|
Andrey Gorchakov
Gorchakov, or Gortchakoff (russian: Горчако́в), is a Russian princely family of Rurikid stock that is descended from the Rurikid sovereigns of Peremyshl, Russia. Aleksey Gorchakov The family first achieved prominence during the reign of Catherine II. Prince Aleksey Ivanovich (1769–1817) served with distinction under his uncle Suvorov in the Turkish Wars, and took part as a general officer in the Italian and Swiss operations of 1799, and in the war against Napoleon in Poland in 1806–1807 (Battle of Heilsberg). He succeeded Barclay de Tolly as the Minister of War in 1813. His brother Andrei Ivanovich Gorchakov (1776–1855) was a general in the Russian army who took a conspicuous part in the final campaigns against Napoleon. Their cousin Princess Pelageya Nikolayevna Gorchakova (1762–1838) was fictionalized by her grandson Leo Tolstoy in '' War and Peace''. Pyotr Gorchakov Prince Peter Dmitrievich Gorchakov (1790–1868) served under Mikhail Kamensky and Mikhail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorchakov Arms
Gorchakov, or Gortchakoff (russian: Горчако́в), is a Russian princely family of Rurikid stock that is descended from the Rurikid sovereigns of Peremyshl, Russia. Aleksey Gorchakov The family first achieved prominence during the reign of Catherine II. Prince Aleksey Ivanovich (1769–1817) served with distinction under his uncle Suvorov in the Turkish Wars, and took part as a general officer in the Italian and Swiss operations of 1799, and in the war against Napoleon in Poland in 1806–1807 (Battle of Heilsberg). He succeeded Barclay de Tolly as the Minister of War in 1813. His brother Andrei Ivanovich Gorchakov (1776–1855) was a general in the Russian army who took a conspicuous part in the final campaigns against Napoleon. Their cousin Princess Pelageya Nikolayevna Gorchakova (1762–1838) was fictionalized by her grandson Leo Tolstoy in ''War and Peace''. Pyotr Gorchakov Prince Peter Dmitrievich Gorchakov (1790–1868) served under Mikhail Kamensky and Mikhail Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Kamensky
Count Mikhail Fedotovich Kamensky (russian: Михаи́л Федо́тович Каме́нский; 19 May 1738 – 12 August 1809) was a Russian Field Marshal prominent in the Catherinian wars and the Napoleonic campaigns. Biography Mikhail Kamensky served as a volunteer in the French army in 1758-1759. He then took part in the Seven Years' War. In 1783, Kamensky was appointed Governor General of Ryazan and Tambov guberniyas. During the war with Turkey, in 1788, he defeated the Turks at the Moldavian settlement of Gangur. When prince Potemkin fell ill and entrusted his command of the army to Mikhail Kakhovsky, Kamensky refused to subordinate himself, referring to his seniority. For this, he was discharged from military service. In 1797, Emperor Paul I granted Kamensky the title of count and made him retire. In 1806, Kamensky was appointed commander-in-chief of the Russian army in Prussia, which had been fighting the French armies of Napoleon. After six days of being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Central and Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later autonomous state, it existed from the 14th century to 1859, when it united with Wallachia () as the basis of the modern Romanian state; at various times, Moldavia included the regions of Bessarabia (with the Budjak), all of Bukovina and Hertsa. The region of Pokuttya was also part of it for a period of time. The western half of Moldavia is now part of Romania, the eastern side belongs to the Republic of Moldova, and the northern and southeastern parts are territories of Ukraine. Name and etymology The original and short-lived reference to the region was ''Bogdania'', after Bogdan I, the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
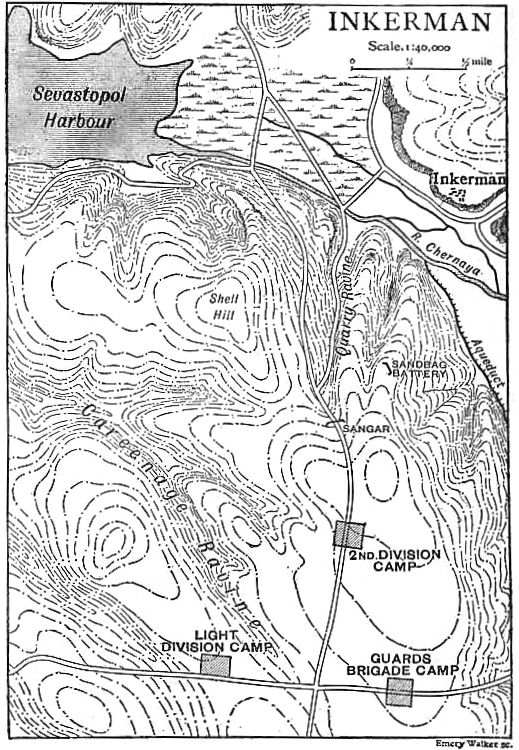
Battle Of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Britain and Second French Empire, France against the Imperial Russian Empire, Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and was followed by the Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855), siege of Sevastopol. The role of troops fighting mostly on their own initiative due to the foggy conditions during the battle has earned the engagement the name "The Soldier's Battle." Prelude to the battle The allied armies of Britain, France, Sardinia, and the Ottoman Empire had landed on the west coast of Crimea on 14 September 1854, intending to capture the Russian naval base at Sevastopol. The allied armies fought off and defeated the Russian Army at the Battle of Alma, forcing them to retreat in some confusion toward the River Kacha. While the allies could have taken this opportunity to attack Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Alma
The Battle of the Alma (short for Battle of the Alma River) was a battle in the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force (made up of French, British, and Ottoman forces) and Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20September 1854. The allies had made a surprise landing in Crimea on 14September. The allied commanders, Maréchal Jacques Leroy de Saint-Arnaud and Lord Raglan, then marched toward the strategically important port city of Sevastopol, away. Russian commander Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov rushed his available forces to the last natural defensive position before the city, the Alma Heights, south of the Alma River. The allies made a series of disjointed attacks. The French turned the Russian left flank with an attack up cliffs that the Russians had considered unscalable. The British initially waited to see the outcome of the French attack, then twice unsuccessfully assaulted the Russians' main position on their right. Eventually, superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Russia
Nicholas I , group=pron ( – ) was List of Russian rulers, Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland. He was the third son of Paul I of Russia, Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I. Nicholas inherited his brother's throne despite the failed Decembrist revolt against him. He is mainly remembered in history as a reactionary whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, economic growth, and massive industrialisation on the one hand, and centralisation of administrative policies and repression of dissent on the other. Nicholas had a happy marriage that produced a large family; all of their seven children survived childhood. Nicholas's biographer Nicholas V. Riasanovsky said that he displayed determination, singleness of purpose, and an iron will, along with a powerful sense of duty and a dedication to very hard work. He saw himself as a soldier—a junior officer totally consumed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia. Geopolitical causes of the war included the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the expansion of the Russian Empire in the preceding Russo-Turkish Wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a disagreement over the rights of Christian minorities in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, with the French promoting the rights of Roman Catholics, and Russia promoting those of the Eastern Orthodox Church. The churches worked out their differences with the Ottomans and came to an agreement, but both the French Emperor Napoleon III and the Russian Tsar Nicholas I refused to back down. Nicholas issued an ultimatum that demanded the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman Empire be placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second capital city of the Ottoman Empire from 1369 to 1453, before Constantinople became its capital. The city is a commercial centre for woven textiles, silks, carpets and agricultural products and has a growing tourism industry. In 2019 its estimated population was 185,408. Edirne has an attractive location on the rivers Meriç and Tunca and has managed to withstand some of the unattractive development that mars the outskirts of many Turkish cities. The town is famous in Turkey for its liver. ''Ciğer tava'' (breaded and deep-fried liver) is often served with a side of cacık, a dish of diluted strained yogurt with chopped cucumber. Names and etymology The city was founded and named after the Roman emperor Hadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Von Wittgenstein
, title = 1st Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Ludwigsburg-Berleburg , image = Pjotr-christianowitsch-wittgenstein.jpg , image_size = , caption = Portrait by George Dawe , birth_date = , birth_place = Pereiaslav, Kiev Governorate, Russian Empire , death_date = , death_place = Lemberg, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, Austrian Empire , spouse = , issue = , mother = Countess Amalie Ludowika Finck von Finckenstein , father = Christian Louis Casimir, 2nd Count of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Ludwigsburg-Berleburg , house = Sayn-Wittgenstein , religion = Lutheranism , module = Louis Adolf Peter, 1st Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Ludwigsburg-Berleburg (german: Ludwig Adolf Peter Fürst zu Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg; russian: Пётр Христиа́нович Ви́тгенштейн, Pëtr Christiánovič Vítgenštejn; – 11 June 1843), better known as Peter Wittgenstein in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |