4-Aminophenol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an
 It is a precursor to
It is a precursor to
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. T ...
with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it is commonly used as a developer
Developer may refer to:
Computers
* Software developer, a person or organization who develop programs/applications
* Video game developer, a person or business involved in video game development, the process of designing and creating games
* Web d ...
for black-and-white film
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white in a continuous spectrum, producing a grayscale, range of shades of gray, shades of grey.
Media
The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology imp ...
, marketed under the name Rodinal
Rodinal is the trade name of a black and white developing agent produced originally by the German company Agfa based on the chemical 4-aminophenol
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an organic compound with the form ...
.
Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives
The derivative of a function is the rate of change of the function's output relative to its input value.
Derivative may also refer to:
In mathematics and economics
* Brzozowski derivative in the theory of formal languages
* Formal derivative, an ...
''N''-methylaminophenol and ''N'',''N''-dimethylaminophenol are of commercial value.
The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H7NO. Along with its isomer 4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dyes and heterocyclic compounds.Mitchell, S.C. & W ...
and 3-aminophenol.
__TOC__
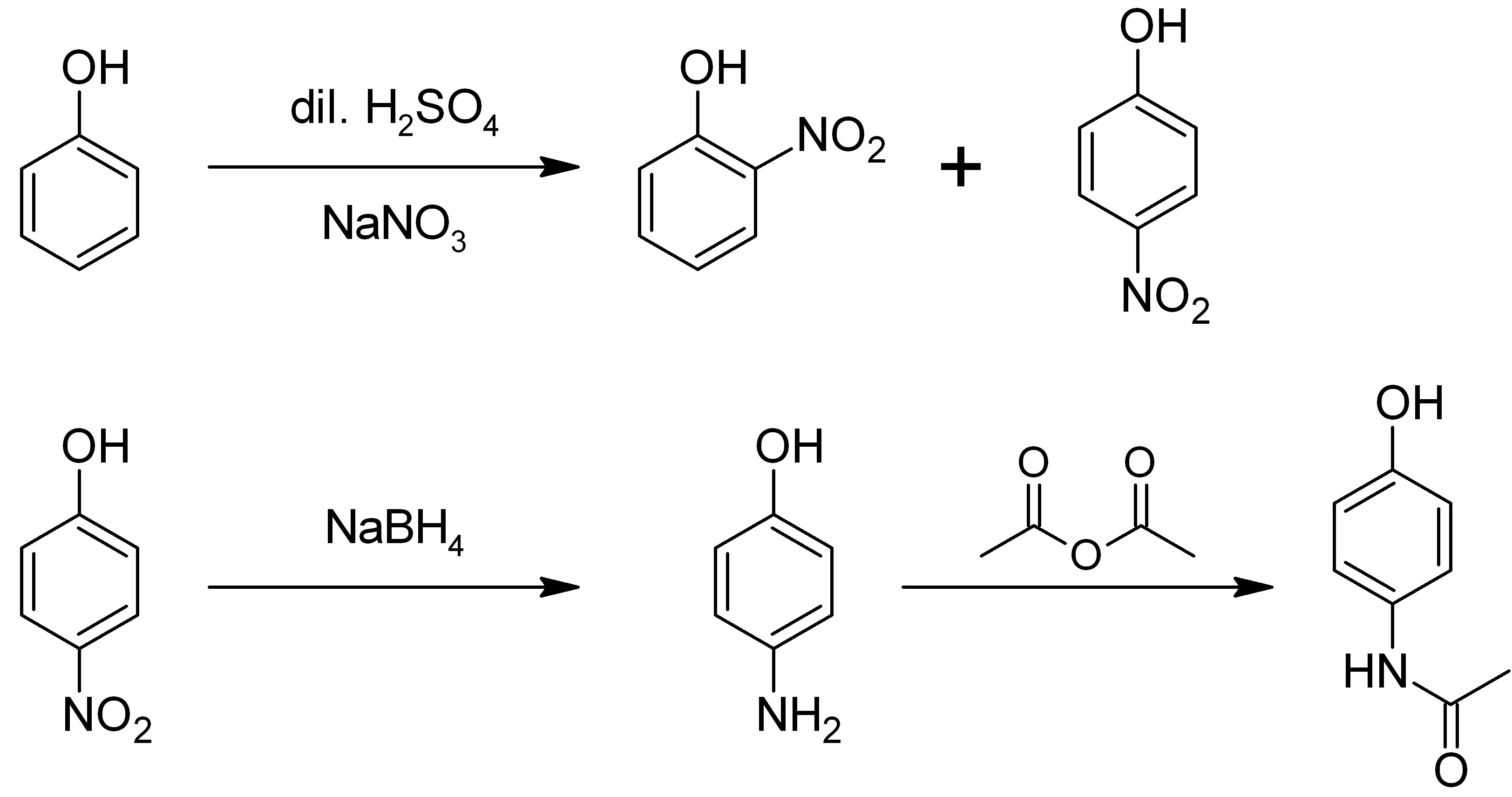
Preparation
From phenol
It is produced fromphenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it ...
by nitration
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols an ...
followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organ ...
of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine
Phenylhydroxylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5NHOH. It is an intermediate in the redox-related pair C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO. Phenylhydroxylamine should not be confused with its isomer α-phenylhydroxylamine or ''O''-phenylhydroxyl ...
, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol (Bamberger rearrangement The Bamberger rearrangement is the chemical reaction of phenylhydroxylamines with strong aqueous acid, which will rearrange to give 4-aminophenols. It is named for the German chemist Eugen Bamberger (1857–1932).
The starting phenylhydroxylam ...
).
:C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O
:C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2
From nitrobenzene
It can be produced from nitrobenzene by electrolytic conversion tophenylhydroxylamine
Phenylhydroxylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5NHOH. It is an intermediate in the redox-related pair C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO. Phenylhydroxylamine should not be confused with its isomer α-phenylhydroxylamine or ''O''-phenylhydroxyl ...
, which spontaneously rearranges to 4-aminophenol.
From 4-nitrophenol
4-nitrophenol can be reduced through a variety of methods, to yield 4-aminophenol. One method involveshydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organ ...
over a Raney Nickel catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
. A second method involves selective reduction of the nitro group
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitr ...
by Tin(II) Chloride
Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula . It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in aci ...
in anhydrous ethanol or ethyl ethanoate.
Uses
4-Aminophenol is a building block used in organic chemistry. Prominently, it is the final intermediate in the industrial synthesis of paracetamol. Treating 4-aminophenol with acetic anhydride gives paracetamol: : It is a precursor to
It is a precursor to amodiaquine
Amodiaquine (ADQ) is a medication used to treat malaria, including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' malaria when uncomplicated. It is recommended to be given with artesunate to reduce the risk of resistance. Due to the risk of rare but serious side effec ...
, mesalazine
Mesalazine, also known as mesalamine or 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), is a medication used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is generally used for mildly to moderately severe disease. I ...
, AM404
AM404, also known as ''N''-arachidonoylaminophenol, is an active metabolite of paracetamol (acetaminophen), responsible for all or part of its analgesic action and anticonvulsant effects. Chemically, it is the amide formed from 4-aminophenol and ...
, parapropamol, B-86810 & B-87836 (c.f. ).
4-Aminophenol converts readily to the diazonium salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
General properti ...
.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aminophenol, 4- Aminophenols