|
Agriculture In Belarus
Agriculture in Belarus can be divided into two segments: livestock production and crop production. Crop production slightly outweighs livestock production in the country's product mix, accounting for around 55% of gross agricultural output since 1995. Agriculture accounted for 7.9% GDP in 2013, while over the same year that sector accounted for only 3% GDP in the EU. Products of animal origin are mainly pork, beef, and poultry. Belarus has about 1.5 million cows, but the milk yields are relatively low (less than 3,000 kg per cow per year). Belarus's main crop products are barley, rye, oats, and wheat, as well as potatoes, flax, rapeseed, and sugarbeets. Cereals and legumes (mainly barley and rye) take up 41% of sown area and another 43% is under crops used for animal feed. Potatoes and vegetables take up 11% of sown area and industrial crops (sugarbeets, flax, and some rapeseed) the remaining 4%. Synopsis Belarus has been characterized by some as a slow land reformer com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus Cattle
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Covering an area of and with a population of 9.4 million, Belarus is the 13th-largest and the 20th-most populous country in Europe. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into seven regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city. Until the 20th century, different states at various times controlled the lands of modern-day Belarus, including Kievan Rus', the Principality of Polotsk, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and the Russian Empire. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution in 1917, different states arose competing for legitimacy amid the Civil War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Farm
A family farm is generally understood to be a farm owned and/or operated by a family; it is sometimes considered to be an Estate (land), estate passed down by inheritance. Although a recurring conceptual model, conceptual and archetype, archetypal distinction is that of a family farm as a smallholding versus corporate farming as large-scale agribusiness, that notion does not accurately describe the realities of farm ownership in many countries. Family farm businesses can take many forms, from smallholder farms to larger farms operated under intensive farming practices. In various countries, most farm families have structured their farm businesses as corporations (such as limited liability company, limited liability companies) or trust (business), trusts, for liability, tax, and business purposes. Thus, the idea of a family farm as a unitary concept or definition does not easily translate across languages, cultures, or centuries, as there are substantial differences in agricultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and seeds. An alternative definition of the term is applied somewhat arbitrarily, often by culinary and cultural tradition. It may exclude foods derived from some plants that are fruits, flowers, nuts, and cereal grains, but include savoury fruits such as tomatoes and courgettes, flowers such as broccoli, and seeds such as pulses. Originally, vegetables were collected from the wild by hunter-gatherers and entered cultivation in several parts of the world, probably during the period 10,000 BC to 7,000 BC, when a new agricultural way of life developed. At first, plants which grew locally would have been cultivated, but as time went on, trade brought exotic crops from elsewhere to add to domestic types. Nowadays, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B. oleracea'' var. ''oleracea''), and belongs to the "cole crops" or brassicas, meaning it is closely related to broccoli and cauliflower (var. ''botrytis''); Brussels sprouts (var. ''gemmifera''); and Savoy cabbage (var. ''sabauda''). A cabbage generally weighs between . Smooth-leafed, firm-headed green cabbages are the most common, with smooth-leafed purple cabbages and crinkle-leafed savoy cabbages of both colours being rarer. Under conditions of long sunny days, such as those found at high northern latitudes in summer, cabbages can grow quite large. , the heaviest cabbage was . Cabbage heads are generally picked during the first year of the plant's life cycle, but plants intended for seed are allowed to grow a second year and must be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ''Malus sieversii'', is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonization of the Americas, European colonists. Apples have Religion, religious and mythology, mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse mythology, Norse, Greek mythology, Greek, and Christianity in Europe, European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after plantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triticale
Triticale (; × ''Triticosecale'') is a hybrid of wheat (''Triticum'') and rye (''Secale'') first bred in laboratories during the late 19th century in Scotland and Germany. Commercially available triticale is almost always a second-generation hybrid, i.e., a cross between two kinds of primary (first-cross) triticales. As a rule, triticale combines the yield potential and grain quality of wheat with the disease and environmental tolerance (including soil conditions) of rye. Only recently has it been developed into a commercially viable crop. Depending on the cultivar, triticale can more or less resemble either of its parents. It is grown mostly for forage or fodder, although some triticale-based foods can be purchased at health food stores and can be found in some breakfast cereals. When crossing wheat and rye, wheat is used as the female parent and rye as the male parent (pollen donor). The resulting hybrid is sterile and must be treated with colchicine to induce polyploidy an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is a refined form of sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars, and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human food. Some other chemical substances, such as glycerol and sugar alcohols, may have a sweet taste, but are not classified as sugar. Sugars are found in the tissues of most plants. Honey and fruits are abundant natural sources of simple sugars. Suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris.'' Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima''). Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugar cane. The low sugar content of the beets makes growing them a marginal proposition unless prices are relatively high. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
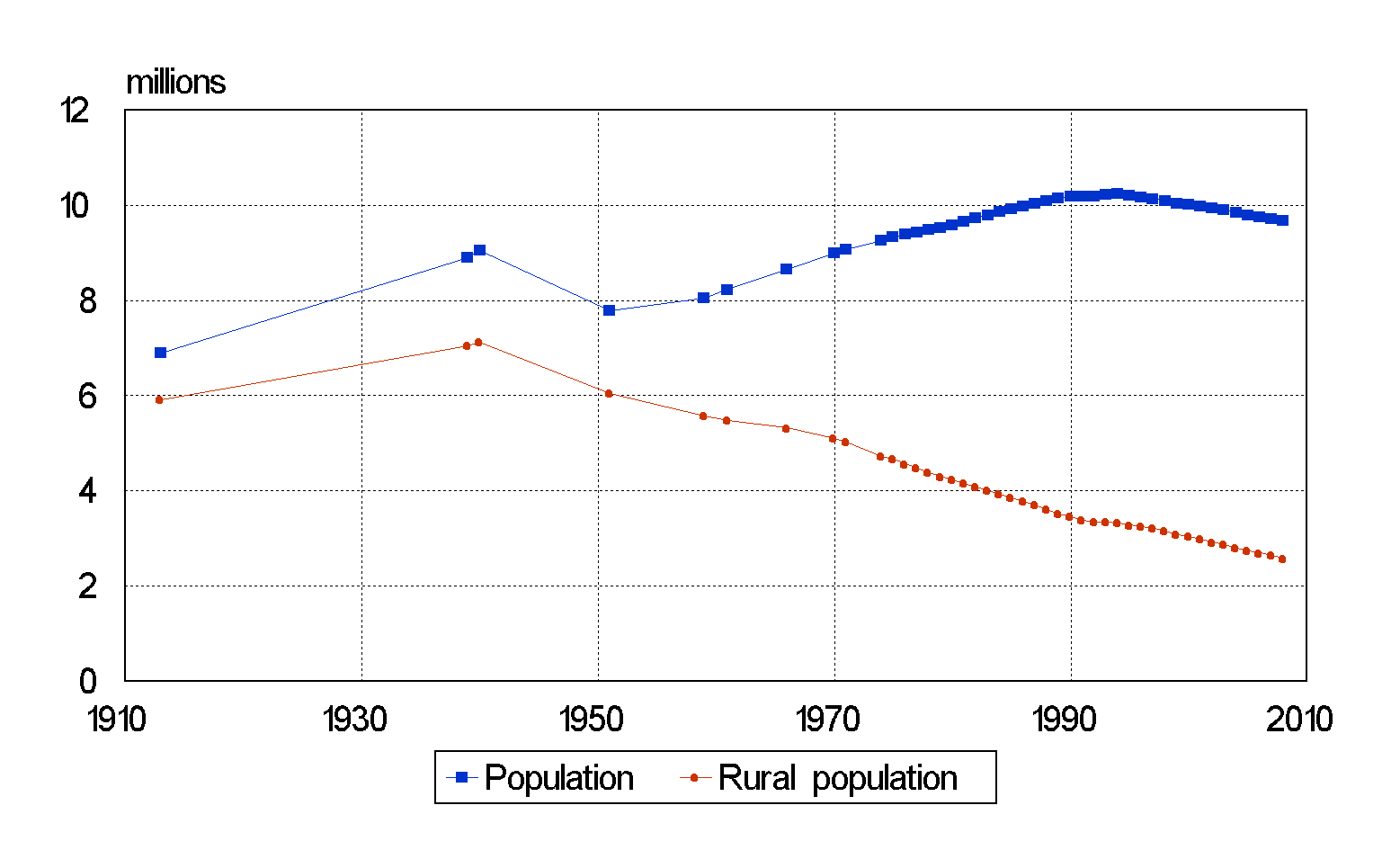
Demographics Of Belarus
The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the population of Belarus, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population. Population The population of Belarus suffered a dramatic decline during World War II, dropping from more than 9 million in 1940 to 7.7 million in 1951. It then resumed its long-term growth, rising to 10 million in 1999. After that the population began a steady decline, dropping to 9.7 million in 2006–2007.Population estimates 1995–2007 , BelStat Originally a highly agrarian country with nearly 80% of its population in rural areas, Belarus has been undergoing a process of continuous |
Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas. Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth. Urbanization refers to the ''proportion'' of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the ''absolute'' number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050 about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. That is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |