|
Biodiversity Literature Repository
The Biodiversity Literature Repository (BLR) is a biodiversity dedicated community created in November 11, 2013, in Zenodo, the open science repository at CERN and part of the European project OpenAIRE. The goal of BLR is to provide a long-term, stable, open repository that allows deposition of Biological classification, bio-taxonomic articles enhanced with custom metadata and links to data extracted from therein and deposited in BLR. As of April 25, 2021, this includes 94,443 taxonomic treatments and 293,457 figures from 48,993 articles which are made findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable FAIR data. Most of the data is uploaded on a continuous basis by Plazi using its TreatmentBank service based on their Plazi workflow, and Pensoft Publishers using BLR as repository for data published in Pensoft Publishers, their journals. The largest single re-user of data is the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), using data from within 33,623 processed articles. Fundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenodo
Zenodo is a general-purpose open repository developed under the European OpenAIRE program and operated by CERN. It allows researchers to deposit research papers, data sets, research software, reports, and any other research related digital artefacts. For each submission, a persistent digital object identifier (DOI) is minted, which makes the stored items easily citeable. Characteristics Zenodo was launched on May 8th 2013 as the successor of the ''OpenAIRE Orphan Records Repository'' to let researchers in any subject area comply with any open science deposit requirement absent an institutional repository. It was relaunched as Zenodo in 2015 to provide a place for researchers to deposit datasets; it allows the uploading of files up to 50 GB. It provides a DOI to datasets and other submitted data that lacks one to make the work easier to cite and supports various data and license types. One supported source is GitHub repositories. Zenodo is supported by CERN "as a margina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenAIRE
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological development. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
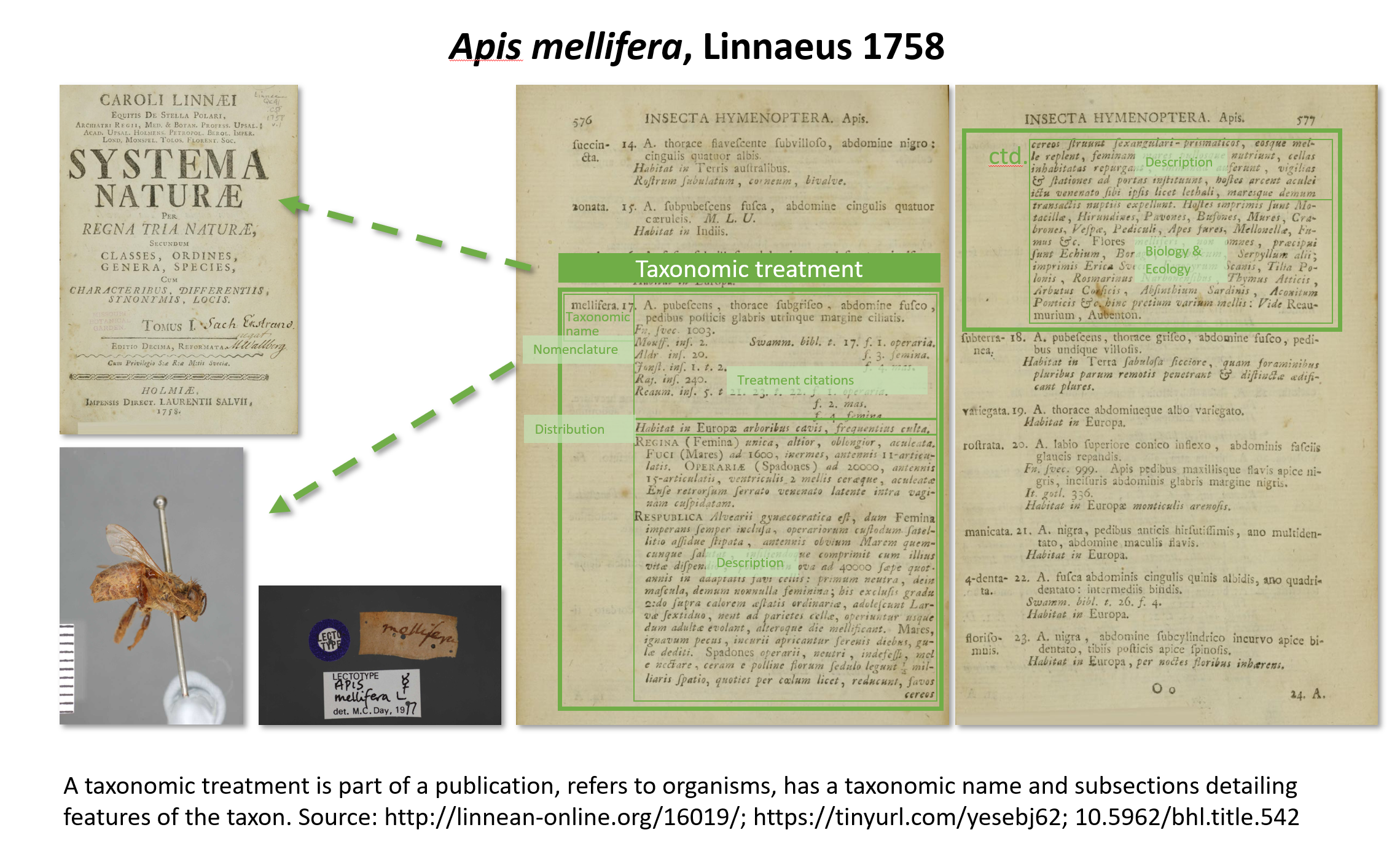
Taxonomic Treatment
Taxonomic treatment refers to a section in a scientific publication documenting the features of a related group of organisms or taxa. Treatments have been the building blocks of how data about taxa are provided, ever since the beginning of modern taxonomy by Linnaeus 1753 for plants and 1758 for animals. Each scientifically described taxon has at least one taxonomic treatment. In today’s publishing, a taxonomic treatment tag is used to delimit such a section. It allows to make this section findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable FAIR data. This is implemented in the Biodiversity Literature Repository, where upon deposition of the treatment a persistent DataCite digital object identifier (DOI) is minted. This includes metadata about the treatment, the source publication and other cited resources, such as figures cited in the treatment. This DOI allows a link from a taxonomic name usage to the respective scientific evidence provided by the author(s), both for human and machin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAIR Data
FAIR data are data which meet principles of findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability (FAIR). The acronym and principles were defined in a March 2016 paper in the journal ''Scientific Data'' by a consortium of scientists and organizations. The FAIR principles emphasize machine-actionability (i.e., the capacity of computational systems to find, access, interoperate, and reuse data with none or minimal human intervention) because humans increasingly rely on computational support to deal with data as a result of the increase in volume, complexity, and creation speed of data. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License The abbreviation is sometimes used to indicate that the dataset or database in question complies with the FAIR principles and also carries an explicit data‑capable open license. FAIR principles, as published by GO FAIR Acceptance and implementation of FAIR data prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plazi
Plazi is a Swiss-based international non-profit association supporting and promoting the development of persistent and openly accessible digital bio-taxonomic literature. Plazi is cofounder of the Biodiversity Literature Repository and is maintaining this digital taxonomic literature repository at Zenodo to provide access to FAIR data converted from taxonomic publications using the TreatmentBank service, enhances submitted taxonomic treatments by creating a version in the XML format Taxpub, and educates about the importance of maintaining open access to scientific discourse and data. It is a contributor to the evolving e-taxonomy in the field of Biodiversity Informatics. The approach was originally developed in a binational National Science Foundation (NSF) and German Research Foundation (DFG) digital library program to the American Museum of Natural History and the University of Karlsruhe, respectively, to create an XML schema modeling the content of bio-systematic literature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensoft Publishers
Pensoft Publishers (also known as: Pensoft) are a publisher of scientific literature based in Sofia, Bulgaria. Pensoft was founded in 1992, by two academics: Lyubomir Penev and Sergei Golovatch. It has published over 1000 academic and professional books and currently publishes over 60 peer-reviewed open access scientific journals including ''ZooKeys'', ''PhytoKeys'', ''Check List'', ''Comparative Cytogenetics'', ''Journal of Hymenoptera Research'', ''Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift,'' and ''Zoosystematics and Evolution''. Pensoft is part of the open-access publishing movement. The Creative Commons Attribution License ( CC-BY) is used for all journal articles. In 2012, Pensoft established a partnership with Encyclopedia of Life called the EOL Open Access Support Project (EOASP) to financially support independent taxonomists, and taxonomists living in developing countries to publish their results in Pensoft journals. Pensoft were notably one of the first publishers to facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Biodiversity Information Facility
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the world; GBIF's information architecture makes these data accessible and searchable through a single portal. Data available through the GBIF portal are primarily distribution data on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes for the world, and scientific names data. The mission of the GBIF is to facilitate free and open access to biodiversity data worldwide to underpin sustainable development. Priorities, with an emphasis on promoting participation and working through partners, include mobilising biodiversity data, developing protocols and standards to ensure scientific integrity and interoperability, building an informatics architecture to allow the interlinking of diverse data types from disparate sources, promoting capacity building and cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia Fund
The Arcadia Fund is a UK charity organization founded by Lisbet Rausing and Professor Peter Baldwin. Established in 2001, the organization provides grants on a worldwide basis focusing on numerous projects outside the UK. The primary focus of the organization is to preserve endangered culture and nature and to provide open access. Its Mission statement outlines the organization's philosophical view to: "serve humanity (and) to preserve cultural heritage and ecosystem's". The organization believes that "once memories, knowledge, skills, variety, and intricacy disappear – once the old complexities are lost – they are hard to replicate or replace" and consequently want to, "build a vibrant, resilient, green future". Since 2002, the fund has provided in excess of $910 million in projects around the world. According to the OECD, Arcadia Fund’s financing for 2019 development increased by 6% to US$55 million. The foundation is controlled by its three trustees (Lisbet Rausing, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Kind
The term in kind (or in-kind) generally refers to goods, services, and transactions not involving money or not measured in monetary terms. It is a part of many spheres, mainly economics, finance, but also politics, work career, food, health and others. There are many different types of in kind actions throughout the mentioned branches, which can be identified and distinguished. In-kind contributions An in-kind contribution is a non-cash contribution of goods or a service. Those are either offered free or at less than usual charge for them. Similarly, when a person or entity pays for services on the committee’s behalf, the payment is also considered as an in-kind contribution. In-kind services and contributions are valued at their fair market value or at their actual cost. In other words, they are valued at what you would pay for them if they were not donated. There are two types of receivers of in-kind contributions: individuals and companies. For individuals, the provider of in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |