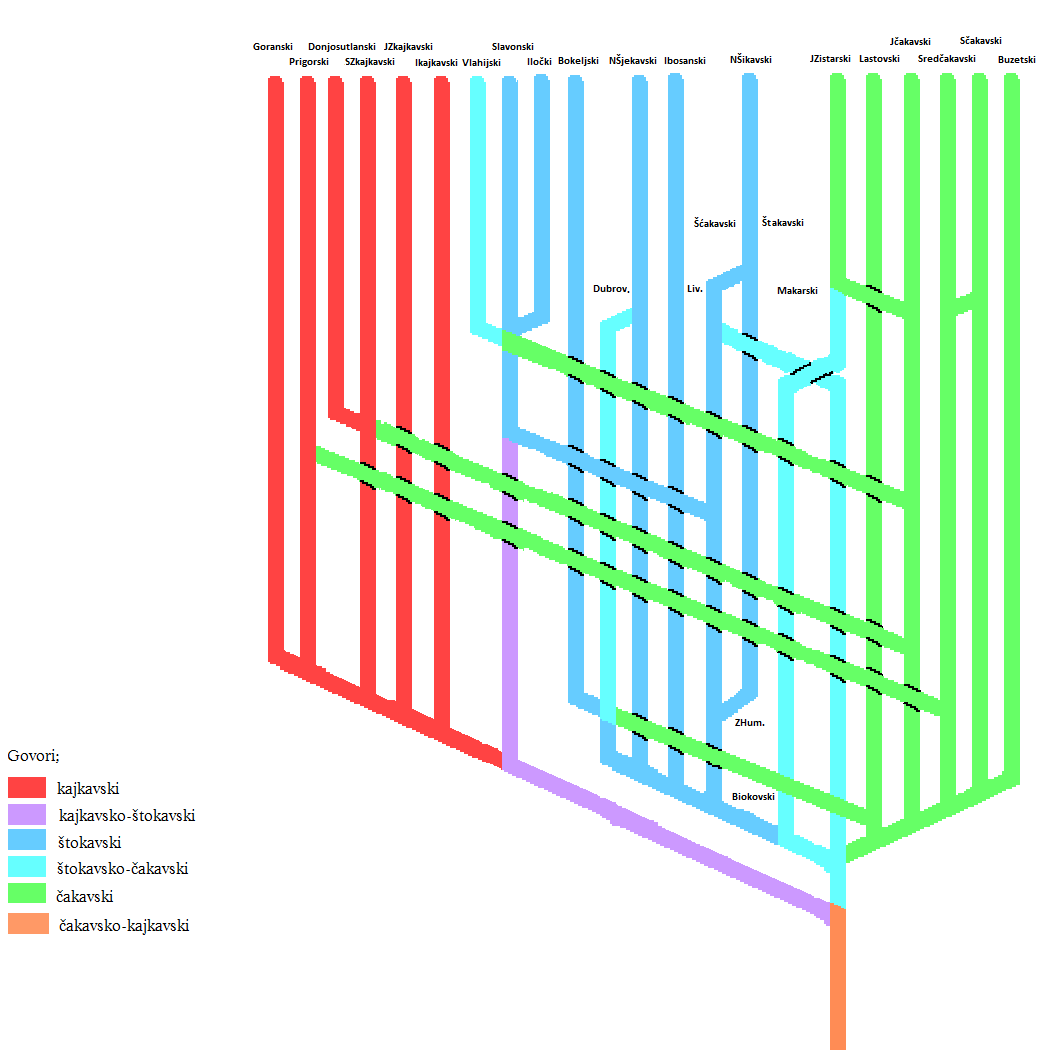
Chakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia or Littoral Croatia), as well as by the Burgenland Croats as Burgenland Croatian in southeastern Austria, northwestern Hungary and southwestern Slovakia as well as few municipalities in southern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Chakavian represents the basis for early literary standards in Croatia, and until the modern age was simply known and understood, along with the Kajkavian and Shtokavian idioms in Croatia, as the Croatian language (''hrvatski jezik''). Legal and liturgical to literary texts until the 16th century, including literary work by "the father of Croatian literature" Marko Marulić and the first Croatian dictionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molise
Molise ( , ; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. Until 1963, it formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Italy. Covering , it is the second smallest region in the country, after the Aosta Valley, and has a population of 287,966 as of 2025. The region is split into two provinces, named after their capitals: Campobasso Province, Campobasso and Isernia Province, Isernia. Campobasso also serves as the regional capital. Geography Molise is bordered by Abruzzo to the north, Apulia to the east, Lazio to the west, and Campania to the south. It has of sandy coastline to the northeast, lying on the Adriatic Sea looking out toward the Tremiti Islands. The countryside of Molise is mostly mountainous, with 55% covered by mountains and most of the rest by hills that go down to the sea. Main sights and monuments Campobasso *Castello Monforte *Terzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, second-largest city on the river Danube. The estimated population of the city in 2025 is 1,782,240. This includes the city's population and surrounding suburban areas, over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a List of cities and towns of Hungary, city and Counties of Hungary, municipality, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,019,479. It is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celts, Celtic settlement transformed into the Ancient Rome, Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Pannonia Inferior, Lower Pannonia. The Hungarian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neretva
The Neretva (, sr-Cyrl, Неретва), also known as Narenta, is one of the largest rivers of the eastern part of the Adriatic basin. Four Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power plants with Dam, large dams (higher than 15 metres) provide flood protection, electricity and water storage. The Neretva is recognized for its natural environment and diverse landscapes. Freshwater ecosystems have suffered from an increasing population and the associated development pressures. One of the most valuable natural resources of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia is its freshwater resource, contained by an abundant spring (hydrosphere), wellspring and clear rivers. Situated between the major regional rivers (Drina river on the east, Una (Sava), Una river on the west and the Sava river) the Neretva basin contains the most significant source of drinking water. The Neretva is notable among rivers of the Dinaric Alps region, especially regarding its diverse ecosystems and habitats, flora and faun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosna (river)
The Bosna ( sr-Cyrl, Босна, ) is the third longest river in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is considered one of the country's three major internal rivers, along with the Neretva and the Vrbas (river), Vrbas. The other three major rivers of Bosnia and Herzegovina are the Una (Sava), Una, to the northwest; the Sava, to the north, and the Drina, to the east. This river is the namesake of Bosnia. The river Bosna flows for . The river is possibly mentioned for the first time during the 1st century AD by Roman historian Marcus Velleius Paterculus under the name ''Bathinus flumen''. Another basic source that is associated with the hydronym ''Bathinus'' is the Salona, Salonitan inscription of the governor of Dalmatia, Publius Cornelius Dolabella (consul 10), Publius Cornelius Dolabella, where it is said that the ''Bathinum'' river divides the Breuci from the Osseriates. Another name could also have beeBasante According to philologist Anton Mayer, the name ''Bosna'' could be derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korčula
Korčula () is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea. It has an area of , is long and on average wide, and lies just off the Dalmatian coast. Its 15,522 inhabitants (2011) make it the second most populous Adriatic island after Krk. The population are almost entirely ethnic Croats (95.74%). The island is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with Rothesay, Bute, Rothesay in Scotland. It is known for Grk, a white wine that is only produced on the island and not exported due to limited production. Geography The island of Korčula belongs to the central Dalmatian archipelago, separated from the Pelješac peninsula by a narrow Strait of Pelješac, between wide. It stretches in the east–west direction, in length of ; on average, it is wide. With an area of , it is the sixth largest List of islands in the Adriatic, Adriatic island. The highest peaks are ''Klupca'', and ''Kom'', high. Main settlements on the island are towns of Korčula (town), Korčula, Blato, Korčula, Blat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hvar
Hvar (; Chakavian: ''Hvor'' or ''For''; ; ; ) is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, located off the Dalmatian coast, lying between the islands of Brač, Vis (island), Vis and Korčula. Approximately long, with a high east–west ridge of Mesozoic limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite, the island of Hvar is unusual in the area for having a large fertile coastal plain, and fresh water springs. Its hillsides are covered in pine forests, with vineyards, olive groves, fruit orchards and lavender fields in the agricultural areas. The climate is characterized by mild winters, and warm summers with many hours of sunshine. The island has 10,678 residents according to the 2021 census, making it the fourth most populated of the List of inhabited islands of Croatia, Croatian islands. History Hvar's location at the north east centre of the Adriatic sailing routes has long made this island an important base for commanding trade up and down the Adriatic, across to Italy and throughout t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brač
Brač is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, with an area of , making it the largest island in Dalmatia, and the third largest in the Adriatic. It is separated from the mainland by the Brač Channel, which is wide.Brački kanal The island's tallest peak, Vidova gora, or Mount St. Vid, stands at , making it the highest point of the Adriatic islands. The island has a population of 13,931, living in twenty-two settlements, ranging from the main town Supetar, with more than 3,400 inhabitants, to Murvica, Split-Dalmatia County, Murvica, where less than two dozen people live. Brač Airport on Brač is the largest airport of all islands surrounding Split, Croatia, Split. Brač is known as a tourist destination, for the Zlatni Rat b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šolta
Šolta (; ; ) is an island in Croatia. It is situated in the Adriatic Sea in the central Dalmatian archipelago. Geography Šolta is located west of the island of Brač, south of Split (city), Split (separated by Split Channel) and east of the Drvenik islands, Drvenik Mali and Drvenik Veli (separated by the Šolta Channel). Its area is . Population In the 2011 census, the municipality of Šolta had a total population of 1,700, in the following naselja, settlements: * Donje Selo, Split-Dalmatia County, Donje Selo, population 159 * Gornje Selo, Split-Dalmatia County, Gornje Selo, population 238 * Grohote, population 449 * Maslinica, population 208 * Nečujam, population 171 * Rogač, population 126 * Srednje Selo, Split-Dalmatia County, Srednje Selo, population 104 * Stomorska, population 245 Island morphology The highest peak of Šolta is the summit Vela Straža which is 236 metres high. On the north-eastern coast of the island there are the large bays of Rogač and Nečujam. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Kingdom of Croatia, the Republic of Venice, the Austrian Empire, and presently the Croatia, Republic of Croatia. Dalmatia is a narrow belt stretching from the island of Rab (island), Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar, Šibenik, and Dubrovnik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |