|
ßĖ¬ilakku
ßĖ¬ilakku (), later known as Pirindu ( and ), was a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite state which existed in southeastern Anatolia in the Iron Age. Name ßĖ¬ilakku The native name of this kingdom is still unknown due to a lack of Hieroglyphic Luwian inscriptions from it during the Iron Age, although it has been tentatively identified with the land of mentioned in the records of Halparuntiyas I of Gurgum. () was the name given by Neo-Assyrian Akkadian sources to this kingdom, and the name of the region which in Graeco-Roman times was called Cilicia was derived from that of ßĖ¬ilakku. Pirindu Following the collapse of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, the country of ßĖ¬ilakku reappeared in Neo-Babylonian Akkadian sources under the name of ( and ). The name was derived from a Luwian name , meaning , corresponding to the later Greek and Turkish appelations of this region as () and , which have the same meanings. It is uncertain whether the Neo-Babylonian name Pirindu is identical to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ßĖ¬iyawa
ßĖ¬iyawa ( hlu, ) or Adanawa ( hlu, ) was a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite state which existed in southeastern Anatolia in the Iron Age. Name The native Luwian name of the kingdom was (), which bears a strong similarity to the name () used to refer to the Achaeans ( grc, ╬æŽć╬▒╬╣╬┐╬╣, translit=Akhaioi, from earlier grc, ╬æŽć╬▒╬╣ŽØ╬┐╬╣, translit=Akhaiwoi), that is to the Mycenaean Greeks, in the Hittite texts of the Bronze Age. The use of this name for the kingdom of ßĖ¬iyawa might have been the result of a migration of Greek populations from Western Anatolia into this region in the early Iron Age. The name was recorded in Semitic languages in several forms: *in Neo-Assyrian sources as: ** (), ** ( and ), **and (); ***the form () also appears in Aramaic sources; *and in Neo-Babylonian sources as (). Another name by which the kingdom of ßĖ¬iyawa was called in its native Hieroglyphic Luwian inscriptions was (). The Phoenician inscriptions from ßĖ¬iyawa also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
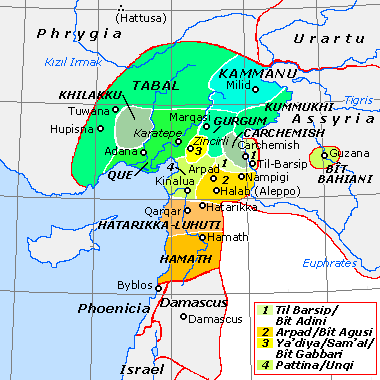
Tabal (region)
Tabal ( akk-x-neoassyr, , translit=m─üt Tabal and , romanized: ) was a region which covered south-east Anatolia during the Iron Age. Name The native name of the region of Tabal is still unknown, although it might have been ( hlu, ), which is attested in inscriptions from Karkami┼Ī. However, in the absence of native Tabalian inscriptions containing this name, this identification cannot yet be confirmed. The origin of the name is also uncertain since it was not used for the Tabalian region in the Late Bronze Age. Tabal As exonym Due to the absence of the name or any other name similar to it in native Central Anatolian sources of the Iron Age and the lack of its attestation to designate this area in Old and Middle Assyrian sources, this name tends to be considered by historians to have been an exonym given to the region by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. was likely an Akkadian term meaning "bank" or "shore" of a body of water, in reference to the kingdom and region of Tabal bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luwian Language
Luwian (), sometimes known as Luvian or Luish, is an ancient language, or group of languages, within the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The ethnonym Luwian comes from ''Luwiya'' (also spelled ''Luwia'' or ''Luvia'') ŌĆō the name of the region in which the Luwians lived. Luwiya is attested, for example, in the Hittite laws. The two varieties of Proto-Luwian or Luwian (in the narrow sense of these names) are known after the scripts in which they were written: Cuneiform Luwian (''CLuwian'') and Hieroglyphic Luwian (''HLuwian''). There is no consensus as to whether these were a single language or two closely related languages. Classification Several other Anatolian languages ŌĆō particularly Carian, Lycian, Lydian and Milyan (also known as Lycian B or Lycian II) ŌĆō are now usually identified as related to Luwian ŌĆō and as mutually connected more closely than other constituents of the Anatolian branch.Anna Bauer, 2014, ''Morphosyntax of the Noun Phrase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Agusi
Bit Agusi or Bit Agushi (also written Bet Agus) was an ancient Aramaean Syro-Hittite state, established by Gusi of Yakhan at the beginning of the 9th century BC. It had included the cities of Arpad, Nampigi (Nampigu) and later on Aleppo Arpad was the capital of the state-kingdom. Bit Agusi stretched from the A'zaz area in the north to Hamath in the south. Chronology According to Dan'el Kahn, there were seven stages of Bit Agusi history in Northern Syria in the ninth and eighth centuries BC. * Stage 1 (858ŌĆōca. 842 BC). Early on, Bit Agusi was apparently free of political alliances with neighbors. Arame, the second king of Bit Agusi, submitted to Assyria freely in 858 BCE, along with many other rulers of the region, including the southern Anatolia. * Stage 2 (841ŌĆō823 BC). A period of Bit Agusi subjugation to Assyria. * Stage 3. Around 823 BC, or maybe a little later, Bit Agusi leads a local alliance opposing Assyrian hegemony, and achieves independence. * Stage 4. Also, soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ermenek
Ermenek is a town and district of Karaman Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. As ancient Germanicopolis (in Isauria; has namesakes), a former bishopric, it remains a Latin Catholic titular see. The district forms the core of the plateau region Ta┼¤eli. According to 2014 census, population of the district is 29,957 of which 11,332 live in the town of Ermenek. Names The town was historically known as Germanicopolis (Greek: ), Germanig and possibly Clibanus; which later mutated to Ermenek. History Germanicopolis was an ancient town in the Roman province of Isauria. ( Hierocl. p. 709; Concil. Chalced. p. 659; Const. Porphyr. ''de Them.'' i. 13.) The city took its name from Germanicus, grandson of first Emperor Octavian Augustus, as several others. The Crusaders sustained a great defeat at the hands of the Seljuks near the city in 1098. It passed to the Turkish dynasty of the Karamanids and became a centre of the Af┼¤ar Turks in 1228. During the Karamanid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadim
Hadim is a town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. According to 2000 census, population of the district is 59,941 of which 16,620 live in the town of Hadim. History The area now known as Hadim was settled by a tribe of Turkmen originating from Bukhara following the Seljuk victory at the battle of Malazgirt. Hadim was well regarded in Ottoman times as a source for Islamic scholars and their training, this is reflected in the villages previous name, Belde-i Hadimül-ilm meaning place which serves the sciences. The scholars of Hadim fulfilled an important role in the Turkification of Anatolia. A notable scholar from Hadim was Seyyid Bayram Veli who founded the village of Dedemli in Hadim district. Bayram Veli was a dervish who had migrated from the region of Khorosan to avoid the incoming Mongol invasion. He was known to give spiritual and religious advice to sultan Alâeddin Keykubat I of the Sultanate of Rum. Hadim had a number of Sayyid familie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bozk─▒r
Bozk─▒r is a town and district of Konya Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. According to 2008 census, population of the district is 31,601 of which 7,212 live in the town of Bozk─▒r. The town occupied a central position in ancient Isauria. The name ''Bozk─▒r'' means steppe in Turkish and after the Turkish settlement in early Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate period, Bozk─▒r was initially the name given to the region extending between the present-day Bozk─▒r town marked by ├ćar┼¤amba Stream and the lands around neighboring Seydi┼¤ehir Seydi┼¤ehir is a town and district of Konya Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. According to a 2000 census, the population of the district is 85,456 of which 48,372 live in the town of Seydi┼¤ehir. History Seydi┼¤ehir has an extensive .... The name Bozk─▒r was eventually adopted for the town. Notes References * Populated places in Konya Province Districts of Konya Province {{Konya-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda (Greek: ╬ø╬¼Žü╬▒╬Į╬┤╬▒), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. According to the 2000 census, the population of the province is 231,872 of which 132,064 live in the town of Karaman. The district covers an area of , and the town lies at an average elevation of . The Karaman Museum is one of the major sights. Etymology The town owes its name to Karaman Bey, who was one of the rulers of the Karamanid dynasty. The former name ''Laranda'' which in turn comes from the Luwian language ''Larawanda'', literally means "sandy, a sandy place". History In ancient times, Karaman was known as Laranda ( el, ╬ø╬¼Žü╬▒╬Į╬┤╬▒). In the 6th century BC it came under Achaemenid rule until 322 BC, when it was destroyed by Perdiccas, a former general of Alexander the Great, after he had defeated Ariarathes I, king of Cappadocia. It lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, ╬”ŽüŽģ╬│╬»╬▒, ''Phryg├Ła'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires of the time. Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Phrygian kings: * Gordias, whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great * Midas, who turned whatever he touched to gold * Mygdon, who warred with the Amazons According to Homer's ''Iliad'', the Phrygians participated in the Trojan War as close allies of the Trojans, fighting against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before Cimmerians sacked the Phrygian capital, Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. TigrisŌĆōEuphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphr├Īt─ōs'' ( grc, ╬ĢßĮÉŽåŽü╬¼Žä╬ĘŽé, as if from Greek ╬ĄßĮ¢ "good" and ŽåŽü╬¼╬ČŽē "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian ÉÄóÉÄ│ÉÄ╝ÉÄĀÉļÉÄó ''Ufr─ütu'', itself from Elamite language, Elamite ÆīæÆģüÆŖÅÆīģÆģ¢ ''├║-ip-ra-tu-i┼Ī''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as ÆīōÆäÆÆēŻ , which read as Sumerian language, Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian language, Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: ╬æ╬╣╬│╬▒╬»╬┐ ╬Ā╬Ł╬╗╬▒╬│╬┐Žé: "Eg├®o P├®lagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midas
Midas (; grc-gre, ╬£╬»╬┤╬▒Žé) was the name of a king in Phrygia with whom several myths became associated, as well as two later members of the Phrygian royal house. The most famous King Midas is popularly remembered in Greek mythology for his ability to turn everything he touched into gold. This came to be called the ''golden touch'', or the ''Midas touch''. The legends told about this Midas and his father Gordias, credited with founding the Phrygian capital city Gordium and tying the Gordian Knot, indicate that they were believed to have lived sometime in the 2nd millennium BC, well before the Trojan War. However, Homer does not mention Midas or Gordias, while instead mentioning two other Phrygian kings, Mygdon and Otreus. The Phrygian city Midaeum was presumably named after him, and this is probably also the Midas that according to Pausanias founded Ancyra (today known as Ankara). Another King Midas ruled Phrygia in the late 8th century BC. Most historians believe this M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |