|
Aerobactin
Aerobactin is a bacterial iron chelating agent (siderophore) found in ''E. coli''. It is a virulence factor enabling ''E. coli'' to sequester iron in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract. Aerobactin is biosynthesized by the oxidation of lysine, catalyzed by the enzyme aerobactin synthase, which is then coupled to citric acid. The gene for this enzyme is found in the aerobactin operon, which is roughly 8 kilobases long and contains 5 or more genes in total. ''Yersinia pestis'' contains genes relating to aerobactin, but they have been inactivated by a frameshift mutation, thus ''Y. pestis'' is no longer able to synthesize aerobactin. Other homologs * Rhizobactin from ''Sinorhizobium'' * Alcaligin from ''Bordetella ''Bordetella'' () is a genus of small (0.2 – 0.7 µm), gram-negative coccobacilli of the phylum Pseudomonadota. ''Bordetella'' species, with the exception of '' B. petrii'', are obligate aerobes, as well as highly fastidious, or difficult ...'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobactin Synthase
In enzymology, an aerobactin synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4 ATP + citrate + 2 N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine + 2 H2O \rightleftharpoons 4 ADP + 4 phosphate + aerobactin The 4 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, citrate, N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine, and H2O, whereas its 3 products are ADP, phosphate, and aerobactin Aerobactin is a bacterial iron chelating agent (siderophore) found in ''E. coli''. It is a virulence factor enabling ''E. coli'' to sequester iron in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract. Aerobactin is biosynthesized by the oxidation .... This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, specifically those forming carbon-nitrogen bonds as acid-D-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is citrate:N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme is also called citrate:6-N-acetyl-6-N-hydroxy-L-lysine ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme participates in lysine degrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderophore
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron-chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is now being appreciated. Siderophores are among the strongest (highest affinity) Fe3+ binding agents known. Phytosiderophores are siderophores produced by plants. Scarcity of soluble iron Despite being one of the most abundant elements in the Earth's crust, iron is not readily bioavailable. In most aerobic environments, such as the soil or sea, iron exists in the ferric (Fe3+) state, which tends to form insoluble rust-like solids. To be effective, nutrients must not only be available, they must be soluble. Microbes release siderophores to scavenge iron from these mineral phases by formation of soluble Fe3+ complexes that can be taken up by active transport mechanisms. Many siderophores are nonribosomal peptides, although several are biosynthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderophores
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron-chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is now being appreciated. Siderophores are among the strongest (highest affinity) Fe3+ binding agents known. Phytosiderophores are siderophores produced by plants. Scarcity of soluble iron Despite being one of the most abundant elements in the Earth's crust, iron is not readily bioavailable. In most aerobic environments, such as the soil or sea, iron exists in the ferric (Fe3+) state, which tends to form insoluble rust-like solids. To be effective, nutrients must not only be available, they must be soluble. Microbes release siderophores to scavenge iron from these mineral phases by formation of soluble Fe3+ complexes that can be taken up by active transport mechanisms. Many siderophores are nonribosomal peptides, although several are biosynthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operon
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be ''co-transcribed'' to define an operon. Originally, operons were thought to exist solely in prokaryotes (which includes organelles like plastids that are derived from bacteria), but since the discovery of the first operons in eukaryotes in the early 1990s, more evidence has arisen to suggest they are more common than previously assumed. In general, expression of prokaryotic operons leads to the generation of polycistronic mRNAs, while eukaryotic operons lead to monocistronic mRNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordetella
''Bordetella'' () is a genus of small (0.2 – 0.7 µm), gram-negative coccobacilli of the phylum Pseudomonadota. ''Bordetella'' species, with the exception of '' B. petrii'', are obligate aerobes, as well as highly fastidious, or difficult to culture. All species can infect humans. The first three species to be described ('' B. pertussis'', '' B. parapertussis'', '' B. bronchiseptica''); are sometimes referred to as the 'classical species'. Two of these (''B. bronchiseptica'' and ''B. pertussis'') are also motile. ''B. pertussis'' and occasionally ''B. parapertussis'' cause pertussis or whooping cough in humans, and some ''B. parapertussis'' strains can colonise sheep. ''B. bronchiseptica'' rarely infects healthy humans, though disease in immunocompromised patients has been reported. ''B. bronchiseptica'' causes several diseases in other mammals, including kennel cough and atrophic rhinitis in dogs and pigs, respectively. Other members of the genus cause similar diseases in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinorhizobium
''Ensifer'' (often referred to in literature by its synonym ''Sinorhizobium'') is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria ( rhizobia), three of which ('' Ensifer meliloti'', ''Ensifer medicae'' and '' Ensifer fredii'') have been sequenced. Etymology The generic epithet ''Ensifer'' derives from the Latin noun ''ensifer'', "sword-bearer". The synonym ''Sinorhizobium'' is a combination of Medieval Latin noun ''sino'' ("China"), the Classical Greek noun ''rhiza'' ("root"), and the Classical Greek noun ''bium'' ("life"). Thus, the Neo-Latin generic epithet of the synonym ''Sinorhizobium'' means "a ''Rhizobium'' isolated from China", in turn referring to the related genus '' Rhizobium'' ("root-associated life form"). Proper name The name ''Ensifer'' was published in 1982 and the name ''Sinorhizobium'' was published in 1988 thus the latter is regarded as a later synonym and by the rules of the Bacteriological Code (1990 Revision) of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
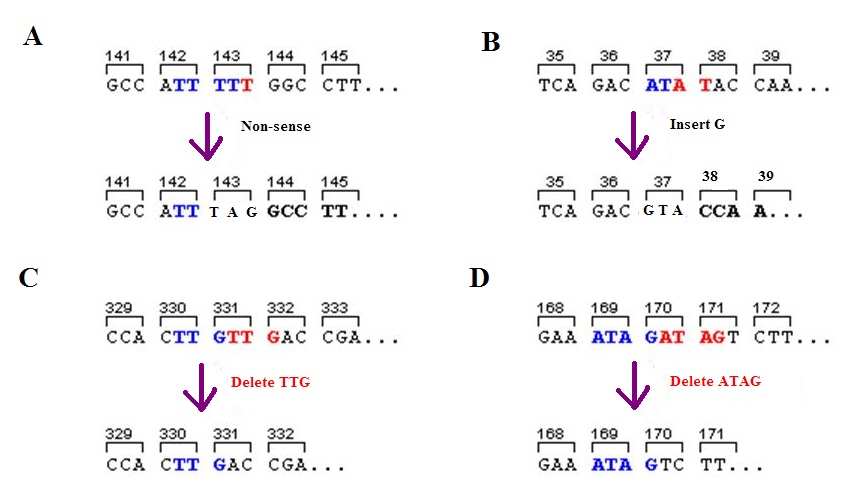
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yersinia Pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly '' Pasteurella pestis'') is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium without spores that is related to both ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' and ''Yersinia enterocolitica''. It is a facultative anaerobic organism that can infect humans via the Oriental rat flea (''Xenopsylla cheopis''). It causes the disease plague, which caused the first plague pandemic and the Black Death, the deadliest pandemic in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic. ''Yersinia pestis'' is a parasite of its host, the rat flea, which is also a parasite of rats, hence ''Y. pestis'' is a hyperparasite. ''Y. pestis'' was discovered in 1894 by Alexandre Yersin, a Swiss/French physician and bacteriologist from the Pasteur Institute, during an epidemic of the plague in Hong Kong. Yersin was a member of the Pasteur school of thought. Kitasato Shibasaburō, a Japanese bacteriologist who practised Koch's me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobase
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding proteins ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |