|
Ahmad Bin Ali Al-Ajmi
Sheikh Ahmad Al-Ajmi (Arabic: الشيخ أحمد بن علي بن محمد آل سليمان العجمي) is a Saudi Quran reciter and imam. Life Ahmad Al-Ajmi attended elementary school in the Al-Mohammadiya School in southern Khobar, went to middle school in Al-Zubair bin Al-Awwam Middle School, went to high school in Khobar Highschool in Khobar (specifically Madinat Al-Umal مدينة العمال) and after finishing high school, he went to Imam Muhammad ibn Saud Islamic University and graduated with a bachelor's degree in sharia. He married a woman from the Al-Badran family and has six children. Ethnicity Sheikh Al-Ajmi is Arab and not Ajami. His surname indicates that he belongs that to the Al Sulaiman branch of the Arab Ajman tribe Al-Ajman or al-'Ijman ( ar, العُجمان, singular Ajmi ar, العجمي) is an Arabian tribal confederation in the Arabian Peninsula, with Ajman spread across Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. Origin Al-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khobar
Khobar ( ar, ٱلْخُبَر, translit=al-Khobar) is a city and governorate in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, situated on the coast of the Persian Gulf. With a population of 457,748 as of 2017, Khobar is part of the 'Triplet Cities' area, or Dammam metropolitan area along with Dammam and Dhahran, forming the residential core of the region. The city was founded alongside Dammam by the Dawasir who moved there in 1923 fearing British persecution with the permission of King Abdulaziz Al Saud. Khobar experienced rapid growth during and after the discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia as it served as the port for the oil exports of Saudi Aramco in the company's early days. Traditionally, Khobar has also been a city of shopkeepers and merchants, and today has several shopping malls in and around it. The city is the newest in the Dammam metropolitan area, facing the Persian Gulf with its 16-km long Corniche Road, which runs parallel to the city's eastern coast. Khobar i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Arab world, and the largest in Western Asia and the Middle East. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. Bahrain is an island country off the east coast. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its capital and largest city is Riyadh. The country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam. Pre-Islamic Arabia, the territory that constitutes modern-day Saudi Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qāriʾ
A Qari (, ar, قَارِئ, plural ''qāriʾūn'', ''qurrāʾ'' or ''qaraʾah'') is a person who recites the Quran with the proper rules of recitation (''tajwid''). Although it is encouraged, a qāriʾ does not necessarily have to memorize the Quran, just to recite it according to the rules of tajwid with melodious sound. Notable Qāri The following list is a partial list of some notable reciters of the Qur'an: Afghanistan * Muhammad ibn Tayfour Sajawandi Bangladesh * Muhammad Ibrahim Ujani (1863–1943) * Abdul Latif Chowdhury Fultali (1913–2008) Iran * Hamed Shakernejad Egypt Reader is referred to as Shaykh al-Maqâriʾ (Arabic: شيخ المقارئ, lit. 'Scholar of the Recitation Schools'). * Muhammad Rifat (1882–1950) * Mohamed Salamah (1899–1982) *Mustafa Ismail (1905–1978) * Mahmoud Khalil Al-Hussary (1917–1980), Shaykh al-Maqâriʾ * Muhammad Siddiq Al-Minshawi (1920–1969), Shaykh al-Maqâriʾ * Kamil Yusuf Al-Bahtimi (1922–1969) *Abdul B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam. For most Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendents of the '' Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Twelver Shiasm there are 14 infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni Islam does not have imams in the same sense as the Shi'a, an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University
Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (), commonly known as Al-Imam University, is a public university in Baladiyah al-Shemal in northern Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. It was founded in 1953. represented by the College of Sharia Sciences (now known as the College of Sharia) and has developed since then until it became a university in 1974. The foundation stone of its current university building was laid on 5 January 1982 during the reign of King Khalid Ibn Abdul-Aziz Al Saud. It was opened in 1990. The university includes 14 colleges, 3 higher institutes, 70 scientific institutes inside the Kingdom, and five institutes outside the Kingdom in Indonesia and Djibouti. It currently has more than 60,000 students and 4,000 faculty members. History Imam Mohammad ibn Saud Islamic University was founded in 1973. The university was named after the emir of Diriyah and founder of First Saudi State, Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin. Colleges College of Engineering * Department of Civil e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor's Degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six years (depending on institution and academic discipline). The two most common bachelor's degrees are the Bachelor of Arts (BA) and the Bachelor of Science (BS or BSc). In some institutions and educational systems, certain bachelor's degrees can only be taken as graduate or postgraduate educations after a first degree has been completed, although more commonly the successful completion of a bachelor's degree is a prerequisite for further courses such as a master's or a doctorate. In countries with qualifications frameworks, bachelor's degrees are normally one of the major levels in the framework (sometimes two levels where non-honours and honours bachelor's degrees are considered separately). However, some qualifications titled bachelor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the Hadith. In Arabic, the term ''sharīʿah'' refers to God's immutable divine law and is contrasted with ''fiqh'', which refers to its human scholarly interpretations. In the historical course, fiqh sects have emerged that reflect the preferences of certain societies and state administrations on behalf of people who are interested in the theoretical (method) and practical application (Ahkam / fatwa) studies of laws and rules, but sharia has never been a valid legal system on its own. It has been used together with " customary (Urf) law" since Omar or the Umayyads. It may also be wrong to think that the Sharia, as a religious argument or belief, is entirely within or related to Allah's commands and prohibitions. Several non-graded crimes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajam
''Ajam'' ( ar, عجم, ʿajam) is an Arabic word meaning mute, which today refers to someone whose mother tongue is not Arabic. During the Arab conquest of Persia, the term became a racial pejorative. In many languages, including Persian, Turkish, Urdu–Hindi, Azerbaijani, Bengali, Kurdish, Gujarati, Malay, Punjabi, and Swahili, ''Ajam'' and ''Ajami'' refer to Iran and Iranians respectively. Etymology According to traditional etymology, the word ''Ajam'' comes from the Semitic root ''ʿ-j-m''. Related forms of the same root include, but are not limited to: * ''mustaʿjim'': mute, incapable of speech * ''ʿajama'' / '' ʾaʿjama'' / ''ʿajjama'': to dot – in particular, to add the dots that distinguish between various Arabic letters to a text (and hence make it easier for a non-native Arabic speaker to read). It is now an obsolete term, since all modern Arabic texts are dotted. This may also be linked to ''ʿajām'' / ''ʿajam'' "pit, seed (e.g. of a date or grape)". * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajman Tribe
Al-Ajman or al-'Ijman ( ar, العُجمان, singular Ajmi ar, العجمي) is an Arabian tribal confederation in the Arabian Peninsula, with Ajman spread across Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. Origin Al-Ajman is a Qahtanite Arab tribe that is descended from Banu Yam tribe. Most of Ajman left their nomadic life and lived in northeastern of Saudi Arabia. History The Ajman were noted for being important players in the politics of eastern Arabia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Their most famous leader (or ''sheikh'') during the 19th-20th century was Rakan bin Hithlain, who is still well known in Arabian tribal lore. He was noted for his poetry and is often known as the maternal grandfather of the current Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia Mohammed bin Salman. In 1861 the Ajman were defeated by Faisal bin Turki, the Imam of the Second Saudi State, after challenging his rule in the 1850s. Faisal bin Turki later married into the tribe. Later they support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
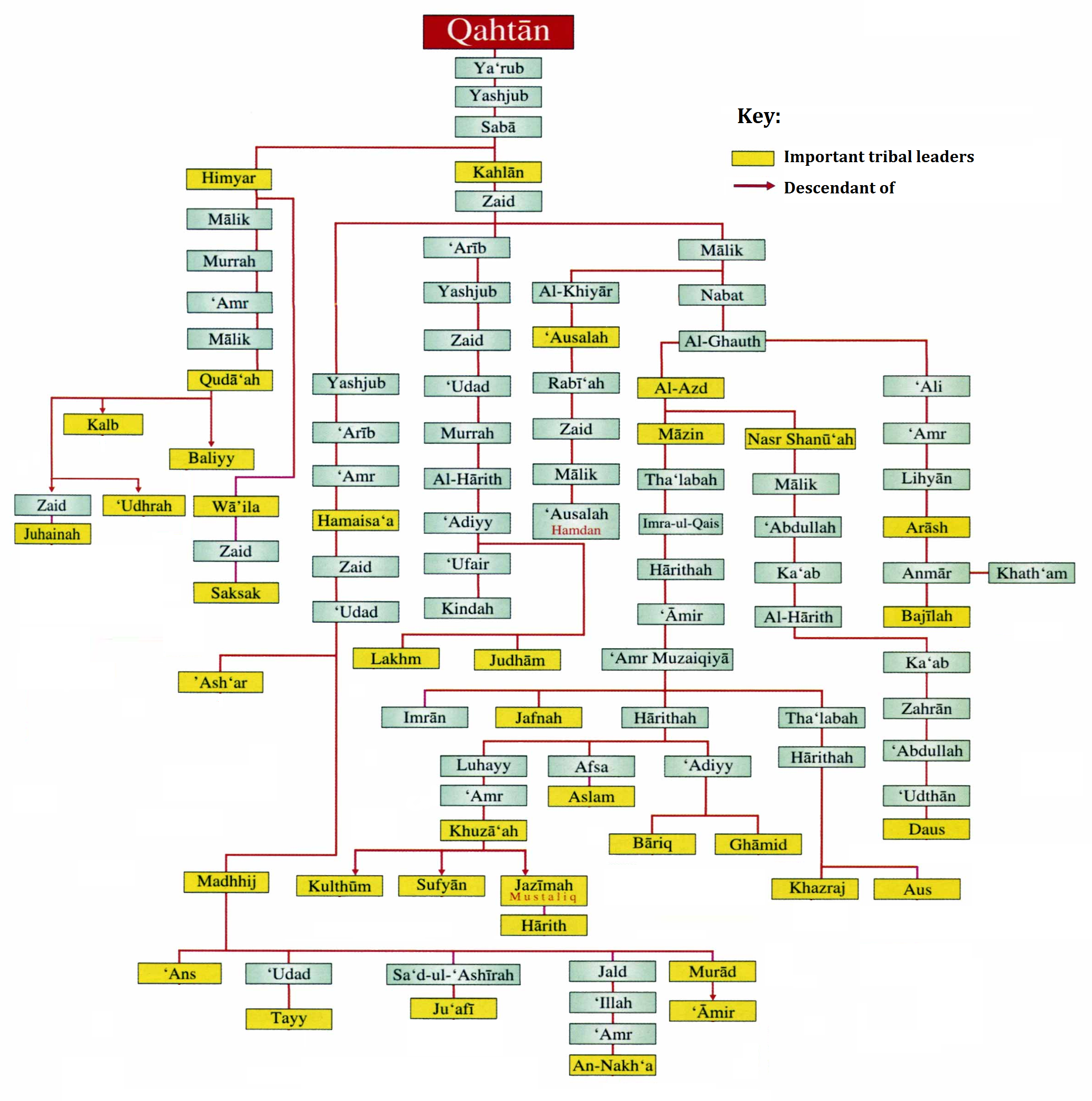
Qahtanites
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs. Traditional Arab genealogy According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |