|
ÓĖā
''Kho khuat'' (ÓĖā ÓĖéÓĖ¦ÓĖö, ''khuat'' is Thai for 'bottle') is the third letter of the Thai alphabet. It is a high consonant in the Thai tripartite consonant system (Ó╣äÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ©Ó╣ī, informally ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖŻÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ╣Ó╣ł). It represents the sound has an initial consonant and ╠Üas a final consonant. The letter is now rarely used, being replaced universally by '' kho khai'' (ÓĖé Ó╣äÓĖéÓ╣ł). There are currently no words using ''kho khuat'' in Thai language according to the Royal Institute Dictionary of 1999, the official standard current dictionary of the Thai language. However, ''kho khuat'' still has an entry in most dictionaries stating that it is obsolete, and is included on alphabet charts in order to preserve the traditional count of 44 Thai consonants. History Origins Early evidence of ''kho khuat'' can be found in the Ram Khamhaeng Inscription from the Sukhothai Period, which contains 11 words containing the letter. Additionally, there are a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Script
The Thai script ( th, ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖŻÓ╣äÓĖŚÓĖó, ) is the abugida used to write Thai, Southern Thai and many other languages spoken in Thailand. The Thai alphabet itself (as used to write Thai) has 44 consonant symbols ( th, ÓĖ×ÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖŹÓĖŖÓĖÖÓĖ░, ''phayanchana''), 16 vowel symbols ( th, ÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓĖ░, ''sara'') that combine into at least 32 vowel forms and four tone diacritics ( th, ÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖüÓĖĢÓ╣ī or ÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖĢ, or ) to create characters mostly representing syllables. Although commonly referred to as the "Thai alphabet", the script is in fact not a true alphabet but an abugida, a writing system in which the full characters represent consonants with diacritical marks for vowels; the absence of a vowel diacritic gives an implied 'a' or 'o'. Consonants are written horizontally from left to right, and vowels following a consonant in speech are written above, below, to the left or to the right of it, or a combination of those. History The Thai alphabet is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Alphabet
The Thai script ( th, ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖŻÓ╣äÓĖŚÓĖó, ) is the abugida used to write Thai, Southern Thai and many other languages spoken in Thailand. The Thai alphabet itself (as used to write Thai) has 44 consonant symbols ( th, ÓĖ×ÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖŹÓĖŖÓĖÖÓĖ░, ''phayanchana''), 16 vowel symbols ( th, ÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓĖ░, ''sara'') that combine into at least 32 vowel forms and four tone diacritics ( th, ÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖüÓĖĢÓ╣ī or ÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖĢ, or ) to create characters mostly representing syllables. Although commonly referred to as the "Thai alphabet", the script is in fact not a true alphabet but an abugida, a writing system in which the full characters represent consonants with diacritical marks for vowels; the absence of a vowel diacritic gives an implied 'a' or 'o'. Consonants are written horizontally from left to right, and vowels following a consonant in speech are written above, below, to the left or to the right of it, or a combination of those. History The Thai alphabet is der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
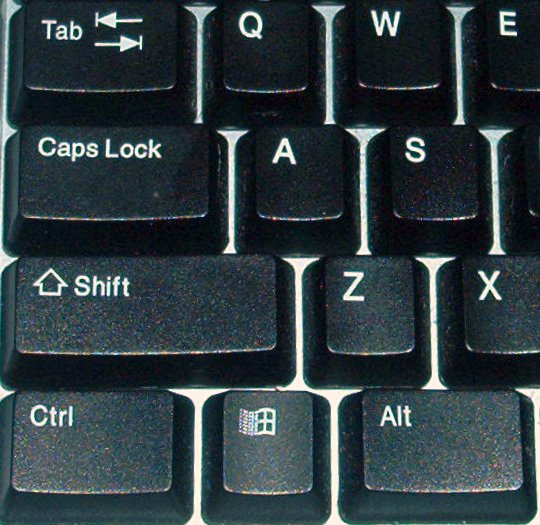
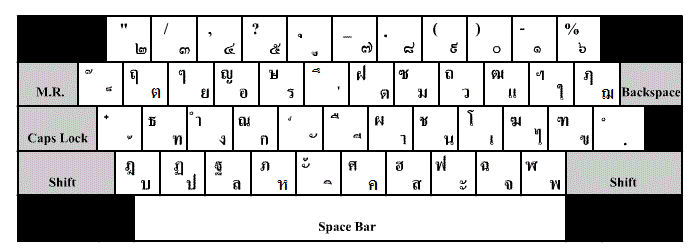
Thai-script Typewriter
Typewriters with the capability to print the Thai script were first developed in 1891 by Edwin Hunter McFarland, based on double-keyboard Smith Premier models. They became widely popular, especially for government use, though their production was discontinued in 1915 and newer shift-based layouts were subsequently developed by Edwin's brother George B. McFarland. The traditional keyboard layout, now known as Thai Kedmanee keyboard layout, Kedmanee, was introduced in 1931 and became the ''de facto'' standard, remaining popular even when the newer Pattachote layout, introduced in 1965, was officially endorsed by the government but failed to gain traction. The use of typewriters rapidly declined toward the end of the 20th century, when they were displaced by personal computers, though their layouts served as precursors to those of modern computer keyboards. The typewriter modified Thai Thai typography, typography and Thai orthography, orthography in several ways, most significantly e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai D├│n Language
Tai D├│n (, "The White Tai refer to themselves and their language as tayŌü┤ d╔ön┬▓, probably because of the white blouses worn by the women. The usual word for 'white' in White Tai is d╔ön┬▓" (p. 8). Hudak, T. J. (2008). ''William J. GedneyŌĆÖs comparative Tai source book''. Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press.), also known as Tai Khao or White Tai, is a Tai language of northern Vietnam, Laos and China. Classification Tai D├│n is classified as belonging to the Tai-Kadai language group, located in the Tai languages and Southwestern Tai languages subgroups. Geographical distribution In China, White Tai (Tai Khaw ÕéŻńÜō) people are located in the following townships of Yunnan province, with about 40,000 people (Gao 1999).Gao Lishi ķ½śń½ŗÕŻ½. 1999. Õ鯵ŚÅµö»ń│╗µÄóÕŠ«. õĖŁÕŹŚµ░æµŚÅÕŁ”ķÖóÕŁ”µŖź (Õō▓ÕŁ”ńżŠõ╝Üń¦æÕŁ”ńēł). 1999 Õ╣┤ń¼¼1 µ£¤ (µĆ╗ń¼¼96 µ£¤). * Jinping County ķćæÕ╣│ÕÄ┐: Mengla Township Õŗɵŗēõ╣Ī and Zhemi Township ĶĆģń▒│õ╣Ī (along the banks of the Zhemi River ĶĆģń▒│µ▓│ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamite Warrior
''Dynamite Warrior'' ( th, ÓĖģÓĖÖÓ╣äÓĖ¤ÓĖÜÓĖ┤ÓĖÖ (modern: ÓĖäÓĖÖÓ╣äÓĖ¤ÓĖÜÓĖ┤ÓĖÖ), Transliteration, translit. Khon Fai Bin) is a 2006 Thai martial arts film, martial arts Western (genre), Western film directed by Chalerm Wongpim and starring Dan Chupong (from ''Born to Fight (2004 film), Born to Fight''). Plot The story is set in 1890s Thailand, Siam. Siang is a young Muay Thai warrior and Rocket Festival, rocketry expert, raised in a Buddhism in Thailand, Buddhist temple, who steals back domestic buffalo, water buffalo taken from poor Isan farmers by unscrupulous cattle raiding, cattle raiders. He is searching for a man with a tattoo in the chest who killed his parents. A local nobleman, Lord Waeng, wants to create a market for his steam tractors, so he hires a hulking convict, the Thief to burn the farmhouses, kill all the cattle traders, take the farmers as hostages at an outside near the farmhouse and round up all the water buffalo for slaughter, depriving farmers of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kho Khon
Kho or KHO may refer to: *Kho, the Hokkien romanization of the Chinese surname Xu (surname) *Kho (cooking technique), a cooking technique in Vietnamese cuisine * Kho (costume) (or Bakhu), a traditional outfit worn by Bhutia, ethnic Tibetans of Sikkim * Kho people, a people of Pakistan *Kho language, or Khowar, a language of Pakistan * Kara Harp Okulu (KHO), a Turkish military academy * Kho kho, a South Asian sport *Khao Kho, a mountain in Phetchabun Province, Thailand People with the name *Baldwin Kho (born 1971), Filipino visual artist and humanitarian *Elisa Olga Kho, Philippine politician *Hayden Kho (born 1980), Filipino cosmetic surgeon, entrepreneur, actor and model *Kho Sin-Kie (born 1912), Indonesian-born tennis player who represented the Republic of China in the Davis Cup *Kho Orluk (born 1580), Oirat prince and Tayishi of the Torghut-Oirat tribe *Kho Jabing (1984ŌĆō2016), Malaysian man sentenced to death for murder in Singapore *Kho Nai Guan (1956ŌĆō2002), Singaporean mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phya Anuman Rajadhon
Phya Anuman Rajadhon ( th, ÓĖ×ÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖŖÓĖśÓĖÖ; , also spelled ''Phaya Anuman Rajadhon'' or ''Phray─ü Anuman Rajadhon''; December 14, 1888 ŌĆō July 12, 1969), was one of modern Thailand's most remarkable scholars. He was a self-trained linguist, anthropologist and ethnographer who became an authority on the culture of Thailand. His name was Yong Sathiankoset ( th, ÓĖóÓĖć Ó╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖÉÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖŻÓ╣éÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖ©ÓĖ©); Phraya Anuman Rajadhon was his noble title. He also took his family name, Sathiankoset, as a pen name by which he is well known. His prolific work and his interest in a multitude of culture-related fields, from folklore to sociology, set the foundations for a long-lasting cultural awareness among young Thai scholars. Phraya Anuman Rajadhon was the first Thai scholar to conduct a serious study of Thai folkloristics, taking notes on the nocturnal village spirits of Thai folklore. He established that since such spirits were not represented in painting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''P─üli Canon'' or ''Tipiß╣Łaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Therav─üda'' Buddhism.Stargardt, Janice. ''Tracing Thoughts Through Things: The Oldest Pali Texts and the Early Buddhist Archaeology of India and Burma.'', Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, 2000, page 25. Early in the language's history, it was written in the Brahmi script. Origin and development Etymology The word 'Pali' is used as a name for the language of the Theravada canon. The word seems to have its origins in commentarial traditions, wherein the (in the sense of the line of original text quoted) was distinguished from the commentary or vernacular translation that followed it in the manuscript. K. R. Norman suggests that its emergence was based on a misunderstanding of the compound , with being interpreted as the name of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shift Key
The Shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row. The Shift key's name originated from the typewriter, where one had to press and hold the button to shift up the case stamp to change to capital letters; the shift key was first used in the Remington No. 2 Type-Writer of 1878; the No. 1 model was capital-only. On the US layout and similar keyboard layouts, characters that typically require the use of the shift key include the parentheses, the question mark, the exclamation point, and the colon. When the caps lock key is engaged, the shift key may be used to type lowercase letters on many operating systems, though not on macOS. Labeling The keyboard symbol for the Shift key (which is called Level 2 Select key in the international standard series ISO/IEC 9995) is given in ISO/IEC 9995-7 as symbol 1, and in ISO 7000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Languages
The Tai or ZhuangŌĆōTai languages ( th, ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ®ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖŚ or , transliteration: or ) are a branch of the KraŌĆōDai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spoken of the TaiŌĆōKadai languages, including Standard Thai or Siamese, the national language of Thailand; Lao or Laotian, the national language of Laos; Myanmar's Shan language; and Zhuang, a major language in the Southwestern China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, spoken by the Zhuang (ÕŻ») people, the largest minority ethnic group in China, with a population of 15.55 million, living mainly in Guangxi, the rest scattered across Yunnan, Guangdong, Guizhou and Hunan provinces. Name Cognates with the name ''Tai'' (''Thai, Dai'', etc.) are used by speakers of many Tai languages. The term ''Tai'' is now well-established as the generic name in English. In his book '' The Tai-Kadai Languages'' Anthony Diller claims that Lao scholars he has met are not pleased with Lao being regarded as a Tai language. k╔ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez language, Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional (although in less formal contexts, all three types of script may be termed alphabets). The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which the symbols cannot be split into separate consonants and vowels. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain F├®vrier (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic languages, Ethiopic term "abugi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)