|
BARD1
BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BARD1'' gene. The human BARD1 protein is 777 amino acids long and contains a RING finger domain (residues 46-90), four ankyrin repeats (residues 420-555), and two tandem BRCT domains (residues 568-777). Function Most, if not all, BRCA1 heterodimerizes with BARD1 in vivo. BARD1 and BRCA1 form a heterodimer via their N-terminal RING finger domains. The BARD1-BRCA1 interaction is observed in vivo and in vitro and is essential for BRCA1 stability. BARD1 shares homology with the two most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING motif and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The RING motif is a cysteine-rich sequence found in a variety of proteins that regulate cell growth, including the products of tumor suppressor genes and dominant protooncogenes, and developmentally important genes such as the polycomb group of genes. The BARD1 protein also contains three tandem ankyrin repeats. The BARD1/BRCA1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
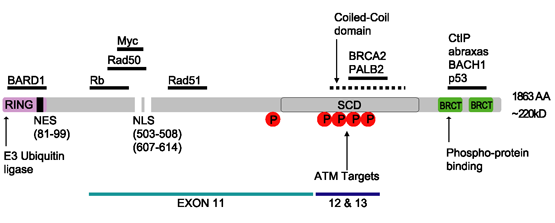
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSTF2
Cleavage stimulation factor 64 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CSTF2'' gene. This gene encodes a nuclear protein with an RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain. The protein is a member of the cleavage stimulation factor (CSTF) complex that is involved in the 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNAs. Specifically, this protein binds GU-rich elements within the 3'-untranslated region of mRNAs. Interactions CSTF2 has been shown to interact with CSTF3, SUB1, SYMPK, BARD1 and BRCA1 Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a h .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSTF1
Cleavage stimulation factor 50 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CSTF1'' gene. This gene encodes one of three subunits which combine to form cleavage stimulation factor (CSTF). CSTF is involved in the polyadenylation and 3' end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Similar to mammalian G protein beta subunits, this protein contains transducin-like repeats. Several transcript variants with different 5' UTR, but encoding the same protein, have been found for this gene. Interactions CSTF1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with BARD1. References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-20-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora B Kinase
Aurora kinase B is a protein that functions in the attachment of the mitotic spindle to the centromere. Function Chromosomal segregation during mitosis as well as meiosis is regulated by kinases and phosphatases. The Aurora kinases associate with microtubules during chromosome movement and segregation. Aurora kinase B localizes to microtubules near kinetochores, specifically to the specialized microtubules called K-fibers, and Aurora kinase A (MIM 603072) localizes to centrosomes (Lampson et al., 2004).[supplied by OMIM] In cancerous cells, over-expression of these enzymes causes unequal distribution of genetic information, creating aneuploidy, aneuploid cells, a hallmark of cancer. Discovery In 1998, Aurora kinase B was identified in humans by a polymerase chain reaction screen for kinases that are overexpressed in cancers. In the same year, rat Aurora kinase B was identified in a screen designed to find kinases that altered S. cerevisiae proliferation when overexpressed. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are a human gene and its protein product, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double strand bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewing Sarcoma Breakpoint Region 1
RNA-binding protein EWS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EWSR1'' gene on human chromosome 22, specifically 22q12.2. It is one of 3 proteins in the FET protein family. The q22.2 region of chromosome 22 encodes the N-terminal transactivation domain of the EWS protein and that region may become joined to one of several other chromosomes which encode various transcription factors, see and the FET protein family. The expression of a chimeric protein with the EWS transactivation domain fused to the DNA binding region of a transcription factor generates a powerful oncogenic protein causing Ewing sarcoma and other members of the Ewing family of tumors. These translocations can occur due to chromoplexy, a burst of complex chromosomal rearrangements seen in cancer cells. The normal EWS gene encodes an RNA binding protein closely related to FUS (gene) and TAF15, all of which have been associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Interactions The EWS protein has been shown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankyrin Repeat
The ankyrin repeat is a 33-residue motif in proteins consisting of two alpha helices separated by loops, first discovered in signaling proteins in yeast Cdc10 and ''Drosophila'' Notch. Domains consisting of ankyrin tandem repeats mediate protein–protein interactions and are among the most common structural motifs in known proteins. They appear in bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic proteins, but are far more common in eukaryotes. Ankyrin repeat proteins, though absent in most viruses, are common among poxviruses. Most proteins that contain the motif have four to six repeats, although its namesake ankyrin contains 24, and the largest known number of repeats is 34, predicted in a protein expressed by ''Giardia lamblia''. Ankyrin repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid structure called ankyrin repeat domains. These domains are one of the most common protein–protein interaction platforms in nature. They occur in a large number of functionally diverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCL3
B-cell lymphoma 3-encoded protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL3'' gene. This gene is a proto-oncogene candidate. It is identified by its translocation into the immunoglobulin alpha-locus in some cases of B-cell leukemia. The protein encoded by this gene contains seven ankyrin repeats, which are most closely related to those found in I kappa B proteins. This protein functions as a transcriptional coactivator that activates through its association with NF-kappa B homodimers. The expression of this gene can be induced by NF-kappa B, which forms a part of the autoregulatory loop that controls the nuclear residence of p50 NF-kappa B. Like BCL2, BCL5, BCL6, BCL7A, BCL9, and BCL10, it has clinical significance in lymphoma. Interactions BCL3 has been shown to interact with: * BARD1, * C-Fos, * C-jun, * C22orf25, * COPS5, * EP300, * HTATIP, * NFKB1, * NFKB2, * PIR, and * NR2B1. Clinical significance Genetic variations in ''BCL3'' gene ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCC3
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCC3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a subunit of the BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex (BRCC), which is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. This protein is also thought to be involved in the cellular response to ionizing radiation and progression through the G2/M checkpoint. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Repair of DNA damage BRCC36, the protein product of the ''BRCC3'' gene, is a deubiquitinating enzyme and a core component of the deubiquitin complex BRCA1-A.Rabl J. BRCA1-A and BRISC: Multifunctional Molecular Machines for Ubiquitin Signaling. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 31;10(11):1503. doi: 10.3390/biom10111503. PMID: 33142801; PMCID: PMC7692841 BRCA1, as distinct from BRCA1-A, is employed in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free homologous recombinational (HR) repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Sequestration of BRCA1 away from the DN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCT Domain
BRCA1 C Terminus (BRCT) domain is a family of evolutionarily related proteins. It is named after the C-terminal domain of BRCA1, a DNA-repair protein that serves as a marker of breast cancer susceptibility. The BRCT domain is found predominantly in proteins involved in cell cycle checkpoint functions responsive to DNA damage, for example as found in the breast cancer DNA-repair protein BRCA1. The domain is an approximately 100 amino acid tandem repeat, which appears to act as a phospho-protein binding domain. Examples Human proteins containing this domain include: * BARD1; BRCA1 * CTDP1; TDT or DNTT * ECT2 * LIG4 * MCPH1; MDC1 * NBN * PARP1; PARP4; PAXIP1; PES1 * REV1; RFC1; TOPBP1; TP53BP1; XRCC1 DNA repair protein XRCC1, also known as X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''XRCC1'' gene. XRCC1 is involved in DNA repair, where it complexes with DNA ligase III. Function XRCC1 is invol ... References External l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRE (gene)
BRCA1-A complex subunit BRE is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRE'' gene. Repair of DNA damage BRE, the protein product of the BRE (gene), is a core component of the deubiquitin complex BRCA1-A. Other core components of the BRCA1-A complex are the BRCC36 protein (BRCC3 gene), MERIT40 protein (BABAM1 gene), and RAP80 protein ( UIMC1 gene). BRCA1, as distinct from BRCA1-A, is employed in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free homologous recombinational (HR) repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Sequestration of BRCA1 away from the DNA damage site suppresses homologous recombination and redirects the cell in the direction of repair by the process of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The role of BRCA1-A appears to be to bind BRCA1 with high affinity and withdraw it away from the site of DNA damage to the periphery where it remains sequestered, thus promoting NHEJ in preference to HR. Protein-protein interactions BRE (gene) has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAD51
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene ''RAD51''. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA, Archaeal RadA and yeast Rad51. The protein is highly conserved in most eukaryotes, from yeast to humans. Variants Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyA signals exist. Family In mammals, seven recA-like genes have been identified: Rad51, Rad51L1/B, Rad51L2/C, Rad51L3/D, XRCC2, XRCC3, and DMC1/Lim15. All of these proteins, with the exception of meiosis-specific DMC1, are essential for development in mammals. Rad51 is a member of thRecA-like NTPases Function In humans, RAD51 is a 339-amino acid protein that plays a major role in homologous recombination of DNA during double strand break r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |