Bateshwar Hindu Temples, Madhya Pradesh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bateshwar Hindu temples (romanised: baṭeśvar; /bəʈeːɕvər/) are a group of nearly 200 sandstone
Construction and Conception: Maṇḍapikā Shrines of Central India
''East and West'', Vol. 26, No. 3/4 (September - December 1976), page 415, Figure 21 caption, context: 409-418 Cunningham reports that one of the inscriptions was dated
 In north-northeast corner of the site was a large platform of about length and breadth, with an integrated platform projection of a square with side. Cunningham speculated that this may have been the largest temple at the Bateshvara site before its destruction, and he noted that not a stone remains near the platform to offer further clues as to what the lost temple was like. Cunningham also noted that one of the small temples to the northwest of the Bhuteshwara temple had a short inscription dated Samvat 1107 (1050 CE), thus establishing the
In north-northeast corner of the site was a large platform of about length and breadth, with an integrated platform projection of a square with side. Cunningham speculated that this may have been the largest temple at the Bateshvara site before its destruction, and he noted that not a stone remains near the platform to offer further clues as to what the lost temple was like. Cunningham also noted that one of the small temples to the northwest of the Bhuteshwara temple had a short inscription dated Samvat 1107 (1050 CE), thus establishing the
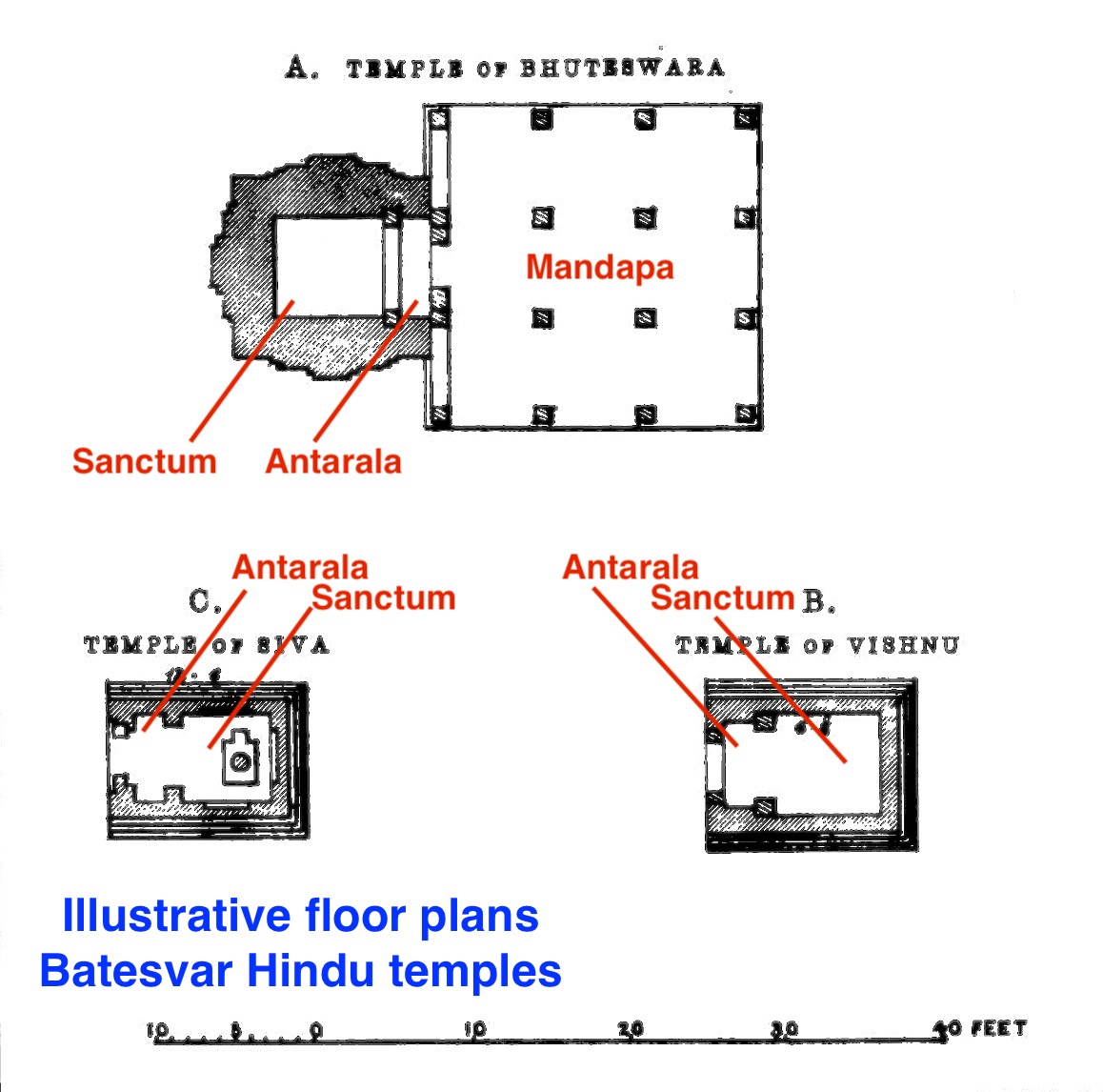
 According to Michael Meister, the Bateshwar site illustrates the conception and construction of "Mandapika shrine" concept in central India. It is reducing the Hindu temple idea to its basics, in a simple concept that is one step further from the single cave cell design. This design has roots in more ancient Hindu temples found in this region such as one that survives at Mahua and has a Sanskrit inscription that calls the design as ''sila mandapika'' (literally, a "stone pandal or pavilion". This has vedi-platform roots that combines the traditional square plan with various combinations of Hindu temple architecture elements. The temples explore a square sanctum mounted on a basement platform (''jagati'') that is rectangular, states Meister, so as to incorporate a small ''praggriva'' (porch).
These temples have a "simple pillared wall topped by a broad, flat-edged awning which extends beyond the sanctum to shade the entry as well. The square pillars rest directly on the vedibandha, and are crowned by "leaf capitals, their shafts engraved with decorative medallions. At its best this type has a very individual and decorative quality, still like a wooden or ivory box, intervening bands of meandering foliage especially vital, the whole framed by the flat, deeply shadowed vedibandha mouldings and the crisp chadya (with saw-tooth edge) above", according to Meister. The significance of these temples is that they fuse and experiment with a variety of temple building ideas, such as topping the nagara sikharas that may have been dominant by that time possibly in western India, on the simplest of temple grid plans with more ancient roots in central India.Michael W. Meister (1976)
According to Michael Meister, the Bateshwar site illustrates the conception and construction of "Mandapika shrine" concept in central India. It is reducing the Hindu temple idea to its basics, in a simple concept that is one step further from the single cave cell design. This design has roots in more ancient Hindu temples found in this region such as one that survives at Mahua and has a Sanskrit inscription that calls the design as ''sila mandapika'' (literally, a "stone pandal or pavilion". This has vedi-platform roots that combines the traditional square plan with various combinations of Hindu temple architecture elements. The temples explore a square sanctum mounted on a basement platform (''jagati'') that is rectangular, states Meister, so as to incorporate a small ''praggriva'' (porch).
These temples have a "simple pillared wall topped by a broad, flat-edged awning which extends beyond the sanctum to shade the entry as well. The square pillars rest directly on the vedibandha, and are crowned by "leaf capitals, their shafts engraved with decorative medallions. At its best this type has a very individual and decorative quality, still like a wooden or ivory box, intervening bands of meandering foliage especially vital, the whole framed by the flat, deeply shadowed vedibandha mouldings and the crisp chadya (with saw-tooth edge) above", according to Meister. The significance of these temples is that they fuse and experiment with a variety of temple building ideas, such as topping the nagara sikharas that may have been dominant by that time possibly in western India, on the simplest of temple grid plans with more ancient roots in central India.Michael W. Meister (1976)
Construction and Conception: Maṇḍapikā Shrines of Central India
''East and West'', Vol. 26, No. 3/4 (September - December 1976), pages 415-417, context: 409-418
 The site was visited and its ruins reported by Alexander Cunningham in 1882 as a "collection of more than 100 temples large and small to the southeast of Paravali Padavali", the latter with a "very fine old temple".Eastern Rajputana Tour Report
The site was visited and its ruins reported by Alexander Cunningham in 1882 as a "collection of more than 100 temples large and small to the southeast of Paravali Padavali", the latter with a "very fine old temple".Eastern Rajputana Tour Report
A Cunningham, Archaeological Survey of India, Volume XX, pages 107, 110-112 Bateshwar was notified by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) as a protected site in 1920. Limited recovery, standardized temple numbering, ruins isolation with photography, and site conservation effort was initiated during the colonial British era. Several scholars studied the site and included them in their reports. For example, the French archeologist Odette Viennot published a paper in 1968 that included a discussion and photographs of the numbered Batesvar temples.O. VIENNOT (1968)
Le problème des temples à toit plat dans l'Inde du Nord
Arts Asiatiques, Vol. 18 (1968), École française d’Extrême-Orient, pages 40-51 with Figures 50, 53-56, 76, 80-82 and 88 context: 23-84 (in French) In 2005, the ASI began an ambitious project to collect all the ruins, reassemble them and restore as many temples as possible, under an initiative led by the ASI Bhopal region's Superintending Archaeologist K.K. Muhammed. Under Muhammed's leadership, some 60 temples were restored. Muhammed has continued to campaign for the site's further restoration and calls it "my place of pilgrimage. I come here once in every three months. I am passionate about this temple complex."
File:Bateshwar Temple Complex - 1.jpg, Ruins at the Batesvar site
File:Bateshwar Temple Complex - 3.jpg, Restored temples
File:Bateshwar Temples (16313906851).jpg, Two similar temples, some differences
File:Vishnu Temple, Bateshwar.jpg, Vishnu temple at Batesvar
File:Vishnu Temple at Bateshwar (16129557249).jpg, Vishnu temple interior from ruins
File:Vishnu Temple at Bateshwar (16313711321).jpg, Vishnu temple, recreated by ASI
Hindu temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hin ...
s and their ruins in north Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
in post-Gupta, early Gurjara-Pratihara
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of th ...
style of North Indian temple architecture. It is about north of Gwalior and about east of Morena
Morena is the headquarter city of Morena district, in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is governed by a municipality corporation. It is also the administrative headquarters of the Chambal division. It is from Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
G ...
town. The temples are mostly small and spread over about site. They are dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu and Shakti - representing the three major traditions within Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
. The site is within the Chambal River valley ravines, on the north-western slope of a hill near Padavali known for its major medieval era Vishnu temple. The Bateshwar temples were built between the 8th and the 10th-century. The site is likely named after the Bhuteshvar Temple, the largest Shiva temple at the site. It is also referred to as Batesvar temples site or Batesara temples site.
The temples as they now appear are in many cases reconstructed from the fallen stones in a project begun by the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexand ...
in 2005. Dacoit Nirbhay Singh Gujjar
Nirbhay Singh Gurjar (1957 – 7 November 2005)
was an Indian criminal and one of the last dacoits of the Chambal and known as the "Last Lion of Chambal". He terrorized the Chambal ravines in India, the lawless zone at the cusp of two states U ...
and his gang helped Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexand ...
restore the temple complex.
According to the Madhya Pradesh Directorate of Archaeology, this group of 200 temples were built during the reign of Gurjara-Pratihara Dynasty
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the ...
. According to Michael Meister, an art historian and a professor specializing in Indian temple architecture, the earliest temples in the Bateshwar group near Gwalior are likely from the 750-800 CE period.Michael W. Meister (1976)Construction and Conception: Maṇḍapikā Shrines of Central India
''East and West'', Vol. 26, No. 3/4 (September - December 1976), page 415, Figure 21 caption, context: 409-418 Cunningham reports that one of the inscriptions was dated
Samvat
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a s ...
1107 or 1050 AD.
The temples were destroyed after the 13th century; it is not clear if this was by an earthquake, or Muslim forces.
Description
The site is mentioned in historical literature as Dharon or Paravali, later as Padavali. The local name for the group of temples is Batesvar or Bateshwar temples. According to the Cunningham's report of 1882, the site was a "confused assemblage of more than one hundred temples of various sizes, but mostly small". The largest standing temple was of Shiva, wrote Cunningham, and the temple was locally called Bhutesvara. However, to his surprise the temple had a relief of Garuda on top, leading him to speculate that the temple may have been a Vishnu temple before it was damaged and reused. The Bhutesvara temple had a square sanctum with a side, with a relatively small 20 square feet ''mahamandapa''. The sanctum doorway was flanked by river goddesses Ganga and Yamuna. The tower superstructure was a pyramidal square starting off from a sided square seated on a flat roof, then rhythmically tapering off. The standing temples, stated Cunningham, all had sides made from single slabs set upright, above which sat flat roofs then pyramidal top as a part of their architecture. The site had a water tank cut into the hill rock, with rows of small temples arranged to form a street to the tank. Cunningham also reported seeing Shiva linga inside one of the temples, a trimurti statue, a Ganesha, Shiva and Parvati together around this temple. Next to the Shiva temple was a Vishnu temple, about the same size as the Siva temple, again a square sanctum of side with river goddesses Ganga and Yamuna flanking the doorway on its jambs. In north-northeast corner of the site was a large platform of about length and breadth, with an integrated platform projection of a square with side. Cunningham speculated that this may have been the largest temple at the Bateshvara site before its destruction, and he noted that not a stone remains near the platform to offer further clues as to what the lost temple was like. Cunningham also noted that one of the small temples to the northwest of the Bhuteshwara temple had a short inscription dated Samvat 1107 (1050 CE), thus establishing the
In north-northeast corner of the site was a large platform of about length and breadth, with an integrated platform projection of a square with side. Cunningham speculated that this may have been the largest temple at the Bateshvara site before its destruction, and he noted that not a stone remains near the platform to offer further clues as to what the lost temple was like. Cunningham also noted that one of the small temples to the northwest of the Bhuteshwara temple had a short inscription dated Samvat 1107 (1050 CE), thus establishing the floruit
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicatin ...
for the site.
The ASI team ruins identification and restoration efforts since 2005 have yielded the following additional information about the site:
*Some of the temples had a Nataraja
Nataraja () also known as Adalvallaan () is a depiction of the Hindu deities, Hindu god Shiva as the divine cosmic dancer. His dance is called Tandava.''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2015) The pose and artwork are described in many Hindu texts ...
on the ''kirti-mukha''
*Reliefs with "exquisite carving" of Lakulisa
*Reliefs of Siva holding the hand of Parvati
*Reliefs narrating the legend of ''Kalyana-sundaram'', or the marriage of Shiva and Parvati with Vishnu, Brahma and others attending
*Small sculptures of women playing the lute, veena or drums in Vishnu temples, suggesting that music profession in pre-11th century India encouraged women to participate as musicians
*Amorous couples in various stages of courtship and intimacy (mithuna, kama scenes)
*Secular scenes such as men riding elephants, men wrestling, lions
*Friezes with narratives from the ''Bhagavata Purana'' such as Krishna leela scenes such as Devaki holding baby Krishna who is suckling her breasts in prison that is guarded by a woman; Baby Krishna draining away the life of the demon with poisoned breasts, etc.
According to Gerd Mevissen, the Batesvar temples complex has many interesting lintels, such as one with Navagraha, many with Dashavatara (ten avatars of Vishnu) of the Vaishnavism tradition, frequent display of Saptamatrikas (seven mothers) from the Shaktism tradition. The presence of Navagraha lintel suggests, states Mevissen, that the temple complex must be dated after 600 CE. The diversity of the theological themese at the site suggest that Batesvar (also called Batesara) was once a hub for temple-related arts and artists.
Significance
 According to Michael Meister, the Bateshwar site illustrates the conception and construction of "Mandapika shrine" concept in central India. It is reducing the Hindu temple idea to its basics, in a simple concept that is one step further from the single cave cell design. This design has roots in more ancient Hindu temples found in this region such as one that survives at Mahua and has a Sanskrit inscription that calls the design as ''sila mandapika'' (literally, a "stone pandal or pavilion". This has vedi-platform roots that combines the traditional square plan with various combinations of Hindu temple architecture elements. The temples explore a square sanctum mounted on a basement platform (''jagati'') that is rectangular, states Meister, so as to incorporate a small ''praggriva'' (porch).
These temples have a "simple pillared wall topped by a broad, flat-edged awning which extends beyond the sanctum to shade the entry as well. The square pillars rest directly on the vedibandha, and are crowned by "leaf capitals, their shafts engraved with decorative medallions. At its best this type has a very individual and decorative quality, still like a wooden or ivory box, intervening bands of meandering foliage especially vital, the whole framed by the flat, deeply shadowed vedibandha mouldings and the crisp chadya (with saw-tooth edge) above", according to Meister. The significance of these temples is that they fuse and experiment with a variety of temple building ideas, such as topping the nagara sikharas that may have been dominant by that time possibly in western India, on the simplest of temple grid plans with more ancient roots in central India.Michael W. Meister (1976)
According to Michael Meister, the Bateshwar site illustrates the conception and construction of "Mandapika shrine" concept in central India. It is reducing the Hindu temple idea to its basics, in a simple concept that is one step further from the single cave cell design. This design has roots in more ancient Hindu temples found in this region such as one that survives at Mahua and has a Sanskrit inscription that calls the design as ''sila mandapika'' (literally, a "stone pandal or pavilion". This has vedi-platform roots that combines the traditional square plan with various combinations of Hindu temple architecture elements. The temples explore a square sanctum mounted on a basement platform (''jagati'') that is rectangular, states Meister, so as to incorporate a small ''praggriva'' (porch).
These temples have a "simple pillared wall topped by a broad, flat-edged awning which extends beyond the sanctum to shade the entry as well. The square pillars rest directly on the vedibandha, and are crowned by "leaf capitals, their shafts engraved with decorative medallions. At its best this type has a very individual and decorative quality, still like a wooden or ivory box, intervening bands of meandering foliage especially vital, the whole framed by the flat, deeply shadowed vedibandha mouldings and the crisp chadya (with saw-tooth edge) above", according to Meister. The significance of these temples is that they fuse and experiment with a variety of temple building ideas, such as topping the nagara sikharas that may have been dominant by that time possibly in western India, on the simplest of temple grid plans with more ancient roots in central India.Michael W. Meister (1976)Construction and Conception: Maṇḍapikā Shrines of Central India
''East and West'', Vol. 26, No. 3/4 (September - December 1976), pages 415-417, context: 409-418
Modern history
 The site was visited and its ruins reported by Alexander Cunningham in 1882 as a "collection of more than 100 temples large and small to the southeast of Paravali Padavali", the latter with a "very fine old temple".Eastern Rajputana Tour Report
The site was visited and its ruins reported by Alexander Cunningham in 1882 as a "collection of more than 100 temples large and small to the southeast of Paravali Padavali", the latter with a "very fine old temple".Eastern Rajputana Tour ReportA Cunningham, Archaeological Survey of India, Volume XX, pages 107, 110-112 Bateshwar was notified by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) as a protected site in 1920. Limited recovery, standardized temple numbering, ruins isolation with photography, and site conservation effort was initiated during the colonial British era. Several scholars studied the site and included them in their reports. For example, the French archeologist Odette Viennot published a paper in 1968 that included a discussion and photographs of the numbered Batesvar temples.O. VIENNOT (1968)
Le problème des temples à toit plat dans l'Inde du Nord
Arts Asiatiques, Vol. 18 (1968), École française d’Extrême-Orient, pages 40-51 with Figures 50, 53-56, 76, 80-82 and 88 context: 23-84 (in French) In 2005, the ASI began an ambitious project to collect all the ruins, reassemble them and restore as many temples as possible, under an initiative led by the ASI Bhopal region's Superintending Archaeologist K.K. Muhammed. Under Muhammed's leadership, some 60 temples were restored. Muhammed has continued to campaign for the site's further restoration and calls it "my place of pilgrimage. I come here once in every three months. I am passionate about this temple complex."
Gallery
See also
*Siddhachal Caves
Siddhachal Caves are Jain cave monuments and statues carved into the rock face inside the Urvashi valley of the Gwalior Fort in northern Madhya Pradesh, India. There are the most visited among the five groups of Jain rock carvings on the Gwalior F ...
*Teli ka Mandir
Teli ka Mandir, also known as Telika Temple, is a Hindu temple located within the Gwalior Fort in Madhya Pradesh, India. Dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu and Matrikas, it has been variously dated between the early 8th and early 9th century CE.
It is an ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Dehejia, V. (1997). ''Indian Art''. Phaidon: London. . * * * *Harle, J.C., ''The Art and Architecture of the Indian Subcontinent'', 2nd edn. 1994, Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Gwalior topics Hindu temples in Madhya Pradesh Tourist attractions in Morena district