|
Apusozoa
The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presence of an organic shell or theca under the dorsal surface of the cell. The name derives from the Ancient Greek words for footless () and animal (). This phylum is currently defined as containing the Breviata and the Apusomonadida. However, it currently usually is viewed as paraphyletic, with the Breviata as more basal. The opisthokonts appear to have emerged as sister of the apusomonadida. It has been suggested that the Mantamonadida be classified in Apusozoa. The ancyromonadida appear to be Varisulca, Planomonadida, shifting them possibly more basal than the Amoebozoa, or less basal. While some classification systems have placed Hemimastigida in Apusozoa, 2018 research indicated that hemimastigotes (/Hemimastix/Spironemidae) are thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusozoa
The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presence of an organic shell or theca under the dorsal surface of the cell. The name derives from the Ancient Greek words for footless () and animal (). This phylum is currently defined as containing the Breviata and the Apusomonadida. However, it currently usually is viewed as paraphyletic, with the Breviata as more basal. The opisthokonts appear to have emerged as sister of the apusomonadida. It has been suggested that the Mantamonadida be classified in Apusozoa. The ancyromonadida appear to be Varisulca, Planomonadida, shifting them possibly more basal than the Amoebozoa, or less basal. While some classification systems have placed Hemimastigida in Apusozoa, 2018 research indicated that hemimastigotes (/Hemimastix/Spironemidae) are thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
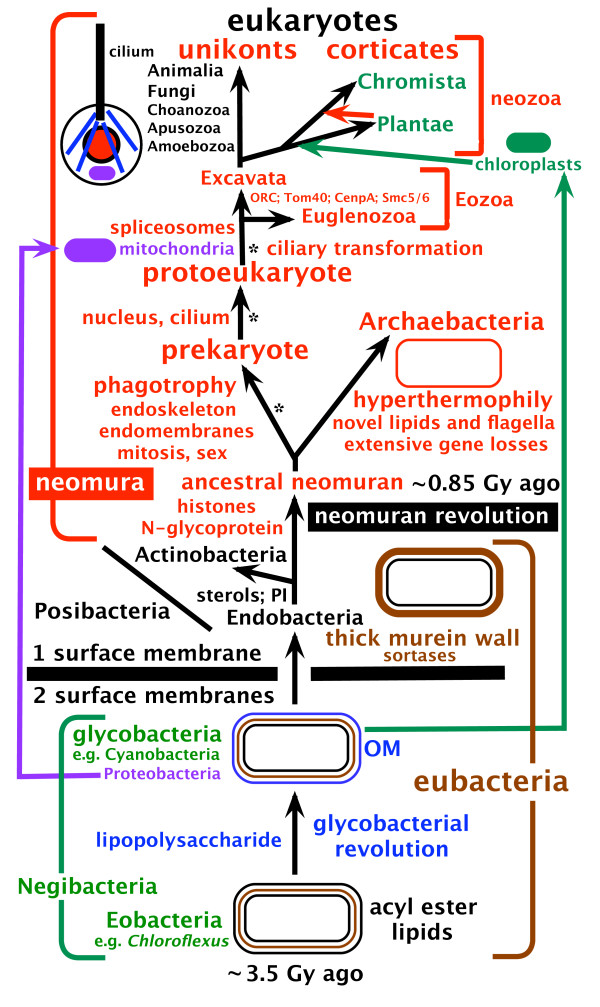
Amorphea Phyla
Amorphea are members of a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. The International Society of Protistologists, the recognised body for taxonomy of protozoa, recommended in 2012 that the term Unikont be changed to Amorphea because the name "Unikont" is based on a hypothesized synapomorphy that the ISP authors and other scientists later rejected. It includes amoebozoa, opisthokonts, and possibly Apusozoa. Taxonomic revisions within this group Cavalier-Smith has proposed two new phyla: Sulcozoa, which consists of the subphyla Apusozoa ( Apusomonadida and Breviatea), and Varisulca, which includes the subphyla Diphyllatea, Discocelida, Mantamonadidae, Planomonadida and Rigifilida. The validity of this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varisulca
Varisulca was a proposed basal Podiate taxon. It encompassed several lineages of heterotrophic protists, most notably the ancyromonads (planomonads), collodictyonids (diphylleids), rigifilids (''Rigifila'', ''Micronuclearia'') and mantamonadids. Recent evidence suggests that the latter three are closely related to each other, forming a clade called CRuMs, but that this is unlikely to be specifically related to ancyromonads Cavalier-Smith had proposed the new subphylum Varisulca which consists of the classes Hilomonadea, Diphyllatea and Glissodiscea. The validity of this proposed taxonomy has yet to ruled upon by the Society of Protistologists. It is unlikely to be widely accepted, since Varisulca appears to be paraphyletic or polyphyletic (ancyromonads are not inferred to be the sister group to CRuMs). Glissodiscea and Multirhiza (a taxon encompassing Diphyllatea and Glissodiscea) also appear paraphyletic or polyphyletic, since ''Mantamonas'' belongs to CRuMs but ancyrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantamonadida
The Mantamonadidae are of Motility, free-living heterotrophic flagellates that move primarily by gliding on surfaces (rather than swimming). There is one genus, ''Mantamonas''. It has been suggested previously that the Mantamonadidae be classified in Apusozoa as sister of the Apusomonadida, Apusmonadida on the basis of Ribosomal RNA, rRNA analyses. However, mantamonads are currently placed in CRuMs on the basis of phylogenomic analyses that identify their closest relatives as the collodictyonids (=diphylleids) and ''Rigifila''. Taxonomy * Order Mantamonadida Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 ** Family Mantamonadidae Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 *** Genus ''Mantamonas'' Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 **** Species ''Mantamonas plastica'' Cavalier-Smith & Glücksman 2011 Phylogeny References Podiata orders {{eukaryote-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusomonadida
The Apusomonadida are a group of protozoan zooflagellates that glide on surfaces, and mostly consume prokaryotes. They are of particular evolutionary interest because they appear to be the sister group to the Opisthokonts, the clade that includes both animals and fungi. Together with the Breviatea, these form the Obazoa clade. Taxonomy * Class Apusomonadea Tedersoo 2017 ** Order Apusomonadida Karpov & Mylnikov 1989 hecomonadales Lee 1989*** Family Apusomonadidae Karpov & Mylnikov 1989 **** Genus ''Amastigomonas'' de Saedeleer 1931 ***** Species '' A. caudata'' Mylnikov 1989 'Amastigomonas borokensis'' Hamar 1979***** Species '' A. debruynei'' de Saedeleer 1931 ***** Species '' A. marisrubri'' Mylnikov & Mylnikov 2012 **** Genus ''Multimonas'' Cavalier-Smith 2010 ***** Species '' M. koreensis'' Heiss et al. 2015 ***** Species '' M. marina'' (Mylnikov 1989) Cavalier-Smith 2010 'Cercomonas marina'' Mylnikov 1989; ''Amastigomonas marina'' (Mylnikov 1989) Mylnikov 1999***** Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supra-kingdom
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla. Traditionally, some textbooks from the United States and Canada used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria/Eubacteria) while textbooks in Great Britain, India, Greece, Brazil and other countries use five kingdoms only (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, ''funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms When Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature into biology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemimastigote
Hemimastigophora is a group of single-celled eukaryotic organisms with a single family, Spironemidae, first identified in 1988. Over the next 30 years, different authors proposed placing these organisms in various branches of the eukaryotes. In 2018 Lax ''et al''. reported the first genetic information for Spironemidae, and suggest that they are from an ancient lineage of eukaryotes which constitute a separate clade from all other eukaryotic kingdoms. It is potentially related to the Telonemia. History of classification Hemimastigophora was established in 1988 by Foissner ''et al''., as a new phylum with a single family, Spironemidae. Its placement on the eukaryote tree of life was unclear, but the authors suggested that the structure of its pellicle and cell nucleus indicated a close relationship with Euglenozoa. For 30 years after the description of the group, no genetic information was available. During that time, researchers proposed that it should be classified in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusomonas
''Apusomonas'' is a genus of Apusozoa The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the prese ... erected by A. G. Aléxéieff in 1924. It includes the species ''Apusomonas proboscidea''. References Apusomonadida Eukaryote genera {{Unikont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as "dinoflagellate" and "choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated protists found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178. Includes freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single layer teak and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal / flat. The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of eukaryotes. Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theca
In biology, a theca (plural thecae) is a sheath or a covering. Botany In botany, the theca is related to plant's flower anatomy. The theca of an angiosperm consists of a pair of microsporangia that are adjacent to each other and share a common area of dehiscence called the stomium. Larry Hufford, "The origin and early evolution of angiosperm stamens" i''The Anther: form, function, and phylogeny'' William G. D'Arcy and Richard C. Keating (editors), Cambridge University Press, 1996, 351pp, p.60, (from Google Books) Any part of a microsporophyll that bears microsporangia is called an anther. Most anthers are formed on the apex of a filament. An anther and its filament together form a typical (or filantherous) stamen, part of the male floral organ. The typical anther is bilocular, i.e. it consists of two thecae. Each theca contains two microsporangia, also known as pollen sacs. The microsporangia produce the microspores, which for seed plants are known as pollen grains. If t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |