|
Hadim
Hadim is a town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. According to 2000 census, population of the district is 59,941 of which 16,620 live in the town of Hadim. History The area now known as Hadim was settled by a tribe of Turkmen originating from Bukhara following the Seljuk victory at the battle of Malazgirt. Hadim was well regarded in Ottoman times as a source for Islamic scholars and their training, this is reflected in the villages previous name, Belde-i Hadimül-ilm meaning place which serves the sciences. The scholars of Hadim fulfilled an important role in the Turkification of Anatolia. A notable scholar from Hadim was Seyyid Bayram Veli who founded the village of Dedemli in Hadim district. Bayram Veli was a dervish who had migrated from the region of Khorosan to avoid the incoming Mongol invasion. He was known to give spiritual and religious advice to sultan Alâeddin Keykubat I of the Sultanate of Rum. Hadim had a number of Sayyid familie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedemli
Dedemli is a town in Konya Province, Turkey Geography Dedemli is in the rural area of Hadim district which is a part of Konya Province. Dedemli is on Toros Mountains, at an altitude of . It is situated just at the west of headwaters of Göksu River and a few kilometers north of Korualan another mountain town. Midtown coordinates are . Dedemli is quite far from the main highways. The distances to Hadim is and to Konya is . The population is 2088 as of 2011 History According to legend, the town had been founded by a sheikh Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ... (Islamic scholar) named Bayram Seydi Veli from Khorosan in the 15th century. In fact the name of the town means ''with my grandfather'' where grandfather in this context, means sheikh. In 1968, the town was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konya Province
Konya Province ( tr, ), in southwest Central Anatolia, is the largest province of Turkey. The Province, provincial Capital (political), capital is the city of Konya. Its traffic code is 42. The Kızılören solar power plant in Konya will be able to produce 22.5 megawatts of electricity over an area of 430,000 square meters. Demographics In 2011 the Konya Metropolitan Municipality had a population close to 1.1 million, out of the 2 million in the Konya Province (76.2% of the population in Konya Province lives in the city, while the remainder live in the villages, sub-districts and districts.) Language census Official first language results (1927-1965) Divisions The province of Konya is divided into thirty-one Districts of Turkey, districts three of which (Meram, Selçuklu and Karatay, Konya, Karatay) form part of Konya, Konya city. The following districts are located in the Mediterranean Region: Ahırlı, Beyşehir, Bozkır, Derebucak, Hadim, Hüyük, Konya, Hüyük, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Turkey
The 81 provinces of Turkey are divided into 973 districts (''ilçeler''; sing. ''ilçe''). In the early Turkish Republic and in the Ottoman Empire, the corresponding unit was the ''kaza''. Most provinces bear the same name as their respective provincial capital districts. However, many urban provinces, designated as greater municipalities, have a center consisting of multiple districts, such as the provincial capital of Ankara province, The City of Ankara, comprising nine separate districts. Additionally four provinces, Kocaeli, Sakarya, İçel and Hatay have their capital district named differently from their province, as İzmit, Adapazarı, Mersin and Antakya respectively. A district may cover both rural and urban areas. In many provinces, one district of a province is designated the central district (''merkez ilçe'') from which the district is administered. The central district is administered by an appointed provincial deputy governor and other non-central districts b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization ( tr, Türkleştirme) describes a shift whereby populations or places received or adopted Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly applied to mean specifically Turkish rather than merely Turkic, therefore referring to the Ottoman Empire, and the Turkish nationalist policies of the Republic of Turkey toward ethnic minorities in Turkey. As the Turkic states developed and grew, there were many instances of this cultural shift. The earliest instance of Turkification took place in Central Asia, when by the 6th century AD migration of Turkic tribes from Inner Asia caused a language shift among the Iranian peoples of the area. Also, by the 8th century AD, Turkification of Kashgar was completed by Qarluq Turks, who also Islamized the population. Turkification of Anatolia occurred in the time of the Seljuk Empire and Sultanate of Rum, when Anatolia had been a diverse an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud I
Mahmud I ( ota, محمود اول, tr, I. Mahmud, 2 August 1696 13 December 1754), known as Mahmud the Hunchback, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1730 to 1754. He took over the throne after the Patrona Halil rebellion and he kept good relations with the Mughal and Safavid Empires. Early life He was born at Edirne Palace on 2 August 1696, the son of Mustafa II (1664–1703); his mother was Saliha Valide Sultan. Mahmud I was the older half-brother of Osman III (1754–57). He developed a humped back. His father Mustafa II mostly lived in Edirne. Mahmud passed his childhood in Edirne. On 18 May 1702 he started his education in Edirne. When his father deposed himself from the throne he was brought to Istanbul and locked up in Kafes where he spent 27 years of his life. It is not known what kind of culture he acquired during this time, since he continued to play chess, write poetry, and deal with music. In addition for childhood and youth, there were dangers, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Orthodox church which lasted from 360 AD until the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman Empire in 1453. It served as a mosque until 1935, when it became a museum. In 2020, the site once again became a mosque. The current structure was built by the eastern Roman emperor Justinian I as the Christian cathedral of Constantinople for the state church of the Roman Empire between 532 and 537, and was designed by the Greek geometers Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles. It was formally called the Church of the Holy Wisdom () and upon completion became the world's largest interior space and among the first to employ a fully pendentive dome. It is considered the epitome of Byzantine architecture and is said to have "changed the history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ja'far Al-Sadiq
Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī al-Ṣādiq ( ar, جعفر بن محمد الصادق; 702 – 765 CE), commonly known as Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq (), was an 8th-century Shia Muslim scholar, jurist, and theologian.. He was the founder of the Jaʿfarī school of Islamic jurisprudence and the sixth Imam of the Twelver and Ismāʿīlī denominations of Shīʿa Islam. The traditions (''ḥadīth'') recorded from al-Ṣādiq and his predecessor, Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī al-Bāqir, are said to be more numerous than all the ''ḥadīth'' reports preserved from the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the other Shīʿīte Imams combined. Among other theological contributions, he elaborated the doctrine of '' '' (divinely inspired designation of each Imam by the previous Imam) and '' '' (the infallibility of the Imams), as well as that of (religious dissimulation under prosecution). Al-Ṣādiq is also important to Sunnīs as a jurist and transmitter of ''ḥadīth'', and a teacher to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyid
''Sayyid'' (, ; ar, سيد ; ; meaning 'sir', 'Lord', 'Master'; Arabic plural: ; feminine: ; ) is a surname of people descending from the Prophets in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandsons, Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali, sons of Muhammad's daughter Fatimah, Fatima and his cousin and son-in-law Ali (Ali ibn Abi Talib). While in the Islamic golden age, early islamic period the title Al-Sayyid was applied on all the members of the of Banu Hashim, banu hashim, the tribe of Muhammad. But later on the title was made specific to those of Hasanids, Hasani and Hussaini descent, Primarily by the List of Fatimid caliphs, Fatimid Caliphs. Female ''sayyids'' are given the titles ''sayyida'', ''syeda'', ''alawiyah'' . In some regions of the Islamic world, such as in Iraq, the descendants of Muhammad are given the title ''Emir, amīr'' or ''mīr'', meaning "aristocrats", "commander", or "ruler". In Shia Islam the son of a non Sayyid father and a Sayyida mother claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Rum
fa, سلجوقیان روم () , status = , government_type = Hereditary monarchyTriarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262) , year_start = 1077 , year_end = 1308 , p1 = Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynastyByzantine Empire , p2 = Seljuk Empire , p3 = Danishmends , p4 = Mengujekids , p5 = Saltukids , p6 = Artuqids , s1 = Anatolian beyliks , s2 = Ilkhanate, , event_pre = Battle of Manzikert , date_pre = 1071 , event_start = Division from the Seljuk Empire , event1 = Battle of Köse Dağ , date_event1 = 1243 , event_end = Karamanid conquest , image_flag = Double-headed eagle of the Sultanate of Rum.svg , flag_size = 100px , flag_type = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayqubad I
Alā ad-Dīn Kayqubād ibn Kaykhusraw ( fa, علاء الدين كيقباد بن كيخسرو; tr, I. Alâeddin Keykûbad, 1190–1237), also known as Kayqubad I, was the Seljuq Sultan of Rûm who reigned from 1220 to 1237. He expanded the borders of the sultanate at the expense of his neighbors, particularly the Mengujek Beylik and the Ayyubids, and established a Seljuq presence on the Mediterranean with his acquisition of the port of Kalon Oros , later renamed Ala'iyya in his honor. The sultan, sometimes styled Kayqubad the Great, is remembered today for his rich architectural legacy and the brilliant court culture that flourished under his reign. Kayqubad's reign represented the apogee of Seljuq power and influence in Anatolia, and Kayqubad himself was considered the most illustrious prince of the dynasty. In the period following the mid-13th century Mongol invasion, inhabitants of Anatolia frequently looked back on his reign as a golden age, while the new rulers of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
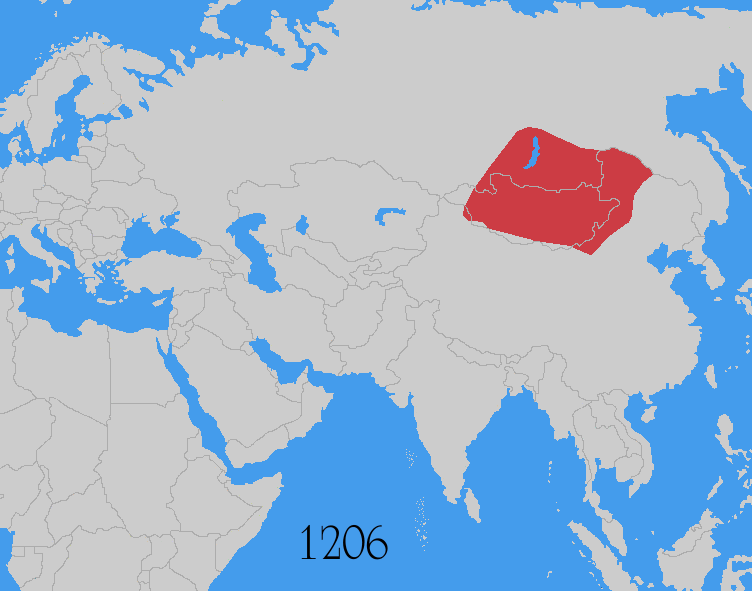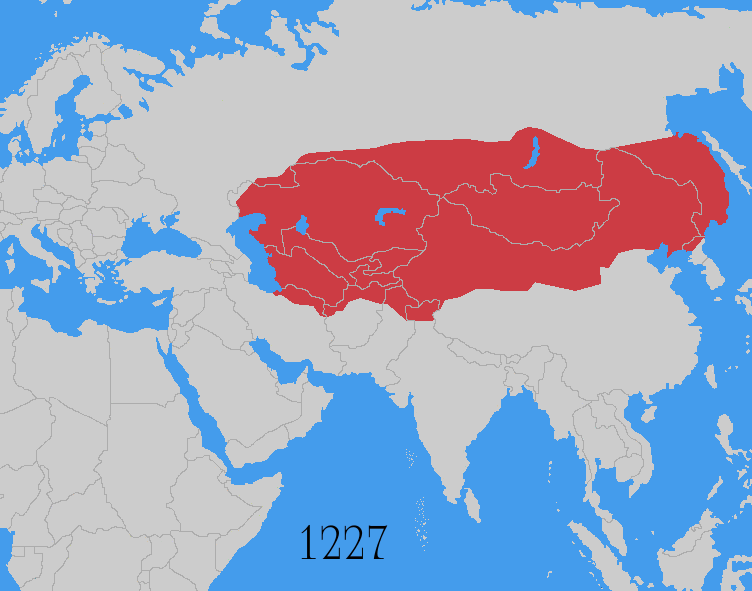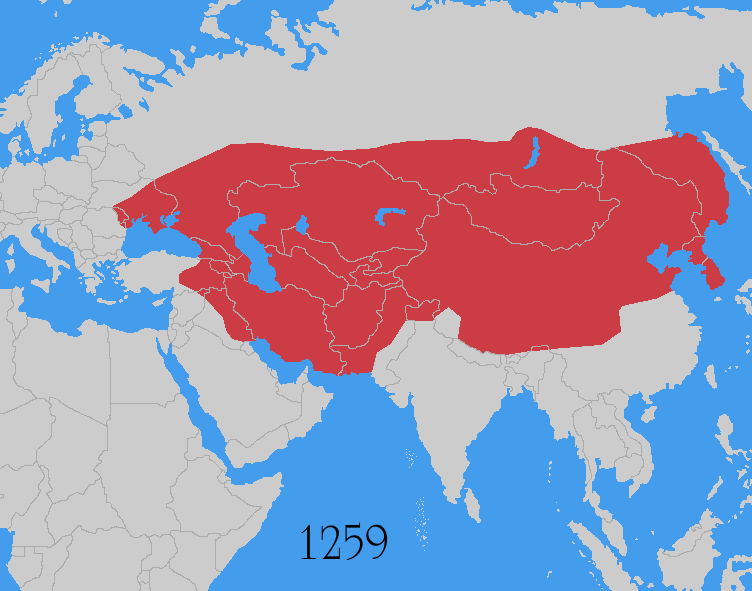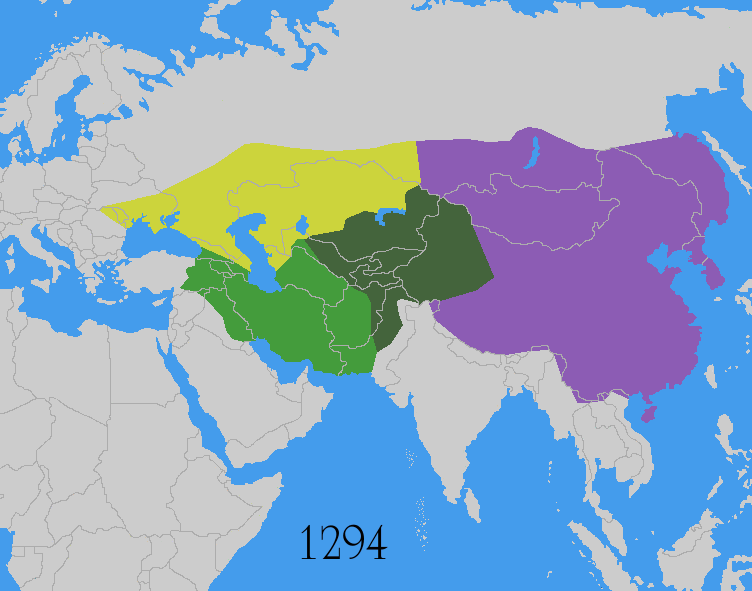
Mongol Invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)