|
Mantamonadida
The Mantamonadidae are of Motility, free-living heterotrophic flagellates that move primarily by gliding on surfaces (rather than swimming). There is one genus, ''Mantamonas''. It has been suggested previously that the Mantamonadidae be classified in Apusozoa as sister of the Apusomonadida, Apusmonadida on the basis of Ribosomal RNA, rRNA analyses. However, mantamonads are currently placed in CRuMs on the basis of phylogenomic analyses that identify their closest relatives as the collodictyonids (=diphylleids) and ''Rigifila''. Taxonomy * Order Mantamonadida Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 ** Family Mantamonadidae Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 *** Genus ''Mantamonas'' Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 **** Species ''Mantamonas plastica'' Cavalier-Smith & Glücksman 2011 Phylogeny References Podiata orders {{eukaryote-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantamonadida
The Mantamonadidae are of Motility, free-living heterotrophic flagellates that move primarily by gliding on surfaces (rather than swimming). There is one genus, ''Mantamonas''. It has been suggested previously that the Mantamonadidae be classified in Apusozoa as sister of the Apusomonadida, Apusmonadida on the basis of Ribosomal RNA, rRNA analyses. However, mantamonads are currently placed in CRuMs on the basis of phylogenomic analyses that identify their closest relatives as the collodictyonids (=diphylleids) and ''Rigifila''. Taxonomy * Order Mantamonadida Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 ** Family Mantamonadidae Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 *** Genus ''Mantamonas'' Cavalier-Smith Glücksman et al. 2011 **** Species ''Mantamonas plastica'' Cavalier-Smith & Glücksman 2011 Phylogeny References Podiata orders {{eukaryote-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRuMs
CRuMs is a proposed clade of microbial eukaryotes, whose name is an acronym of the following constituent groups: i) collodictyonids also known as diphylleids, ii) rigifilids and iii) mantamonadids as sister of the Amorphea. It more or less supersedes Varisulca, as Ancyromonadida Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated protists found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and ... are inferred not to be specifically related to the orders Collodictyonida, Rigifilida and Mantamonadida. Phylogeny References {{Taxonbar, from=Q59153571 Eukaryote subphyla Podiata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collodictyonidae
Collodictyonidae (also Diphylleidae) is a group of aquatic, unicellular eukaryotic organisms with two to four terminal flagella. They feed by phagocytosis, ingesting other unicellular organisms like algae and bacteria. The most remarkable fact of this clade is its uncertain position in the tree of life. Recent molecular analyses place Collodictyonids (e.g. Collodictyon) in a clade also containing Rigifilida and Mantamonadidae. This clade has been named CRuMs and is sister to Amorphea. Phylogeny Taxonomy * Class Diphyllatea Cavalier-Smith 2003 nisomonadea; Diphyllatia Cavalier-Smith 2003** Order Diphylleida Cavalier-Smith 1993 ollodictyonida *** Family Sulcomonadidae Cavalier-Smith 2012 **** Genus '' Sulcomonas'' Brugerolle 2006 ***** Species ''S. lacustris'' Brugerolle 2006 *** Family Diphylleidae Cavalier-Smith 1993 ollodictyonidae Brugerolle et al. 2002**** Genus ''Diphylleia'' Massart 1920 non Michaux 1803 'Aulacomonas'' Skuja 1939">Aulacomonas.html" ;"title="'Aula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusozoa
The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presence of an organic shell or theca under the dorsal surface of the cell. The name derives from the Ancient Greek words for footless () and animal (). This phylum is currently defined as containing the Breviata and the Apusomonadida. However, it currently usually is viewed as paraphyletic, with the Breviata as more basal. The opisthokonts appear to have emerged as sister of the apusomonadida. It has been suggested that the Mantamonadida be classified in Apusozoa. The ancyromonadida appear to be Varisulca, Planomonadida, shifting them possibly more basal than the Amoebozoa, or less basal. While some classification systems have placed Hemimastigida in Apusozoa, 2018 research indicated that hemimastigotes (/Hemimastix/Spironemidae) are thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphea
Amorphea are members of a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. The International Society of Protistologists, the recognised body for taxonomy of protozoa, recommended in 2012 that the term Unikont be changed to Amorphea because the name "Unikont" is based on a hypothesized synapomorphy that the ISP authors and other scientists later rejected. It includes amoebozoa, opisthokonts, and possibly Apusozoa. Taxonomic revisions within this group Cavalier-Smith has proposed two new phyla: Sulcozoa, which consists of the subphyla Apusozoa ( Apusomonadida and Breviatea), and Varisulca, which includes the subphyla Diphyllatea, Discocelida, Mantamonadidae, Planomonadida and Rigifilida. The validity of this propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigifilida
Rigifilida is a clade of non-ciliate phagotrophic eukaryotes. It consists of two genera: ''Micronuclearia'' and '' Rigifila''. Characteristics Cells of rigifilids are covered with either a single or a double-layered submembrane pellicular lamina that makes them rigid in consistence. Slender branching filopodia emanate from a ventral aperture of the cell and are employed to collect bacteria upon which they feed and to attach the organism to the substratum. Around this aperture, the pellicle is reflexed around forming a peristomial collar. Other notable features are flat and irregular shaped mitocondrial cristae, a single dorsal nucleus and the lack of centrioles and cilia. Phylogeny Taxonomy Rigifilida is currently placed in CRuMs. *Order Rigifilida Cavalier-Smith 2012 icronucleariida Cavalier-Smith 2008** Family Rigifilidae Yabuki & Cavalier-Smith 2012 *** Genus '' Rigifila'' Yabuki & Cavalier-Smith 2012 **** Species '' Rigifila ramosa'' Yabuki & Cavalier-Smith 2012 ** Fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malawimonadea
Malawimonadidae is a group of unicellular eukaryotes of outsize importance in understanding eukaryote phylogeny. Phylogeny Taxonomy * Phylum Neolouka Cavalier-Smith 2013 ** Class Malawimonadea Cavalier-Smith 2003 *** Order Malawimonadida Cavalier-Smith 2003 **** Family Malawimonadidae O’Kelly & Nerad 1999 ***** Genus '' Gefionella'' Heiss, Ekelund & Simpson 2018 ****** Species '' G. okellyi'' Heiss, Ekelund & Simpson 2018 ***** Genus ''Malawimonas ''Malawimonas'' is a Loukozoa genus, possible sister of the Podiata. History of the discovery of Malawimonads In 1993, Charles J O’ Kelly studied the jakobid groups flagellates and implications for the early diversification of eukaryotes and ...'' O’Kelly & Nerad 1999 ****** Species '' M. californiana'' ****** Species '' M. jakobiformis'' O’Kelly & Nerad 1999 References Excavata families {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
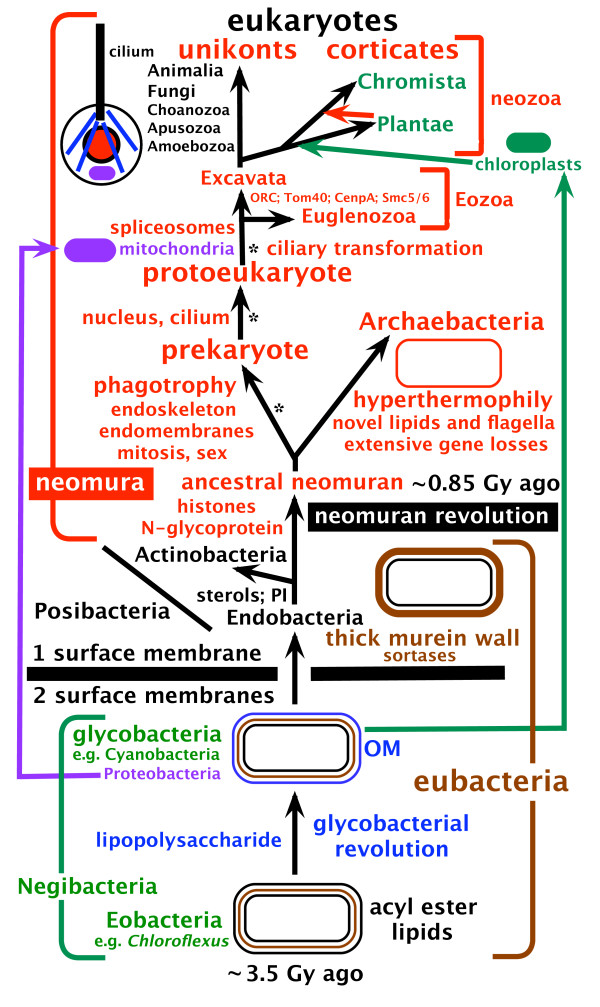
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as "dinoflagellate" and "choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms that do not possess a means of self-locomotion and are normally immobile. Motility differs from mobility, the ability of an object to be moved. The term vagility encompasses both motility and mobility; sessile organisms including plants and fungi often have vagile parts such as fruits, seeds, or spores which may be dispersed by other agents such as wind, water, or other organisms. Motility is genetically determined, but may be affected by environmental factors such as toxins. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system provide the majority of mammalian motility. In addition to animal locomotion, most animals are motile, though some are vagile, described as having passive locomotion. Many bacteria and other microorganisms, and multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |