|
Battle Of Willems
The Battle of Willems (10 May 1794) saw a Republican French army under Jean-Charles Pichegru oppose Coalition forces commanded by Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany, as part of a French attempt to defeat an Allied counteroffensive and continue its own 1794 offensive in the Low Countries, which had already seen success with the battle of Mouscron and the capture of the important cities of Menin and Courtrai. The battle was a French tactical defeat, but victory in the battle of Courtrai the next day, coupled with the Duke of York's realisation that he was badly outnumbered, led to Allied withdrawal and a strategic victory for the French, who retained their hold on Menin and Courtrai. During this action, French infantry formed in squares and repulsed Coalition cavalry for the first time during the war. The fighting occurred during the War of the First Coalition near Kortrijk, Belgium, located about west of Brussels. Background Plans For the spring 1794 campaign, Lazare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition (french: Guerre de la Première Coalition) was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797 initially against the Kingdom of France (1791-92), constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, French Republic that succeeded it. They were only loosely allied and fought without much apparent coordination or agreement; each power had its eye on a different part of France it wanted to appropriate after a French defeat, which never occurred. Noah Shusterman – ''De Franse Revolutie (The French Revolution).'' Veen Media, Amsterdam, 2015. (Translation of: ''The French Revolution. Faith, Desire, and Politics.'' Routledge, London/New York, 2014.) Chapter 7 (p. 271–312) : The federalist revolts, the Vendée and the beginning of the Terror (summer–fall 1793). Relations between the French revolutionaries and neighbouring monarchies had deteriorated following the Declaration of Pillnitz in August 1791. Eight mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
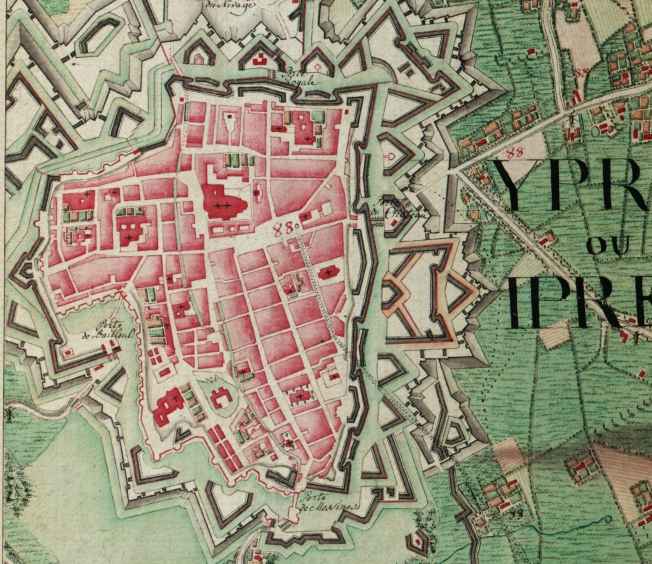
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge, Hollebeke, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge, Voormezele, Zillebeke, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants. During the First World War, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres between German and Allied forces. History Origins before First World War Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee on the banks of which it was founded. During the Middle Ages, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish city with a population of 40,000 in 1200 AD, renow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Victor Marie Moreau
Jean Victor Marie Moreau (, 14 February 1763 – 2 September 1813) was a French general who helped Napoleon Bonaparte to power, but later became a rival and was banished to the United States. Biography Rise to fame Moreau was born at Morlaix in Brittany. His father was a successful lawyer, and instead of allowing Moreau to enter the army, as he attempted to do, insisted on Moreau studying law at the University of Rennes. Young Moreau showed no inclination for law, but reveled in the freedom of student life. Instead of taking his degree, he continued to live with the students as their hero and leader, and formed them into a sort of army, which he commanded as their provost. When 1789 came, he commanded the students in the daily affrays which took place at Rennes between the young noblesse and the populace. In 1791, Moreau was elected a lieutenant colonel of the volunteers of Ille-et-Vilaine. With them he served under Charles François Dumouriez, and in 1793 the good order o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Commune de Dunkerque (59183) INSEE It lies from the border. It has the third-largest French harbour. The population of the commune in 2019 was 86,279. Etymology and language use The name of Dunkirk derives from '' or ' |
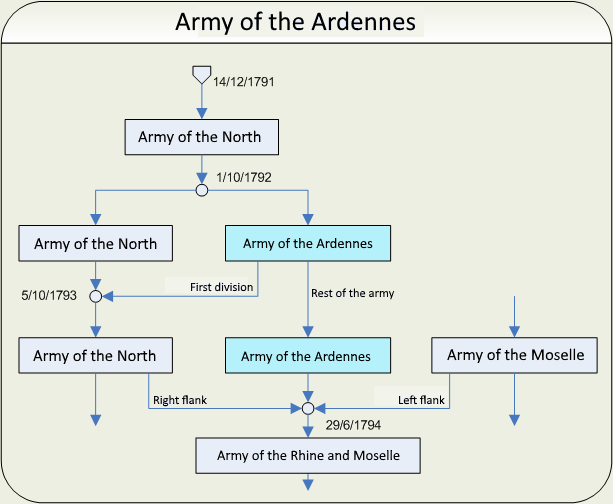
Army Of The Ardennes
The Army of the Ardennes (''armée des Ardennes'') was a French Revolutionary Army formed on the first of October 1792 by splitting off the right wing of the Army of the North, commanded from July to August that year by La Fayette. From July to September 1792 General Dumouriez also misused the name Army of the Ardennes for the right wing of what was left of the Army of the North after the split, encamped at Sedan and the name of Army of the North for the left flank of the army. It was reorganized by a decree of the Conseil exécutif on the first of March 1793, leading to only the right flank of the army keeping the name of Army of the Ardennes. The first division of the Army of the Ardennes re-merged back into the Army of the North on 5 October 1793, at which date the rest of the Army of the Ardennes continued as the Army of the Ardennes until 29 June 1794, when it merged with the Army of the North's right wing and the Army of the Moselle's left wing to form the Army of Sambr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Landau (1793)
The siege of Landau (20 August – 23 December 1793) saw a corps from the Kingdom of Prussia commanded by Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen lay siege to a 3,800-man French Republican garrison led by Joseph Marie Tennet de Laubadère. Since the Prussians lacked siege cannons, they tried to starve the French defenders into surrender by blockading the city. In late December, the French ''Army of the Moselle'' under Lazare Hoche and ''Army of the Rhine'' under Jean-Charles Pichegru defeated the Coalition armies opposed to them, forcing the Prussians to raise the War of the First Coalition siege. Almost two months after Landau was surrounded, the Coalition army won a victory in the First Battle of Wissembourg, driving the ''Army of the Rhine'' deep into Alsace. The French government placed a priority on relieving Landau, so Pichegru's army began a sustained offensive against Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser's Coalition army in the Battle of Haguenau. The effort finall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Wissembourg (1793)
The Second Battle of Wissembourg from 26 December 1793 to 29 December 1793 saw an army of the First French Republic under General Lazare Hoche fight a series of clashes against an army of Austrians, Prussians, Bavarians, and Hessians led by General Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser. There were significant actions at Wœrth on 22 December and Geisberg on 26 and 27 December. In the end, the French forced their opponents to withdraw to the east bank of the Rhine River. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition phase of the French Revolutionary Wars. Background During the First Battle of Wissembourg on 13 October 1793, the Lines of Weissenburg, defended by the French Army of the Rhine, were stormed by an Austrian-Allied army under Wurmser. A month later, Austrian engineer Franz von Lauer compelled Fort-Louis on the Rhine to surrender to the Allies. The French government responded to the crisis by sending reinforcements from the Army of the Moselle. On 17 November, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Haguenau (1793)
The Battle of Haguenau (18 November – 22 December 1793) saw a Republican French army commanded by Jean-Charles Pichegru mount a persistent offensive against a Coalition army under Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser during the War of the First Coalition. In late November, Wurmser pulled back from his defenses behind the Zorn River and assumed a new position along the Moder River at Haguenau. After continuous fighting, Wurmser finally withdrew to the Lauter River after his western flank was turned in the Battle of Froeschwiller on 22 December. Haguenau is a city in Bas-Rhin department of France, located north of Strasbourg. Consisting of troops from Habsburg Austria, Hesse-Kassel and Electoral Bavaria, plus French Royalists, the Coalition army broke through the French frontier defenses in the First Battle of Wissembourg on 13 October 1793 and overran Alsace as far as the Zorn River. The French government reacted to the emergency by appointing Pichegru to lead the ''Army of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Rhine (1791–1795)
The Army of the Rhine (french: Armée du Rhin) was formed in December 1791, for the purpose of bringing the French Revolution to the German states along the Rhine River. During its first year in action (1792), under command of Adam Philippe Custine, the Army of the Rhine participated in several victories, including Mainz, Frankfurt and Speyer. Subsequently, the army underwent several reorganizations and merged with the Army of the Moselle to form the Army of the Rhine and Moselle on 20 April 1795. Revolutionary Wars The Army of the Rhine (''Armée du Rhin'') was one of the main French Revolutionary armies operated in the Rhineland theater, principally in the Rhine River valley, from 1791 to 1795. At its creation, the Army of the Rhine had 88,390 men. It was formed on 14 December 1791, to defend France's eastern frontier in conjunction with two other armies, the Army of the North (France), Army of the North and the Army of the Center (name changed in October 1792 to Army of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maubeuge
Maubeuge (; historical nl, Mabuse or nl, Malbode; pcd, Maubeuche) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It is situated on both banks of the Sambre (here canalized), east of Valenciennes and about from the Belgian border. History Maubeuge (ancient ''Malbodium'', from Latin, derived from the Old Frankish name ''Malboden'', meaning "assizes of Boden") owes its origin to Maubeuge Abbey, a double monastery, for men and women, founded in the 7th century by Saint Aldego, the relics of whom are preserved in the church. It subsequently belonged to the territory of Hainaut. The town was part of the Spanish Netherlands and changed hands a number of times before it was finally ceded to France in the 1678 Treaty of Nijmegen. As part of Vauban's ''pré carré'' plan that protected France's northern borders with a double line of fortresses, it was extensively fortified as directed by Louis XIV of France. Besieged in 1793 by Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouchain
Bouchain (; vls, Boesem) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It lies halfway between Cambrai and Valenciennes. Bouchain, seat of the early medieval County of Ostrevent, was taken by Arnulf I, Count of Flanders, in the 10th century and eventually subsumed into the County of Hainaut. During the War of the Spanish Succession, when the town was fortified, Bouchain was besieged twice. On 12 September 1711 it was seized from the French after a 34 day siege by the Grand Alliance led by the Duke of Marlborough. It was again besieged, and recaptured by French forces, on 19 October 1712 after an 18 day siege. Population International relations It is twinned with Halesworth and Eitorf. Heraldry See also * Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 648 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg City
Luxembourg ( lb, Lëtzebuerg; french: Luxembourg; german: Luxemburg), also known as Luxembourg City ( lb, Stad Lëtzebuerg, link=no or ; french: Ville de Luxembourg, link=no; german: Stadt Luxemburg, link=no or ), is the capital city of the Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and the Communes of Luxembourg, country's most populous commune. Standing at the confluence of the Alzette and Pétrusse rivers in southern Luxembourg, the city lies at the heart of Western Europe, situated by road from Brussels, from Paris, and from Cologne. The city contains Luxembourg Castle, established by the Franks in the Early Middle Ages, around which a settlement developed. , Luxembourg City has a population of 128,514 inhabitants, which is more than three times the population of the country's second most populous commune (Esch-sur-Alzette). The city's population consists of 160 nationalities. Foreigners represent 70% of the city's population, whilst Luxembourgers represent 30% of the populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |