|
Bateshwar Hindu Temples, Madhya Pradesh
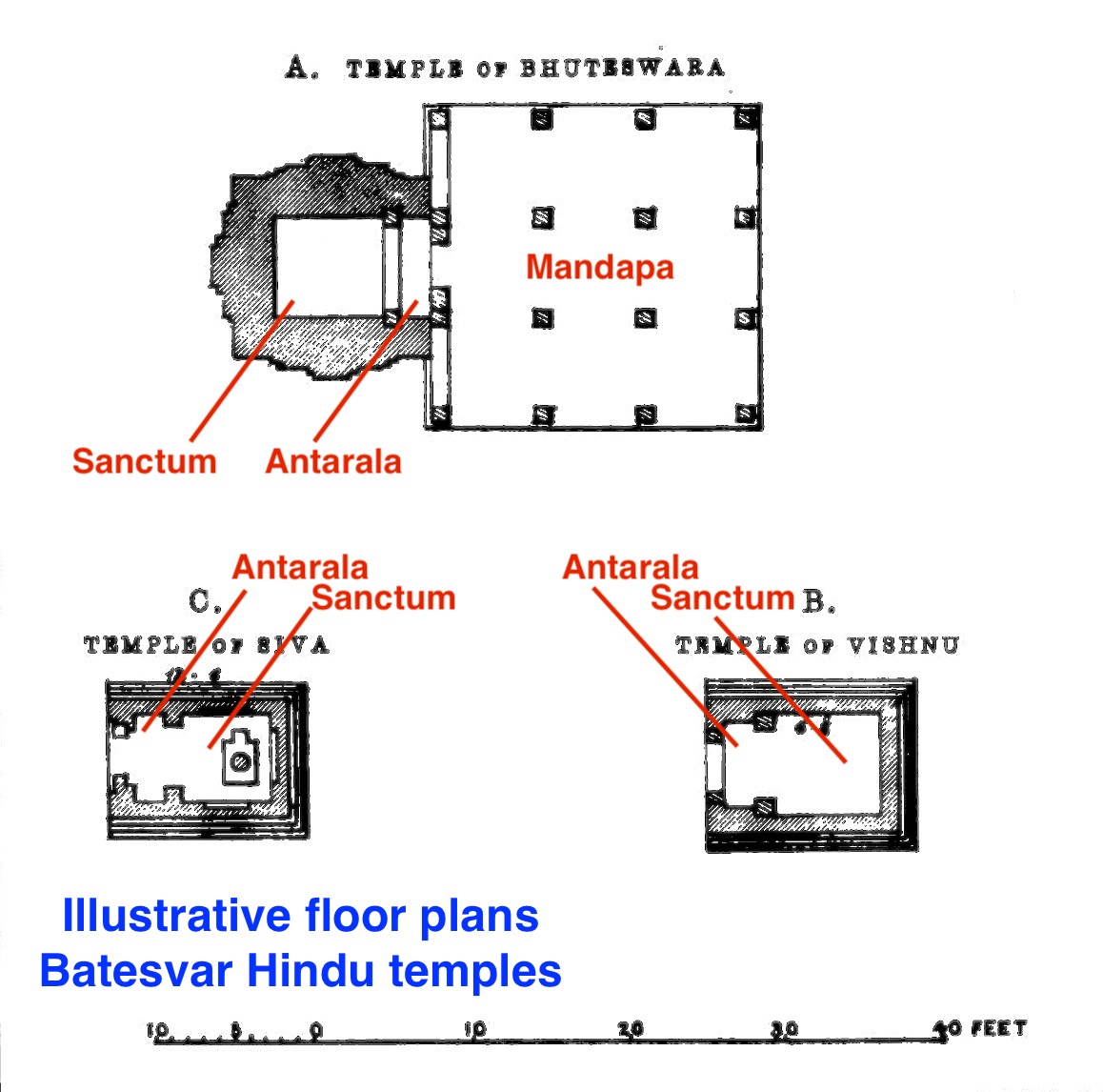
The Bateshwar Hindu temples (romanised: baṭeśvar; Help:IPA/Hindi, /bəʈeːɕvər/) are a group of nearly 200 sandstone Hindu temples and their ruins in north Madhya Pradesh in post-Gupta, early Gurjara-Pratihara style of North Indian temple architecture. It is about north of Gwalior and about east of Morena town. The temples are mostly small and spread over about site. They are dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu and Shakti - representing the three major traditions within Hinduism. The site is within the Chambal River valley ravines, on the north-western slope of a hill near Padavali known for its major medieval era Vishnu temple. The Bateshwar temples were built between the 8th and the 10th-century. The site is likely named after the Bhuteshvar Temple, the largest Shiva temple at the site. It is also referred to as Batesvar temples site or Batesara temples site. The temples as they now appear are in many cases reconstructed from the fallen stones in a project begun by the Archaeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nirbhay Singh Gujjar
Nirbhay Singh Gurjar (1957 – 7 November 2005) was an Indian criminal and one of the last dacoits of the Chambal and known as the "Last Lion of Chambal". He terrorized the Chambal ravines in India, the lawless zone at the cusp of two states Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh for 31 years. Life Gujjar was born in Panchdeora village of Jalaun district, Uttar Pradesh and died on 7 November 2005 in Etawah, India. Dacoity career With this Sarpanch, Member of Legislative Assembly (MLA) and Member of Parliament (MP) were elected. Help to ASI According to the Regional Director (North) of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), Mr.K. K. Muhammed, Gurjar and his gang provided much help to Archaeological Survey of India for the restoration of Bateshwar Hindu temples, Madhya Pradesh, that were constructed during the Gurjara-Pratihara empire between 8th to 11th century. Film Indian Bollywood film director Krishna Mishra also made a Hindi movie named as ''Beehad - The Ravine'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teli Ka Mandir
Teli ka Mandir, also known as Telika Temple, is a Hindu temple located within the Gwalior Fort in Madhya Pradesh, India. Dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu and Matrikas, it has been variously dated between the early 8th and early 9th century CE. It is an atypical design for a Hindu temple, as it has a rectangular sanctum instead of the typical square. It integrates the architectural elements of the Nagara style and the Valabhi prasada. The temple is based on a Gurjara Pratihara-Gopagiri style North Indian architecture. The temple is a classic example of a design based on "musical harmonics" in architecture, one that Hermann Goetz called as a masterpiece of late Gupta era Indian art. Location The temple is located inside the fort of Gwalior, north Madhya Pradesh. The city is connected by major highways NH 44 and 46 (Asian Highway 43 and 47), a railway station and airport (IATA: GWL). It is located near other historic Hindu and Jain temples from the medieval era, as well the major group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddhachal Caves
Siddhachal Caves are Jain cave monuments and statues carved into the rock face inside the Urvashi valley of the Gwalior Fort in northern Madhya Pradesh, India. There are the most visited among the five groups of Jain rock carvings on the Gwalior Fort hill. They were built over time starting in the 7th-century, but most are dated to the 15th-century CE. Many of the statues were defaced and destroyed under the orders of the Muslim Emperor Babur of the Mughal dynasty in the 16th century, while a few repaired and restored after the fall of the Mughal dynasty and through the late 19th century. The statues depict all 24 Tirthankaras. They are shown in both seated Padmasana posture as well as standing Kayotsarga posture, in the typical naked form of Jain iconography. The reliefs behind some of them narrate scenes from the Jain legends. The site is about from the South-East Group of Gopachal rock cut Jain monuments and about northwest of the Teli ka Mandir within the Gwalior Fort. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bateshwar Temples (16313836371)
Bateshwar may refer to: *Bateshwar, Uttar Pradesh, a village in India *Wari-Bateshwar ruins The Wari-Bateshwar (Bengali: উয়ারী-বটেশ্বর,''Uari-Bôṭeshshor'') ruins in Narsingdi, Dhaka Division, Bangladesh is one of the earliest urban archaeological sites in Bangladesh. Excavation in the site unearthed a ..., an ancient fort city dating back to 450 BC in Bangladesh * Bateshwar, Morena, an ancient site in Morena district, Madhya Pradesh, India * Bateshwar hills, Purnia district, Bihar, India * Bateshwar Rural Municipality, Nepal {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ruins Of Bateshwar Group Of Temples
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashavatara
The Dashavatara ( sa, दशावतार, ) are the ten primary avatars of Vishnu, a principal Hindus, Hindu god. Vishnu is said to descend in the form of an avatar to restore cosmic order. The word ''Dashavatara'' derives from , meaning "ten", and , roughly equivalent to "incarnation". The list of included avatars varies across sects and regions, particularly in respect to the inclusion of Balarama (brother of Krishna) or Gautama Buddha. Though no list can be uncontroversially presented as standard, the "most accepted list found in Puranas and other texts is [...] Krishna, Buddha." Most draw from the following set of figures, in this order: Matsya; Kurma; Varaha; Narasimha; Vamana; Parashurama; Rama; Krishna or Balarama; Gautama Buddha in Hinduism, Buddha or Krishna; and Kalki. In traditions that omit Krishna, he often replaces Vishnu as the source of all avatars. Some traditions include a regional deity such as Vithoba or Jagannath in penultimate position, replacing Krish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nataraja
Nataraja () also known as Adalvallaan () is a depiction of the Hindu god Shiva as the divine cosmic dancer. His dance is called Tandava.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2015) The pose and artwork are described in many Hindu texts such as the ''Tevaram'', ''Thiruvasagam'' in Tamil and ''Anshumadbhed agama'' and ''Uttarakamika agama'' in Sanskrit and Grantha texts, the dance murti featured in all major Hindu temples of Shaivism, and is a well-known sculptural symbol in India and popularly used as a symbol of Indian culture, in particular as one of the finest illustrations of Hindu art. He is commonly referred as Koothan(), Sabesan() and Ambalavanan () in various Tamil texts. The sculpture is symbolic of Shiva as the lord of dance and dramatic arts, with its style and proportions made according to Hindu texts on arts. Tamil Devotional texts such as Tirumurai (The twelve books of Southern Shaivism) speaks that Nataraja is the form of Shiva in which he does Creation, destruction, Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use la, flōruit is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are wills attested by John Jones in 1204, and 1229, and a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)". The term is often used in art history when dating the career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th To 10th Century Batesvar Hindu Temples Plan Madhya Pradesh India
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra. * the first number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samvat
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shaka era, Shalivahana Shaka (Based on the Shalivahana, King Shalivahana, also the Indian national calendar) found in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the solar c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
.jpg)
