|
Ardennes Offensive - Operation
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel; both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian (382.7 to 387.7 million years ago), as were several other named ranges of the same greater range. The Ardennes proper stretches well into Germany and France (lending its name to the Ardennes department and the former Champagne-Ardenne region) and geologically into the Eifel (the eastern extension of the Ardennes Forest into Bitburg-Prüm, Germany); most of it is in the southeast of Wallonia, the southern and more rural part of Belgium (away from the coastal plain but encompassing more than half of the country's total area). The eastern part of the Ardennes forms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semois
The Semois (; ''Simwès'' in Walloon, often under elided form ''Smwès''; ''Semoy'', ''Sesbach'' in German, ''Setzbaach'' in Luxemburgish of Arlon; and known as the ''Semoy'' in France) is a river flowing from the Ardennes uplands of Belgium and France towards the Meuse, of which it is a right tributary. The source of the Semois is in Arlon, Wallonia, in the Belgian province of Luxembourg, close to the border with the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Flowing in a roughly westerly direction, it enters France after passing through the Belgian village of Bohan-sur-Semois and forms about of the Belgian–French border. It joins the Meuse further downstream in Monthermé. The total length of the river is . Other places on the banks of the Semois are Chiny, Florenville, Herbeumont, Bouillon (including the localities of Dohan and Poupehan), and Vresse-sur-Semois Vresse-sur-Semois (, literally ''Vresse on Semois''; wa, Vresse) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitburg-Prüm
The Eifelkreis Bitburg-Prüm ( lb, Äifelkrees Béibreg-Prüm) is a district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) Luxembourg, Belgium and the districts of Euskirchen, Vulkaneifel, Bernkastel-Wittlich and Trier-Saarburg. History There are three different historical regions: the abbey and the city of Prüm have been directly subordinate to the Holy Roman Emperor in medieval times; later the free city became the principality of Prüm, occupying large portions in the north. The southwest including the town of Bitburg was a part of the Duchy of Luxemburg from the 10th to the 15th century. Later it was a part of the Seventeen Provinces and hence under Spanish and then Austrian rule. After the Napoleonic Wars the region was handed over to Prussia. The eastern parts of the district, including the town of Kyllburg, were part of the Prince-bishopric of Trier. When Prussia gained all these regions about 1815, it established the three district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal De Botrange
Signal de Botrange is the highest point in Wallonia and in Belgium, located in the ''High Fens'' (''Hautes Fagnes'' in French, ''Hohes Venn'' in German, ''Hoge Venen'' in Dutch), at . It is the top of a broad plateau and a road crosses the summit, passing an adjacent café. It is also the highest point in the Ardennes and in the European part of the Benelux. For several decades a meteorological station was installed at signal de Botrange. Since 1999, it was replaced by an automatic station of the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium installed on Mount Rigi (scientific station of the High Fens - University of Liège), which is between the Signal and Baraque Michel which was formerly the highest point in Belgium prior to the annexation of the Eastern Cantons in 1919. Signal de Botrange experiences stronger winds than the centre of Belgium. Average and extreme temperatures are usually lower than at any other place in Belgium: the minimum temperature recorded () does not, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastogne
Bastogne (; nl, Bastenaken, ; german: Bastnach/Bastenach; lb, Baaschtnech) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Luxembourg in the Ardennes, Belgium. The municipality consists of the following districts: Bastogne, Longvilly, Noville, Villers-la-Bonne-Eau, and Wardin. The town is situated on a ridge in the Ardennes at an elevation of . History At the time of the Roman conquest the region of Bastogne was inhabited by the Treveri, a tribe of Gauls. A form of the name Bastogne was first mentioned only much later, in 634, when the local lord ceded these territories to the St Maximin's Abbey, near Trier. A century later, the Bastogne area went to the nearby Prüm Abbey. The town of Bastogne and its marketplace are again mentioned in an 887 document. By the 13th century, Henry VII, Holy Roman Emperor and count of Luxemburg, was minting coins in Bastogne. In 1332, John the Blind, his son, granted the city its charter and had it encircled by defensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupen
Eupen (, ; ; formerly ) is the capital of German-speaking Community of Belgium and is a city and municipality in the Belgian province of Liège, from the German border (Aachen), from the Dutch border (Maastricht) and from the "High Fens" nature reserve (Ardennes). The town is also the capital of the Euroregion Meuse-Rhine. First mentioned in 1213 as belonging to the Duchy of Limburg, possession of Eupen passed to Brabant, Burgundy, the Holy Roman Empire and France before being given in 1815 to Prussia, which became part of the new German Empire in 1871. In 1919, after the First World War, the Treaty of Versailles transferred Eupen and the nearby municipality of Malmedy from Germany to Belgium. German remains the official language in Eupen (also spoken in the form of the Eupen dialect), and the city serves as the capital for Belgium's German-speaking Community. The city has a small university, the ', offering bachelor's degrees in Education and Nursing. In 2010, Eupen's ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charleville-Mézières
or ''Carolomacérienne'' , image flag=Flag of Charleville Mezieres.svg Charleville-Mézières () is a commune of northern France, capital of the Ardennes department, Grand Est. Charleville-Mézières is located on the banks of the river Meuse. History Charleville and Mézières were originally separate communities on opposite banks of the Meuse, about from one another. Charleville was founded by Charles Gonzaga, the 8th duke of Mantua, in 1606. Its inhabitants were known as Carolopolitans (' or ''Carolopolitaines''). It was prosperous from the 17th century, although its fortifications were dismantled under LouisXIV in 1687 and it passed into French hands in 1708. It was plundered by the Prussians in 1815. France's royal armaments factory was formerly located there and gave its name to the Charleville musket, before being relocated and divided between Tulle and Châtellerault. In the 19th century, the city continued to produce arms through private firms, as well as nails, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verviers
Verviers (; wa, Vervî) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium. The municipality consists of the following districts: Ensival, Heusy, Lambermont, Petit-Rechain, Stembert, and Verviers. It is also the center of an agglomeration that includes Dison and Pepinster, making it the second biggest in the province and an important regional center, located roughly halfway between Liège and the German border. Water has played an important role in the town's economy, notably in the development first of its textile and later its tourist industries. As a result, many fountains have been built in Verviers, leading it to be named Wallonia's "Water Capital". The seats of the two Walloon public institutions for water distribution and water treatment are located in the town. History Early history Various flint and bone fragments, as well as Roman coins, were found in this area, attesting to the early settlements in the region. In the 4th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Fens
The High Fens (german: Hohes Venn; french: Hautes Fagnes; nl, Hoge Venen), which were declared a nature reserve in 1957, are an upland area, a plateau region in Liège Province, in the east of Belgium and adjoining parts of Germany, between the Ardennes and the Eifel highlands. The High Fens are the largest nature reserve or park in Belgium, with an area of ; it lies within the German-Belgian natural park ''Hohes Venn-Eifel'' (), in the Ardennes. Its highest point, at above sea level, is the Signal de Botrange near Eupen, and also the highest point in Belgium. A tower high was built here that reaches above sea level. The reserve is a rich ecological endowment of Belgium covered with alpine sphagnum raised bogs (not "fens" as the name would imply) both on the plateau and in the valley basin; the bogs, which are over 10,000 years old, with their unique subalpine flora, fauna and microclimate, are key to the conservation work of the park. In 1966, the European Council awarded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
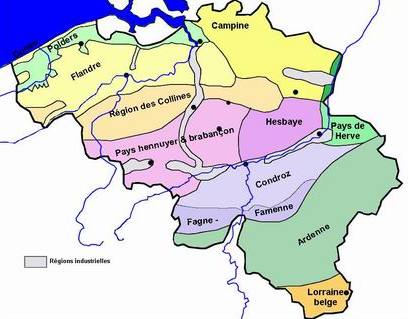
Régions Naturelles De Belgique
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collectivities, which have a semi-autonomous status). All of the thirteen metropolitan administrative regions (including Corsica ) are further subdivided into two to thirteen administrative departments, with the prefect of each region's administrative centre's department also acting as the regional prefect. The overseas regions administratively consist of only one department each and hence also have the status of overseas departments. Most administrative regions also have the status of regional territorial collectivities, which comes with a local government, with departmental and communal collectivities below the region level. The exceptions are Corsica, French Guiana, Mayotte and Martinique, where region and department functions are managed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardennen Mit Eifel
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel; both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian (382.7 to 387.7 million years ago), as were several other named ranges of the same greater range. The Ardennes proper stretches well into Germany and France (lending its name to the Ardennes department and the former Champagne-Ardenne region) and geologically into the Eifel (the eastern extension of the Ardennes Forest into Bitburg-Prüm, Germany); most of it is in the southeast of Wallonia, the southern and more rural part of Belgium (away from the coastal plain but encompassing more than half of the country's total area). The eastern part of the Ardennes forms the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals; that is, the way in which science is applied to the production of metals, and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)