|
Arthur Forbes (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Arthur Forbes (died 20 March 1891) was a Royal Navy officer who became Commander-in-Chief, Queenstown. Naval career Forbes became commanding officer of the sixth-rate HMS ''Calypso'' in July 1851, commanding officer of the frigate HMS ''Curacoa'' in May 1857 and commanding officer of the second-rate In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer gun ... HMS ''Renown'' in November 1857. His last appointment was as Commander-in-Chief, Queenstown in November 1869 before he retired in May 1871. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Forbes, Arthur 1891 deaths Royal Navy admirals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral (Royal Navy)
Admiral is a senior rank of the Royal Navy, which equates to the NATO rank code OF-9, outranked only by the rank of admiral of the fleet. Royal Navy officers holding the ranks of rear admiral, vice admiral and admiral of the fleet are sometimes considered generically to be admirals. The rank of admiral is currently the highest rank to which a serving officer in the Royal Navy can be promoted, admiral of the fleet being in abeyance except for honorary promotions of retired officers and members of the Royal Family. The equivalent rank in the British Army and Royal Marines is general; and in the Royal Air Force, it is air chief marshal. History The first admirals (1224 to 1523) King Henry III of England appointed the first known English Admiral Sir Richard de Lucy on 29 August 1224. De Lucy was followed by Sir Thomas Moulton in 1264, who also held the title of ''Keeper of the Sea and Sea Ports''. Moulton was succeeded by Sir William de Leybourne, (the son of Sir Roger de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Calypso (1845)
The following ships of the Royal Navy were assigned the name ''Calypso'', after Calypso, a sea nymph in Greek mythology: * , a 16-gun sloop of 342 tons burthen, launched at Graves, Deptford 27 September 1783. She sank during a violent storm on 30 July 1803 with the loss of all her crew when a heavily laden West Indiaman ran afoul of her. * , an 18-gun sloop of the launched at Dudman, Deptford Wharf 2 February 1805; not broken up until 1821. * , a 10-gun . Ordered 1824 for construction at Deptford Dockyard; renamed ''Hyaena'' in 1826; and cancelled 21 February 1831. * ''Calypso'' was to be a 10-gun brig-sloop of the ''Cherokee'' class. Laid down March 1825 at Chatham Dockyard as HMS ''Hyaena''; launched 19 August 1826 and renamed ''Calypso'' that same year; completed as a yacht for the governor of Malta. Later she became a Post Office packet service brig for Royal Navy. She sailed from Halifax, Nova Scotia for Falmouth, Cornwall on 29 January 1833, under the command of Lieutenan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Curacoa (1854)
HMS ''Curacoa'' was a 31-gun ''Tribune''-class screw frigate launched on 13 April 1854 from Pembroke Dockyard. She served in the Mediterranean Station between 1854 until 1857 and was in the Black Sea during the Crimean War. She was part of the Channel Squadron between 1857 until 1859. On 24 October 1858, ''Curacoa'' ran aground on the Pelican Reef, off Smyrna, Ottoman Empire. All onboard were rescued. She was refloated on 26 October with assistance from and taken into Smyrna on 28 October. On 4 February 1859, ''Curacoa'' collided with the British merchant ship ''Fleta'' in the English Channel. She then was sent to North America and West Indies Station and served between 1859 until 1862. Afterward, she went to the Australia Station, where she remained until 1866. She was the flagship of the Australia Station from 20 April 1863 until May 1866, having had her armament reduced to 23 guns in 1863. Curacoa Island, off the Queensland coast, is named after HMS Curacoa (1854) Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Renown (1857)
Eight ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name ''Renown'', whilst three others have borne the name at various stages in their construction: * was a 20-gun fireship, previously the . She was captured in 1651 by and sold in 1654. * was a 30-gun fifth rate, previously the French ship ''Renommée''. She was captured in 1747 by and broken up in 1771. * was a 50-gun fourth rate launched in 1774 and broken up in 1794. * was a 74-gun third rate launched in 1798. She had been built under the name HMS ''Royal Oak'', but was renamed in 1796. She was on harbour service from 1814 and was broken up in 1835. * was a 91-gun second rate launched in 1857 and sold to Prussia in 1870. * HMS ''Renown'' was to have been a , but she was renamed in 1887 and launched later that year. * HMS ''Renown'' was to have been a but she was renamed in 1890 and launched in 1891. * was a unique battleship launched in 1895 and sold for scrap in 1914. * HMS ''Renown'' was to have been a but she was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander-in-Chief, Coast Of Ireland
The Commander-in-Chief, Coast of Ireland was both an admiral's post and a naval formation of the Royal Navy. It was based at Queenstown, now Cobh, in Ireland from 1797 to 1919. The admiral's headquarters was at Admiralty House, Cobh. History The French Revolutionary Wars led to Cobh, then usually known as Ballyvoloon or The Cove of Cork, being developed as a British naval port, and assigned an admiral. The first appointment of an "Admiral Commanding in Ireland" or "Commander-in-Chief, Cork" was in 1797. The post remained unfilled between 1831 and 1843. It was renamed "Commander-in-Chief, Queenstown" in 1849 following a visit by Queen Victoria during which she renamed the town of Cobh "Queenstown". The post became "Senior Officer on the Coast of Ireland" in 1876. The full title of the incumbent following the establishment of the post of Admiral Commanding, Coastguard and Reserves in 1903 was Senior Officer on the Coast of Ireland and Deputy to the Admiral Commanding Coastguard a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck officers were the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
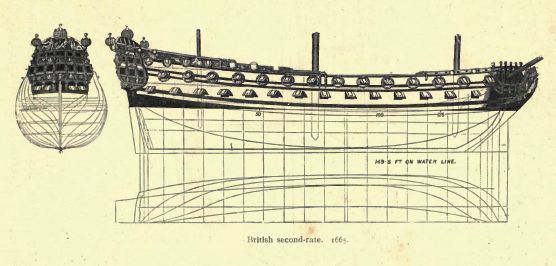
Second-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Warden
Rear Admiral Frederick Warden CB (18 November 1807 – 11 November 1869) was a Royal Navy officer who went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Channel Squadron. Naval career Warden joined the Royal Navy as a cadet in 1820. He served off the coast of Syria during the Oriental Crisis in 1840. Promoted to captain in 1845, he was given command of HMS ''Retribution'' in 1850 and then HMS ''Ajax'' which was used as mobile maritime battery in the Baltic Sea during the Crimean War. He later commanded HMS ''Hibernia'' and then HMS ''Redpole''. He was appointed Commander-in-Chief, Channel Squadron in 1867 and Commander-in-Chief, Queenstown in December 1868. He arrived from Lisbon to take command at Queenstown aboard HMS ''Helicon'', despatch vessel, on 28 December 1868. He died in office in Queenstown on 11 November 1869. He lived at Barham Lodge in Weybridge Weybridge () is a town in the Borough of Elmbridge in Surrey, England, around southwest of central London. The settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Heathcote
Admiral Edmund Heathcote (29 January 1814 – 24 October 1881) was a Royal Navy officer who became Commander-in-Chief, Queenstown. Early life Heathcote was born in Hursley, Hampshire, England. He was the fourth son of Samuel Heathcote and Catherine Pickering. On 14 July 1844, in St. John's, Newfoundland, Edmund married his first wife, Elizabeth Lucy Law with whom he had two sons. In 1850, Lucy bore a third child, whose father was not Edmund; the couple were divorced on 9 March 1851, and Lucy appears to have taken their elder son, William (1845-1884), as well as her young child, to Australia, where her child's father had been transported for seven years penal servitude; William and Lucy both died in Australia. On 19 August 1852, Edmund married Jessie Hill, at St. Paul's Cathedral in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Very soon thereafter, the couple returned to England and settled in Fritham, Hampshire, where their three children were born. Naval career Heathcote became commanding officer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1891 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 ** Paying of old age pensions begins in Germany. ** A strike of 500 Hungarian steel workers occurs; 3,000 men are out of work as a consequence. **Germany takes formal possession of its new African territories. * January 2 – A. L. Drummond of New York is appointed Chief of the Treasury Secret Service. * January 4 – The Earl of Zetland issues a declaration regarding the famine in the western counties of Ireland. * January 5 **The Australian shearers' strike, that leads indirectly to the foundation of the Australian Labor Party, begins. **A fight between the United States and Indians breaks out near Pine Ridge agency. ** Henry B. Brown, of Michigan, is sworn in as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court. **A fight between railway strikers and police breaks out at Motherwell, Scotland. * January 6 – Encounters continue, between strikers and the authorities at Glasgow. * January 7 ** General Miles' force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)