|
Blended Wing Body
A blended wing body (BWB), also known as blended body or hybrid wing body (HWB), is a fixed-wing aircraft having no clear dividing line between the wings and the main body of the craft. The aircraft has distinct wing and body structures, which are smoothly blended together with no clear dividing line.Crane, Dale. ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition''. Newcastle, Washington: Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. . p. 224. This contrasts with a flying wing, which has no distinct fuselage, and a lifting body, which has no distinct wings. A BWB design may or may not be tailless. The main advantage of the BWB is to reduce wetted area and the accompanying form drag associated with a conventional wing-body junction. It may also be given a wide airfoil-shaped body, allowing the entire craft to generate lift and thus reducing the size and drag of the wings. The BWB configuration is used for both aircraft and underwater gliders. History In the early 1920s Nicolas W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
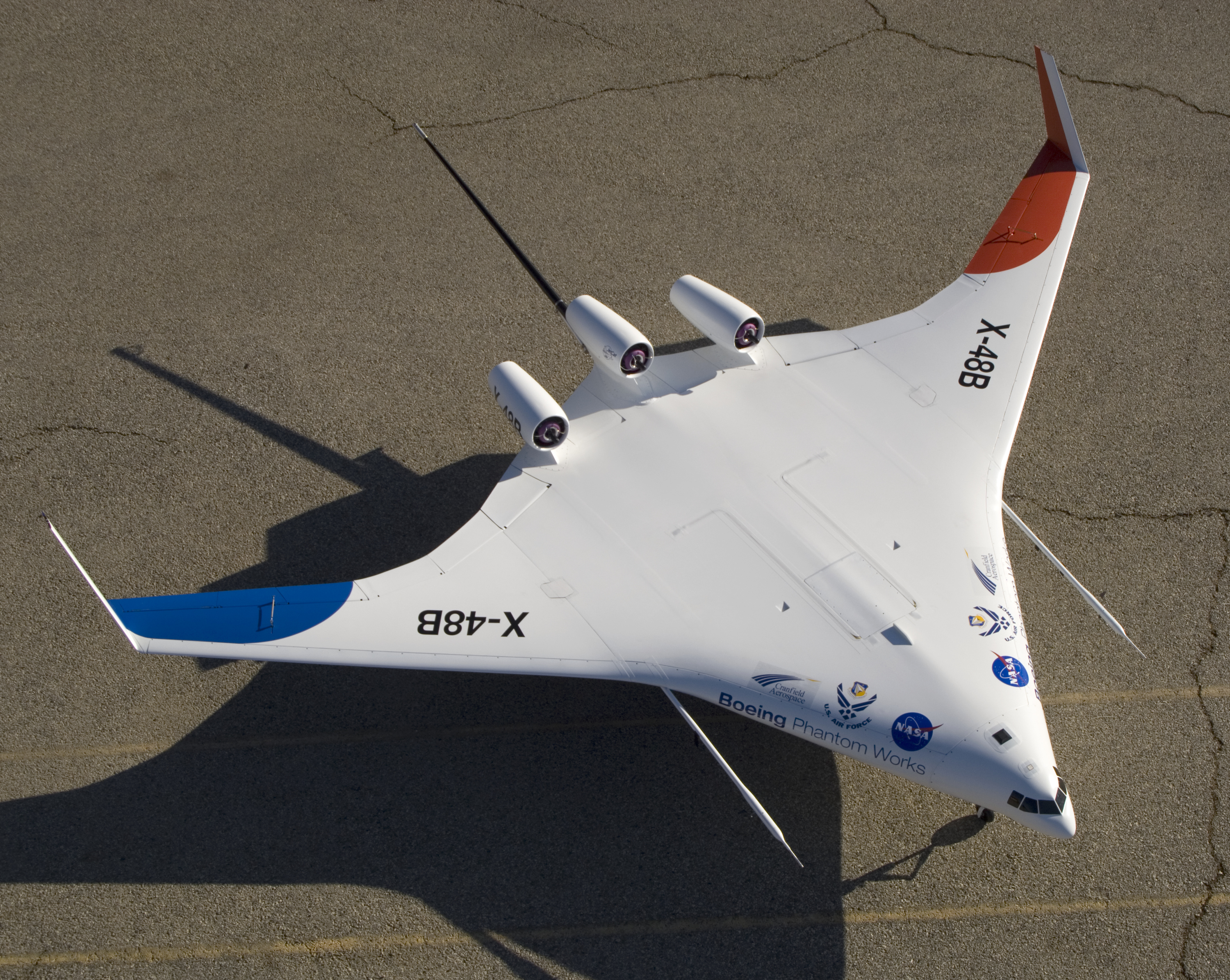
X-48B
The Boeing X-48 is an American experimental unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) built to investigate the characteristics of blended wing body (BWB) aircraft. Boeing designed the X-48 and two examples were built by Cranfield Aerospace in the UK. Boeing began flight testing the X-48B version for NASA in 2007. The X-48B was later modified into the X-48C version, which was flight tested from August 2012 to April 2013. Boeing and NASA plan to develop a larger BWB demonstrator. Design and development Background Boeing had in the past studied a blended wing body design, but found that passengers did not like the theater-like configuration of the mock-up; the design was dropped for passenger airliners, but retained for military aircraft such as aerial refueling tankers."Design of the Blended Wing Body Subsonic Transport."''AIAA Journal of Aircraft,'' Volume 41, Issue 1, January–February 2004, pp. 10–25. * Norris, Guy and Mark Wagner. ''Boeing 787 Dreamliner.'' Minneapolis, Minn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrowbody
A narrow-body aircraft or single-aisle aircraft is an airliner arranged along a single aisle, permitting up to 6-abreast seating in a cabin less than in width. In contrast, a wide-body aircraft is a larger airliner usually configured with multiple aisles and a fuselage diameter of more than , allowing at least seven-abreast seating and often more travel classes. Market Historically, beginning in the late 1960s and continuing through the 1990s, twin engine narrow-body aircraft, such as the Boeing 737 Classic, McDonnell-Douglas MD-80 and Airbus A320 were primarily employed in short to medium-haul markets requiring neither the range nor the passenger-carrying capacity of that period's wide-body aircraft. The re-engined B737 MAX and A320neo jets offer 500 miles more range, allowing them to operate the 3,000 miles transatlantic flights between the eastern U.S. and Western Europe, previously dominated by wide-body aircraft. Norwegian Air Shuttle, JetBlue Airways and TAP Portuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lift (force)
A fluid flowing around an object exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direction. Lift conventionally acts in an upward direction in order to counter the force of gravity, but it can act in any direction at right angles to the flow. If the surrounding fluid is air, the force is called an aerodynamic force. In water or any other liquid, it is called a hydrodynamic force. Dynamic lift is distinguished from other kinds of lift in fluids. Aerostatic lift or buoyancy, in which an internal fluid is lighter than the surrounding fluid, does not require movement and is used by balloons, blimps, dirigibles, boats, and submarines. Planing lift, in which only the lower portion of the body is immersed in a liquid flow, is used by motorboats, surfboards, windsurfers, sailboats, and water-skis. Overview A fluid flowing aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
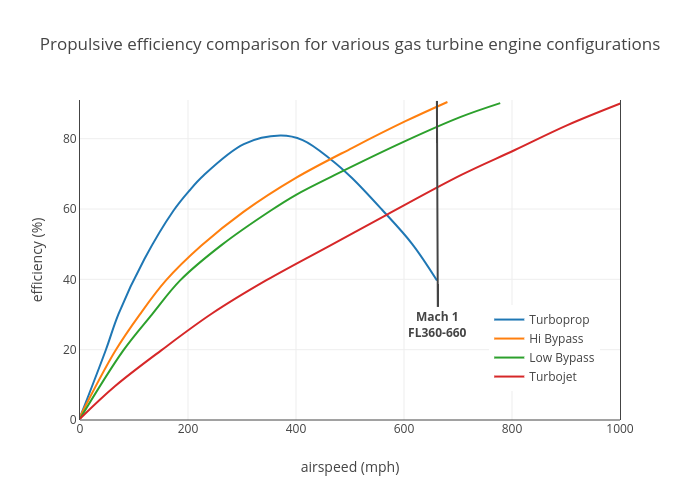
High Bypass
The bypass ratio (BPR) of a turbofan engine is the ratio between the mass flow rate of the bypass stream to the mass flow rate entering the core. A 10:1 bypass ratio, for example, means that 10 kg of air passes through the bypass duct for every 1 kg of air passing through the core. Turbofan engines are usually described in terms of BPR, which together with engine pressure ratio, turbine inlet temperature and fan pressure ratio are important design parameters. In addition, BPR is quoted for turboprop and unducted fan installations because their high propulsive efficiency gives them the overall efficiency characteristics of very high bypass turbofans. This allows them to be shown together with turbofans on plots which show trends of reducing specific fuel consumption (SFC) with increasing BPR. BPR is also quoted for lift fan installations where the fan airflow is remote from the engine and doesn't physically touch the engine core. Bypass provides a lower fuel consumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Drag
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and editorially independent of the university. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "The" in its name on April 23, 1998 under then publisher R. Bruce Journey. In September 2005, it was changed, under its then editor-in-chief and publisher, Jason Pontin, to a form resembling the historical magazine. Before the 1998 re-launch, the editor stated that "nothing will be left of the old magazine except the name." It was therefore necessary to distinguish between the modern and the historical ''Technology Review''. The historical magazine had been published by the MIT Alumni Association, was more closely aligned with the interests of MIT alumni, and had a more intellectual tone and much smaller public circulation. The magazine, billed from 1998 to 2005 as "MIT's Magazine of Innovation," and from 2005 onwards as simply "published by MIT" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Fiber Composite
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications. The binding polymer is often a thermoset resin such as epoxy, but other thermoset or thermoplastic polymers, such as polyester, vinyl ester, or nylon, are sometimes used. The properties of the final CFRP product can be affected by the type of additives introduced to the binding matrix (resin). The most common additive is silica, but other addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A320neo Family
The Airbus A320neo family is a development of the A320 family of narrow-body airliners produced by Airbus. The A320neo family (''neo'' for "new engine option") is based on the previous A319, A320 and A321 ( enhanced variant), which was then renamed A320ceo, for "current engine option". Re-engined with CFM LEAP-1A or Pratt & Whitney PW1000G engines and fitted with sharklets as standard, it is 15% to 20% more fuel efficient than the A320ceo (Enhanced) family. It was launched on 1 December 2010, made its first flight on 25 September 2014 and was introduced by Lufthansa on 25 January 2016. By 2019, the A320neo had a 60% market share against the competing Boeing 737 MAX. , a total of 8,502 A320neo family aircraft had been ordered by more than 130 customers, of which 2,341 aircraft had been delivered. The global A320neo fleet had completed more than 5.51 million flights over 11 million block hours without accidents. Development In 2006 Airbus started the A320 Enhanced ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' Commercial Aircraft (Airbus S.A.S.)'', '' Defence and Space'', and ''Helicopters'', the third being the largest in its industry in terms of revenues and turbine helicopter deliveries. As of 2019, Airbus is the world's largest airliner manufacturer. The company's main civil aeroplane business is conducted through the French company Airbus S.A.S., based in Blagnac, a suburb of Toulouse, with production and manufacturing facilities mostly in the European Union and the United Kingdom but also in China, the United States and Canada. Final assembly production is based in Toulouse, France; Hamburg, Germany; Seville, Spain; Tianjin, China; Mobile, United States; and Montreal, Canada. The company produces and markets the first commercially viable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support services. Boeing is among the largest global aerospace manufacturers; it is the third-largest defense contractor in the world based on 2020 revenue, and is the largest exporter in the United States by dollar value. Boeing stock is included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Boeing is incorporated in Delaware. Boeing was founded by William Boeing in Seattle, Washington, on July 15, 1916. The present corporation is the result of the merger of Boeing with McDonnell Douglas on August 1, 1997. Then chairman and CEO of Boeing, Philip M. Condit, assumed those roles in the combined company, while Harry Stonecipher, former CEO of McDonnell Douglas, became president and COO. The Boeing Company's corporate headquarters is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller and a system of communications with the UAV. The flight of UAVs may operate under remote control by a human operator, as remotely-piloted aircraft (RPA), or with various degrees of autonomy, such as autopilot assistance, up to fully autonomous aircraft that have no provision for human intervention. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Jang, I.; Arvin, F.; Lanzon, A.,A Decentralized Cluster Formation Containment Framework for Multirobot Systems IEEE T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |