|
Ametrida
The little white-shouldered bat (''Ametrida centurio'') is a species of bat from South and Central America. It is the only species within its genus, the name of which translates as "reaper" or "destroyer". Description The little white-shouldered bat is a small phyllostomid bat, with males measuring and females in total length. The fur is generally brown, being paler underneath, and on the forequarters. As the common name suggests, both sexes have a spot of pure white fur on the shoulders near the base of the neck. The wings are also brown, and the uropatagium is hairy; the bats do not possess an external tail. The head has a relatively short, broad snout, with a wide mouth, and a simple, spear-like nose-leaf. The ears are small and triangular, and the eyes large and bulging, with a yellow iris. Distribution and habitat Little white-shouldered bats are found throughout Venezuela, the Guyanas, on the island of Trinidad, and in eastern Colombia, north and central Brazil, and sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), and has a population of 52 million. Colombia's cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a Spanish colony, fusing cultural elements brought by immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by enslaved Africans, as well as with those of the various Amerindian civilizations that predate colonization. Spanish is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Colombia
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Brazil
Bats are mammals of the Order (biology), order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, Bat flight, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin skin, membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the Flying fox#Physical characteristics, flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the Animal echolocation, echolocating microbats. But more r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of South America
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
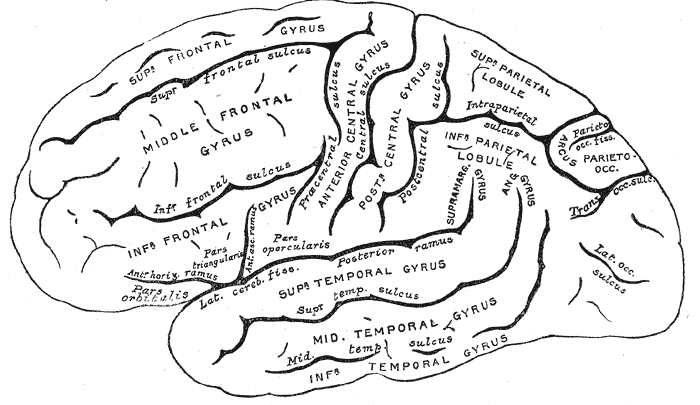
Sulcus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. ''sulci'') is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures. Structure Sulci, the grooves, and gyri, the folds or ridges, make up the folded surface of the cerebral cortex. Larger or deeper sulci are termed fissures, and in many cases the two terms are interchangeable. The folded cortex creates a larger surface area for the brain in humans and other mammals. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex, but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes and also into the two hemispheres as the longitudinal fissure. Importance of expanded surface area As the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum prenatal development, develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric Lateralization of brain function, left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC islands, 80 km (50 miles) off the coast of Venezuela. Unlike much of the Caribbean region, the ABC islands lie outside Hurricane Alley. The islands have an arid climate that attracts visitors seeking warm, sunny weather all year round. Bonaire is a popular snorkeling and scuba diving destination because of its multiple shore diving sites and easy access to the island's fringing reefs. As of 1 January 2019, the island's population totaled 20,104 permanent residents, an increase of about 1,200 since 2015. The island's total land area is ; it is long from north to south, and ranges from wide from east to west. A short west of Bonaire across the sea is the uninhabited islet Klein Bonaire with a total land area of . Klein Bonaire has l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's million people. Panama was inhabited by indigenous tribes before Spanish colonists arrived in the 16th century. It broke away from Spain in 1821 and joined the Republic of Gran Colombia, a union of Nueva Granada, Ecuador, and Venezuela. After Gran Colombia dissolved in 1831, Panama and Nueva Granada eventually became the Republic of Colombia. With the backing of the United States, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, allowing the construction of the Panama Canal to be completed by the United States Army Corps of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of , it is also the List of Caribbean islands by area, fifth largest in the West Indies. Name The original name for the island in the Arawak language, Arawaks' language was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Holy Trinity, Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. History Island Caribs, Caribs and Arawaks lived in Trinidad long before Christopher Columbus encountered the islands on his third voyage on 31 July 1498. The island remained Spanish until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists from the French Caribbean, especially Martinique.Besson, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |