|
AM404
AM404, also known as ''N''-arachidonoylaminophenol, is an active metabolite of paracetamol (acetaminophen), responsible for all or part of its analgesic action and anticonvulsant effects. Chemically, it is the amide formed from 4-aminophenol and arachidonic acid. Pharmacology It is established that AM404 increases concentrations of the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide within the synaptic cleft, contributing to its analgesic activity. This has been well characterised as involving endocannabinoid transporter inhibition, but the precise transporter responsible is yet to be determined. AM404 was originally reported to be an endogenous cannabinoid reuptake inhibitor, preventing the transport of anandamide and other related compounds back from the synaptic cleft, much in the same way that common selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants prevent the reuptake of serotonin. Earlier work on the mechanism of AM404 suggested that the inhibition of fatty acid ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol. At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect, and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear. Paracetamol may relieve pain in acute mild migraine but only slightly in episodic tension headache. However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination helps with both conditions where the pain is mild and is recommended as a first-line treatment for them. Paracetamol is effective for post-surgical pain, but it is inferior to ibuprofen. The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination provides further increase in potency and is superior to either drug alone. The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinically insignificant. The evidence in its favor for the use in low back pain, cancer pain, and neuropathic pain is insufficient. In the sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamide
Anandamide (ANA), also known as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA), is a fatty acid neurotransmitter. Anandamide was the first endocannabinoid to be discovered: it participates in the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors, the same receptors that the psychoactive compound THC in cannabis acts on. Anandamide is found in nearly all tissues in a wide range of animals. Anandamide has also been found in plants, including small amounts in chocolate. The name 'anandamide' is taken from the Sanskrit word '' ananda'', which means "joy, bliss, delight", plus amide. Anandamide is derived from the non-oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid. It is synthesized from ''N''-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways. It is degraded primarily by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme, which converts anandamide into ethanolamine and arachidonic acid. As such, inhibitors of FAAH lead to elevated anandamide leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase (COX), officially known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS), is an enzyme (specifically, a family of isozymes, ) that is responsible for formation of prostanoids, including thromboxane and prostaglandins such as prostacyclin, from arachidonic acid. A member of the animal-type heme peroxidase family, it is also known as prostaglandin G/H synthase. The specific reaction catalyzed is the conversion from arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 via a short-living prostaglandin G2 intermediate. Pharmaceutical inhibition of COX can provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen, exert their effects through inhibition of COX. Those that are specific to the COX-2 isozyme are called COX-2 inhibitors. The active metabolite (AM404) of paracetamol is a COX inhibitor, a fact to which some or all of its therapeutic effect has been attributed. In medicine, the root symbol "COX" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPV1
The transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TrpV1), also known as the capsaicin receptor and the vanilloid receptor 1, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''TRPV1'' gene. It was the first isolated member of the transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor proteins that in turn are a sub-family of the transient receptor potential protein group. This protein is a member of the TRPV group of transient receptor potential family of ion channels. The function of TRPV1 is detection and regulation of body temperature. In addition, TRPV1 provides a sensation of scalding heat and pain (nociception). In primary afferent sensory neurons, it cooperates with TRPA1 (a chemical irritant receptor) to mediate the detection of noxious environmental stimuli. Function TRPV1 is an element of or mechanism used by the mammalian somatosensory system. It is a nonselective cation channel that may be activated by a wide variety of exogenous and endogenous physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocannabinoid Reuptake Inhibitor
Endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitors (eCBRIs), also called cannabinoid reuptake inhibitors (CBRIs), are drugs which limit the reabsorption of endocannabinoid neurotransmitters by the releasing neuron. Pharmacology The method of transport of endocannabinoids through the cell membrane and cytoplasm to their respective degradation enzymes has been rigorously debated for nearly two decades, and a putative endocannabinoid membrane transporter was proposed. However, as lipophilic molecules endocannabinoids readily pass through the cell lipid bilayer without assistance and would more likely need a chaperone through the cytoplasm to the endoplasmic reticulum where the enzyme FAAH is located. More recently fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) and heat shock proteins (Hsp70s) have been described and verified as such chaperones, and their inhibitors have been synthesized. The inhibition of endocannabinoid reuptake raises the amount of those neurotransmitters available in the synaptic cleft and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are endogenous lipid-based retrograde neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors (CBRs), and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the vertebrate central nervous system (including the brain) and peripheral nervous system. The endocannabinoid system remains under preliminary research, but may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre- and postnatal development, various activity of immune system, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory, and in mediating the pharmacological effects of cannabis. The ECS plays an important role in multiple aspects of neural functions, including the control of movement and motor coordination, learning and memory, emotion and motivation, addictive-like behavior and pain modulation, among others. Two primary cannabinoid receptors have been identified: CB1, first cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AM Cannabinoids
Alexandros Makriyannis is a professor in the Department of Medicinal Chemistry at Northeastern University, where his research group has synthesized many new compounds with cannabinoid activity. Some of those are: See also * List of CP cannabinoids * List of JWH cannabinoids * List of HU cannabinoids * List of miscellaneous designer cannabinoids Since the first synthetic cannabinoids were discovered in recreational drug products in 2008, new synthetic cannabinoids with no precedent in the scientific literature continue to be identified. These synthetic cannabinoids appear to be rationally ... References {{Cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
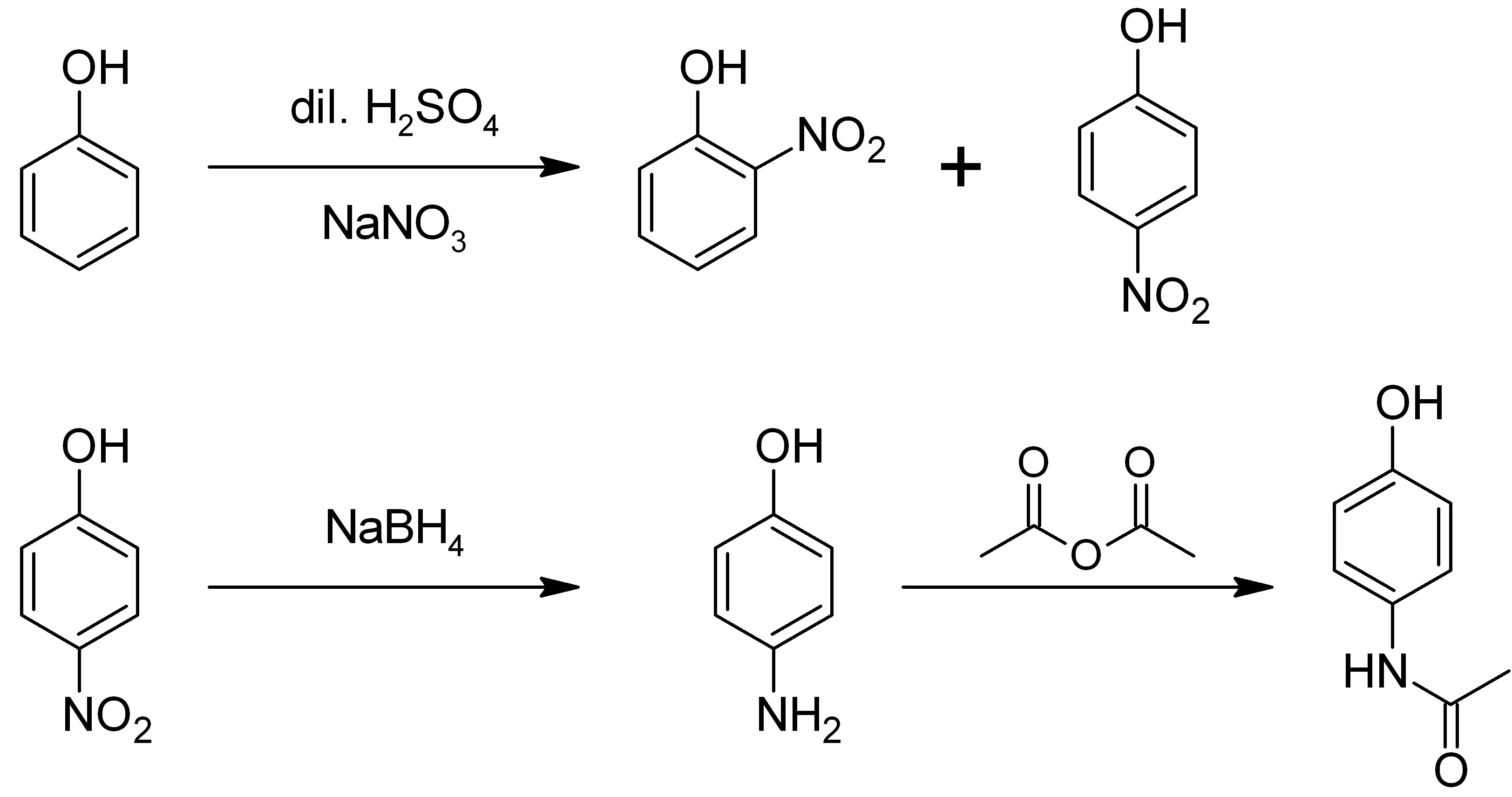
4-Aminophenol
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it is commonly used as a developer for black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal. Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives ''N''-methylaminophenol and ''N'',''N''-dimethylaminophenol are of commercial value. The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol. __TOC__ Preparation From phenol It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol (Bamberger rearrangement). :C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O :C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2 From n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It is typically used to induce cooperation with a medical procedure. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. The opposite condition, when body temperature decreases below normal levels, is known as hypothermia. It results when the homeostatic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Amides
Fatty is a derogatory term for someone who is obese. It may refer also to: People * Mai Fatty, Gambian politician * Roscoe Arbuckle (1887–1933), American actor and comedian * Fatty Briody (1858–1903), American Major League Baseball player * Fatty D (April Fores), American pornographic actress * Bob Fothergill (1897–1938), American Major League Baseball outfielder * William Foulke (footballer) (1874–1916), English cricketer and footballer * Fatty George (1927–1982), Austrian jazz musician * Richard Lamb (1907–1974), Australian racing cyclist * Fatty Lawrence (1903–1976), college gridiron football player * W. T. McLain (1885–1938), college gridiron football player, lawyer, and politician * Charles H. Smith (American football), University of Michigan football player in 1893–1894 * Roland Taylor (1946–2017), retired American Basketball Association and National Basketball Association player * Paul Vautin (born 1959), Australian former rugby league footballer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |