|
Plazi
Plazi is a Swiss-based international non-profit association supporting and promoting the development of persistent and openly accessible digital bio-taxonomic literature. Plazi is cofounder of the Biodiversity Literature Repository and is maintaining this digital taxonomic literature repository at Zenodo to provide access to FAIR data converted from taxonomic publications using the TreatmentBank service, enhances submitted taxonomic treatments by creating a version in the XML format Taxpub, and educates about the importance of maintaining open access to scientific discourse and data. It is a contributor to the evolving e-taxonomy in the field of Biodiversity Informatics. The approach was originally developed in a binational National Science Foundation (NSF) and German Research Foundation (DFG) digital library program to the American Museum of Natural History and the University of Karlsruhe, respectively, to create an XML schema modeling the content of bio-systematic literature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity Literature Repository
The Biodiversity Literature Repository (BLR) is a biodiversity dedicated community created in November 11, 2013, in Zenodo, the open science repository at CERN and part of the European project OpenAIRE. The goal of BLR is to provide a long-term, stable, open repository that allows deposition of Biological classification, bio-taxonomic articles enhanced with custom metadata and links to data extracted from therein and deposited in BLR. As of April 25, 2021, this includes 94,443 taxonomic treatments and 293,457 figures from 48,993 articles which are made findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable FAIR data. Most of the data is uploaded on a continuous basis by Plazi using its TreatmentBank service based on their Plazi workflow, and Pensoft Publishers using BLR as repository for data published in Pensoft Publishers, their journals. The largest single re-user of data is the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), using data from within 33,623 processed articles. Fundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
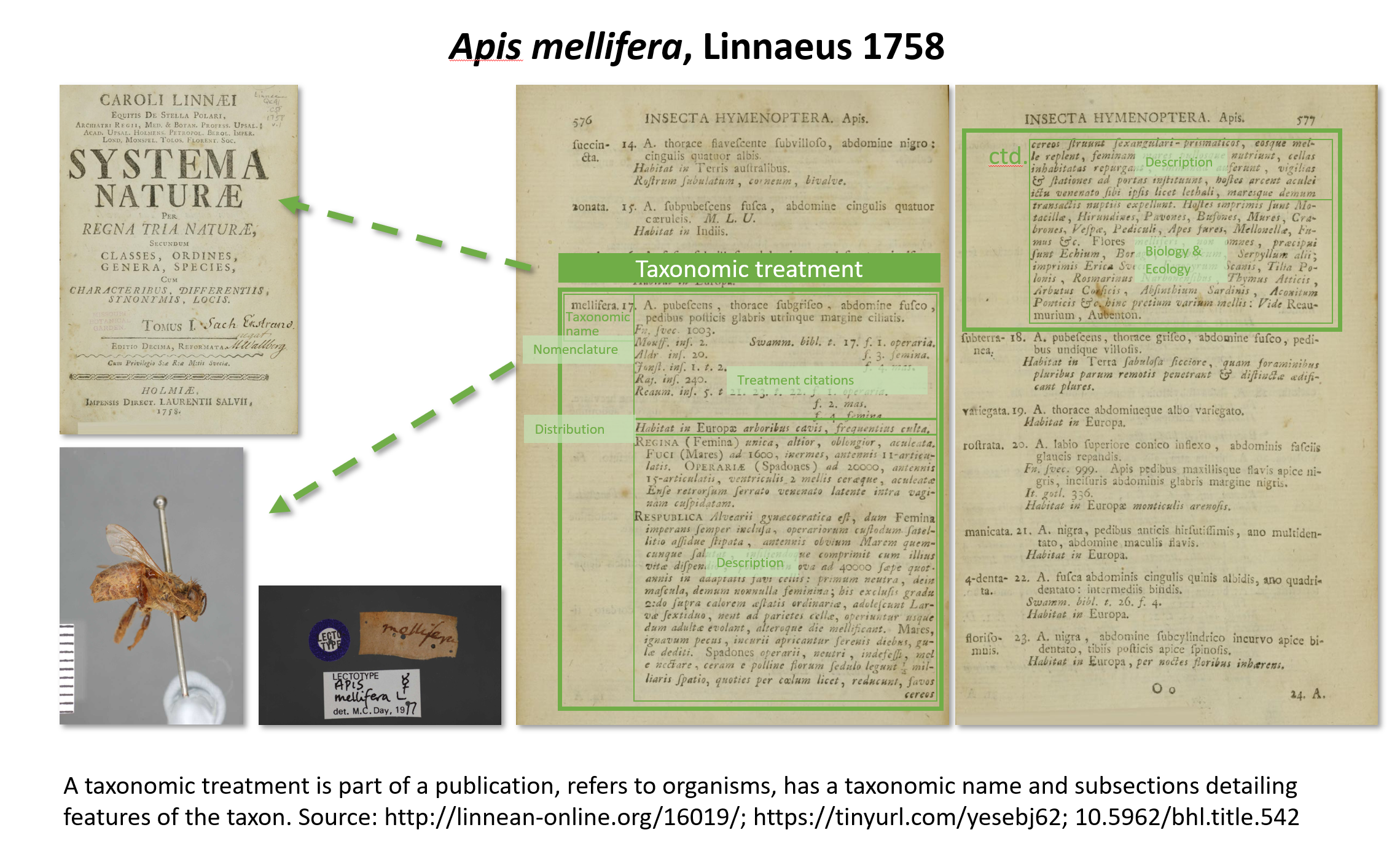
Taxonomic Treatment
Taxonomic treatment refers to a section in a scientific publication documenting the features of a related group of organisms or taxa. Treatments have been the building blocks of how data about taxa are provided, ever since the beginning of modern taxonomy by Linnaeus 1753 for plants and 1758 for animals. Each scientifically described taxon has at least one taxonomic treatment. In today’s publishing, a taxonomic treatment tag is used to delimit such a section. It allows to make this section findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable FAIR data. This is implemented in the Biodiversity Literature Repository, where upon deposition of the treatment a persistent DataCite digital object identifier (DOI) is minted. This includes metadata about the treatment, the source publication and other cited resources, such as figures cited in the treatment. This DOI allows a link from a taxonomic name usage to the respective scientific evidence provided by the author(s), both for human and machin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity Informatics
Biodiversity informatics is the application of informatics techniques to biodiversity information, such as taxonomy, biogeography or ecology. Modern computer techniques can yield new ways to view and analyze existing information, as well as predict future situations (see niche modelling). Biodiversity informatics is a term that was only coined around 1992 but with rapidly increasing data sets has become useful in numerous studies and applications, such as the construction of taxonomic databases or geographic information systems. Biodiversity informatics contrasts with "bioinformatics", which is often used synonymously with the computerized handling of data in the specialized area of molecular biology. Overview Biodiversity informatics (different but linked to bioinformatics) is the application of information technology methods to the problems of organizing, accessing, visualizing and analyzing primary biodiversity data. Primary biodiversity data is composed of names, observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZooBank
ZooBank is an open access website intended to be the official International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) registry of zoological nomenclature. Any nomenclatural acts (e.g. publications that create or change a taxonomic name) need to be registered with ZooBank to be "officially" recognized by the ICZN Code of Nomenclature. Life Science Identifiers (LSIDs) are used as the globally unique identifier for ZooBank registration entries. The ZooBank prototype was seeded with data from Index to Organism Names (http://www.organismnames.com), which was compiled from the scientific literature in ''Zoological Record'' now owned by Thomson Reuters. History ZooBank was officially proposed in 2005 by the executive secretary of ICZN. The registry was live on 10 August 2006 with 1.5 million species entered. The first ZooBank LSIDs were issued on 1 January 2008, precisely 250 years after 1 January 1758, which is the date defined by the ICZN Code as the official start of scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin Core Archive
Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A) is a biodiversity informatics data standard that makes use of the Darwin Core terms to produce a single, self-contained dataset for species occurrence, checklist, sampling event or material sample data. Essentially it is a set of text (CSV) files with a simple descriptor (meta.xml) to inform others how your files are organized. The format is defined in the Darwin Core Text Guidelines. It is the preferred format for publishing data to the GBIF network. __TOC__ Darwin Core The Darwin Core standard has been used to mobilize the vast majority of specimen occurrence and observational records within the GBIF network. The Darwin Core standard was originally conceived to facilitate the discovery, retrieval, and integration of information about modern biological specimens, their spatio-temporal occurrence, and their supporting evidence housed in collections (physical or digital). The Darwin Core today is broader in scope. It aims to provide a stable, standard re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (which shares the acronym "ICZN"). The rules principally regulate: * How names are correctly established in the frame of binominal nomenclature * Which name must be used in case of name conflicts * How scientific literature must cite names Zoological nomenclature is independent of other systems of nomenclature, for example botanical nomenclature. This implies that animals can have the same generic names as plants (e.g. there is a genus '' Abronia'' in both animals and plants). The rules and recommendations have one fundamental aim: to provide the maximum universality and continuity in the naming of all animals, except where taxonomic judgment dictates otherwise. The code is meant to guide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology) Organizations
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon")." Taxonomy is different from mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Organisations Based In Switzerland
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Political international, any transnational organization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Scientific Organizations
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Political international, any transnational organization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity Information Standards
Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG), originally called the Taxonomic Databases Working Group, is a non-profit scientific and educational association that works to develop open standards for the exchange of biodiversity data, facilitating biodiversity informatics. It is affiliated with the International Union of Biological Sciences. It is best known for the Darwin Core standard for exchanging biodiversity, which has been used by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility to collect millions of biological observations from museums and other organizations from around the world. History TDWG was founded in 1985 as the Taxonomic Databases Working Group; the first meeting took place on September 28–30, 1985, at the Conservatory and Botanical Garden of the City of Geneva in Switzerland. The organisation was formed as an international collaboration to promote the wider and more effective dissemination of information about biological organisms. Its name was changed to Taxonomic Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, and composition. Legal definitions Creative works require a cre ... to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |