Władysław II Jagiełło on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło (),Other names include (; ) (see also
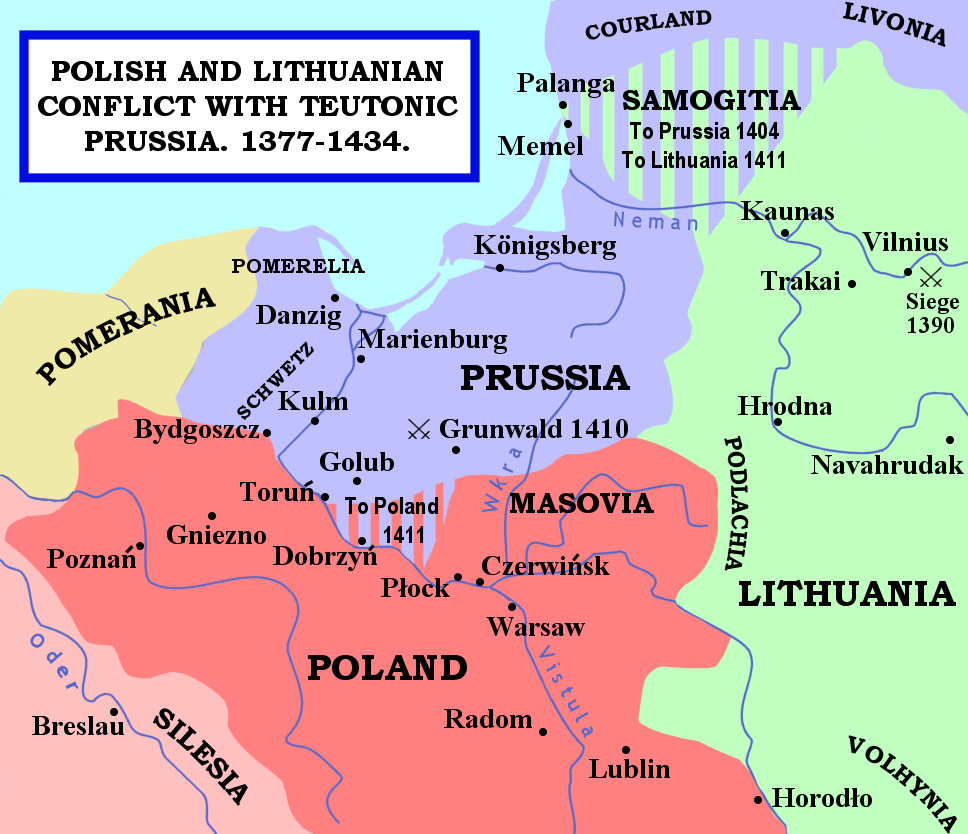 The war ended in 1411 with the Peace of Thorn, in which neither Poland nor Lithuania drove home negotiating advantages home to the full, much to the discontent of the Polish nobility. Poland regained
The war ended in 1411 with the Peace of Thorn, in which neither Poland nor Lithuania drove home negotiating advantages home to the full, much to the discontent of the Polish nobility. Poland regained
Two years later, he married Sophia of Halshany (niece of Uliana Olshanska), who bore him two surviving sons : * Władysław (1424–1444) *
File:Effigy of Jogaila in the Wawel Cathedral in Krakow.jpg,
Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A person ...
) was Grand Duke of Lithuania
This is a list of Lithuanian monarchs who ruled Lithuania from its inception until the fall of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1795. The Lithuanian monarch bore the title of Grand duke, Grand Duke, with the exception of Mindaugas, who was crown ...
beginning in 1377 and starting in 1386, becoming King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
as well. As Grand Duke, he ruled Lithuania from 1377 to 1381 and from 1382 to 1401, at which time he became the Supreme Duke of Lithuania in exchange for naming his cousin Vytautas
Vytautas the Great (; 27 October 1430) was a ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was also the prince of Grodno (1370–1382), prince of Lutsk (1387–1389), and the postulated king of the Hussites.
In modern Lithuania, Vytautas is revere ...
as the new Grand Duke. Władysław II initially served as King of Poland alongside his wife Jadwiga until her death in 1399, and then the sole ruler until his own death in 1434.
Raised a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
in 1386 and baptized as Ladislaus () in Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-five years, and laid the foundation for the centuries-long Polish–Lithuanian union Polish–Lithuanian can refer to:
* Polish–Lithuanian union (1385–1569)
* Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795)
* Polish-Lithuanian identity as used to describe groups, families, or individuals with histories in the Polish–Lithuania ...
. He was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian ( ) or Jagellonian dynasty ( ; ; ), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty (), the House of Jagiellon (), or simply the Jagiellons (; ; ), was the name assumed by a cadet branch of the Lithuanian ducal dynasty of Gediminids upon recep ...
in Poland that bears his name and was previously also known as the Gediminid dynasty
The House of Gediminas (), or simply the Gediminids, were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reigned from the 14th to the 16th century. A cadet branch of this family, known as the Jagiellonian dynasty, reigned also in th ...
in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
. The dynasty ruled both states until 1572,Anna Jagiellon
Anna Jagiellon (, ; 18 October 1523 – 9 September 1596) was King of Poland, Queen of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, Grand Duchess of Lithuania from 1575 to 1587.
Daughter of Polish King and Lithuanian Grand Duke Sigismund I the Ol ...
, the last member of the royal Jagiellon family, died in 1596. and became one of the most influential dynasties in late medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
and early modern Europe
Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of European history between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the mid 15th century to the late 18th century. Histori ...
.
Jogaila was the last pagan ruler of medieval Lithuania. After he became King of Poland, as a result of the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; ; ) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made at Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in regard to his prospectiv ...
, the newly formed Polish-Lithuanian union confronted the growing power of the Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ...
. The allied victory at the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
in 1410, followed by the Peace of Thorn, secured the Polish and Lithuanian borders and marked the emergence of the Polish–Lithuanian alliance as a significant force in Europe. The reign of Władysław II Jagiełło extended Polish frontiers and is often considered the beginning of Poland's Golden Age.
Early life
Lithuania
Little is known of Jogaila's early life, and even his year of birth is uncertain. Previously historians assumed he was born in 1352, but some recent research suggests a later date—about 1362. He was a descendant of theGediminid dynasty
The House of Gediminas (), or simply the Gediminids, were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reigned from the 14th to the 16th century. A cadet branch of this family, known as the Jagiellonian dynasty, reigned also in th ...
and was the son of Algirdas
Algirdas (; , ; – May 1377) was List of Lithuanian monarchs, Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1345 to 1377. With the help of his brother Kęstutis (who defended the western border of the Duchy) he created an empire stretching from the pre ...
, Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his second wife, Uliana of Tver
Uliana Aleksandrovna ( – 17 March 1391) was a grand duchess of Lithuania as the second wife of Algirdas. She was the daughter of Alexander of Tver and Anastasia of Galicia, daughter of Yuri I of Galicia.
Life
After her father and eldes ...
, who was the daughter of the Yaroslavichi prince Aleksandr of Tver. His name had a meaning of more courageous and superior than others, he spent most of his early time in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
, at his father's manor.
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania to which Jogaila succeeded as Grand Duke in 1377 was a political entity composed of two leading, but very different nationalities and two political systems: ethnic Lithuania in the north-west and the vast Ruthenia
''Ruthenia'' is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Rus'. Originally, the term ''Rus' land'' referred to a triangular area, which mainly corresponds to the tribe of Polans in Dnieper Ukraine. ''Ruthenia' ...
n territories of former Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
, comprising the lands of modern Ukraine, Belarus, and parts of western Russia. At first, Jogaila—like his father—based his rule in the southern and eastern territories of Lithuania, while his uncle, Kęstutis, the Duke of Trakai, continued to rule the north-western region.Some historians have called this system a diarchy (; ). However, Rowell suggests that the nature of this dual rule "...reflects political expediency; it certainly does not meet the formal definition of diarchy as 'rule by two independent authorities'...those two leaders were not equal: the grand duke in Vilnius was supreme" (). Jogaila's succession, however, soon placed this system of dual rule under strain.
At the start of his reign, Jogaila was preoccupied with unrest in the Lithuanian Rus' lands. In 1377–78, Andrei of Polotsk, the eldest son of Algirdas, challenged Jogaila's authority and sought to become Grand Duke. In 1380, Andrei and another brother, Dmitry
Dmitry (); Church Slavic form: Dimitry or Dimitri (); ancient Russian forms: D'mitriy or Dmitr ( or ) is a male given name common in Orthodox Christian culture, the Russian version of Demetrios (, ). The meaning of the name is "devoted to, de ...
, sided with Prince Dmitri of Moscow against Jogaila's alliance with emir Mamai
Mamai (Mongolian Cyrillic alphabet, Mongolian Cyrillic: Мамай, ; 1325?–1380/1381) was a powerful Turco-Mongol tradition, Turko-Mongol military commander in Beylerbey rank of the Golden Horde from Kiyat clan. Contrary to popular misconcep ...
, de facto khan of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
. Jogaila failed to support Mamai, lingering in the vicinity of the battlefield, which led to Mamai's army's significant defeat at the hands of Prince Dmitri in the Battle of Kulikovo
The Battle of Kulikovo () was fought between the forces of Mamai, a powerful Mongol military commander of the Golden Horde, and Russian forces led by Grand Prince Dmitry Donskoy, Dmitry of Moscow. The battle took place on 8 September 1380, at Ku ...
. The Muscovites' Pyrrhic victory over the Golden Horde, in the long term, signified, however, the beginning of a slow climb to power by the Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Principality of Moscow, or Muscovy, known as the Principality of Moscow until 1389, was a late medieval Russian monarchy. Its capital was the city of Moscow. Originally established as a minor principality in the 13th century, the gra ...
, which became within a century the most serious rival and threat to the integrity, well-being and survival of Lithuania. However, in 1380 Muscovy was greatly weakened by tremendous losses suffered during the battle and thus, in the same year, Jogaila was free to begin a struggle for supremacy with Kęstutis.
In the north-west, Lithuania faced constant armed incursions from the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
—founded after 1226 to fight and convert the pagan Baltic tribes of Prussians, Yotvingians
Yotvingians, also called Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians, were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prussians. The linguist Petras Būtėnas asserts that they were closest to the Lithuanians. The Yotvingians contributed ...
and Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
. In 1380, Jogaila concluded the secret Treaty of Dovydiškės, directed against Kęstutis. When Kęstutis discovered the plan, the Lithuanian Civil War began. He seized Vilnius, overthrew Jogaila, and pronounced himself grand duke in his place. In 1382, Jogaila raised an army from his father's vassals and confronted Kęstutis near Trakai. Kęstutis and his son Vytautas
Vytautas the Great (; 27 October 1430) was a ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was also the prince of Grodno (1370–1382), prince of Lutsk (1387–1389), and the postulated king of the Hussites.
In modern Lithuania, Vytautas is revere ...
entered Jogaila's encampment for negotiations but were tricked and imprisoned in the Kreva Castle, where Kęstutis was found dead, probably murdered, a week later. Vytautas escaped to the Teutonic fortress of Marienburg and was baptised there under the name Wigand.
Jogaila formulated the Treaty of Dubysa, which rewarded the Knights for their aid in defeating Kęstutis and Vytautas by promising Christianisation and granting them Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five ...
west of the Dubysa river. However, when Jogaila failed to ratify the treaty, the Knights invaded Lithuania in the summer of 1383. In 1384, Jogaila reconciled with Vytautas promising to return his patrimony in Trakai. Vytautas then turned against the Knights, attacking and looting several Prussian castles.
It is known that Jogaila, being ethnic Lithuanian in the male line, himself knew and spoke in the Lithuanian language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of t ...
with Vytautas, his cousin from the Gediminids dynasty. Also, during the Christianization of Samogitia, none of the clergy, who came to Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five ...
with Jogaila, were able to communicate with the natives, therefore Jogaila himself taught the Samogitians about the Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, thus he was able to communicate in the Samogitian dialect of the Lithuanian language. According to the Teutonic Order's testimonial, he could not read nor write, and had to listen to others reading for him.
Baptism and marriage
Jogaila's Russian motherUliana of Tver
Uliana Aleksandrovna ( – 17 March 1391) was a grand duchess of Lithuania as the second wife of Algirdas. She was the daughter of Alexander of Tver and Anastasia of Galicia, daughter of Yuri I of Galicia.
Life
After her father and eldes ...
urged him to marry Sofia, daughter of Prince Dmitri of Moscow, who required him first to convert to Orthodoxy.The historian John Meyendorff suggests Jogaila may have already been an Orthodox Christian: "In 1377, Olgerd of Lithuania died, leaving the Grand Principality to his son Jagiello, an Orthodox Christian..." (). Dmitri, however, made it a condition of the marriage that Jogaila "should be baptized in the Orthodox faith and that he should proclaim his Christianity to all men" (). That option, however, was unlikely to halt the crusades against Lithuania by the Teutonic Knights, who regarded Orthodox Christians as schismatics and little better than heathens. Jogaila chose therefore to accept a Polish proposal to become a Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and marry the eleven-year-old Queen Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig (from German) and in , was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. Born in Buda, she was the youngest daught ...
.Jadwiga had actually been crowned king of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
(), because the Polish political system made no provision for a queen regnant
A queen regnant (: queens regnant) is a female monarch, equivalent in rank, title and position to a king. She reigns ''suo jure'' (in her own right) over a realm known as a kingdom; as opposed to a queen consort, who is married to a reigning ...
(). The nobles of Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
made this offer to Jogaila for many reasons. They wanted to neutralize the dangers posed by Lithuania itself and to secure the fertile territories of Galicia–Volhynia. The Polish nobles saw the offer as an opportunity for increasing their privileges and avoiding Austrian influence, brought by Jadwiga's previous fiancé William, Duke of Austria
William ( – 15 July 1406), known as William the Courteous (), a member of the House of Habsburg and Wilhelm, was Duke of Austria from 1386. As head of the Leopoldian line, he ruled over the Inner Austrian duchies of Carinthia, Styria and Carn ...
.
On 14 August 1385 in Kreva Castle, Jogaila confirmed his prenuptial promises in the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; ; ) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made at Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in regard to his prospectiv ...
(Union of Kreva). The promises included the adoption of Christianity, repatriation of lands "stolen" from Poland by its neighbours, and ''terras suas Lithuaniae et Russiae Coronae Regni Poloniae perpetuo applicare'', a clause interpreted by historians to mean anything from a personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
between Lithuania and Poland to a complete incorporation of Lithuania into Poland. The agreement at Kreva has been described both as far-sighted and as a desperate gamble.It "reflects the exceptional far-sightedness of the political elites ruling both countries" (). It was "a desperate gamble by Jogaila to avert a seemingly inevitable subjugation" ()
Jogaila was duly baptized at the Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral (), formally titled the Archcathedral Basilica of Stanislaus of Szczepanów, Saint Stanislaus and St. Wenceslas, Saint Wenceslaus, () is a Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it ...
in Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
on 15 February 1386 and from then on formally used the name Władysław or Latin versions of it.A Slavic name that roughly translates as ''glorious rule'', Władysław is often Latinised into either Wladislaus or Ladislaus. The choice evoked both Władysław I of Poland, the Elbow-high, who was Queen Jadwiga's great-grandfather and unified the kingdom in 1320, and Saint Ladislaus I of Hungary
Ladislaus I (, , , ; 1040 – 29 July 1095), also known as Saint Ladislas, was King of Hungary from 1077 and King of Croatia from 1091. He was the second son of King Béla I of Hungary and Richeza of Poland, Queen of Hungary, Richeza (or Adela ...
, a king who sided with the pope against the emperor Henry IV and Christianised Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
(). The marriage took place three days later, and on 4 March 1386 Jogaila was crowned King Władysław by archbishop Bodzanta. He was also to be legally adopted by Jadwiga's mother, Elizabeth of Bosnia
Elizabeth of Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Elizabeta Kotromanić, Јелисавета Котроманић ; ; ; – January 1387) was queen consort of Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary and Croatia in personal union with Hungary, Croat ...
, so retaining the throne in the event of Jadwiga's death. He was the first Lithuanian to be crowned as the King of Poland. The royal baptism triggered the conversion of most of Jogaila's court and noblemen, as well as mass baptisms in Lithuanian rivers, a beginning of the final Christianization of Lithuania
The Christianization of Lithuania () occurred in 1387, initiated by the Lithuanian royals Jogaila, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his cousin Vytautas the Great. It signified the official adoption of Catholic Christianity by Li ...
. Though the ethnic Lithuanian nobility
The Lithuanian nobility () or ''szlachta'' of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (, ) was historically a legally privileged hereditary elite class in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Polish Lithuanian Commonwealth (including during period of foreign r ...
were the main converts to Catholicism—both paganism and the Orthodox rite remained strong among the peasants—the king's conversion and its political implications created lasting repercussions for the history of both Lithuania and Poland. On 22 February 1387, he banned Catholics from marriages with Orthodox and demanded those Orthodox who previously married with the Catholics to convert to Catholicism.
Ruler of Lithuania and Poland
Accession
Władysław II Jagiello and Jadwiga reigned as co-monarchs; and though Jadwiga probably had little real power, she took an active part in Poland's political and cultural life. In 1387, she led two successful military expeditions to Red Ruthenia, recovered lands her father,Louis I of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great (; ; ) or Louis the Hungarian (; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. He was the first child of Charles I of Hungary and his wife, Elizabeth of ...
, had transferred from Poland to Hungary, and secured the homage of Voivode Petru I of Moldavia
Petru (Peter) I may have been a Voivode (prince) of Moldavia from the end of 1367 to after July 1368. Several historians, including Constantin Rezachevici and Ioan Aurel Pop, believe him to have been the son of prince Ştefan, oldest son of voivo ...
. In 1390, she also personally opened negotiations with the Teutonic Order. Most political responsibilities, however, fell to Jagiello, with Jadwiga attending to the cultural and charitable activities for which she is still revered.
Soon after Jagiello acceded to the Polish throne, Jagiello granted Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
a city charter like that of Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, modelled on the Magdeburg Law
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages gr ...
; and Vytautas issued a privilege to a Jewish commune of Trakai on almost the same terms as privileges issued to the Jews of Poland in the reigns of Boleslaus the Pious and Casimir the Great. Władysław's policy of unifying the two legal systems was partial and uneven at first but achieved a lasting influence. By the time of the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (; ) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingd ...
in 1569, there was not much difference between the administrative and judicial systems in force in Lithuania and Poland.
One effect of Jagiello's measures was to be the advancement of Catholics in Lithuania at the expense of Orthodox elements; in 1387 and 1413, for example, Lithuanian Catholic boyars were granted special judicial and political privileges denied to the Orthodox boyars. As this process gained momentum, it was accompanied by the rise of both Rus' and Lithuanian identity in the fifteenth century.
Challenges
Jagiello's baptism failed to end thecrusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
of the Teutonic Knights, who claimed his conversion was a sham, perhaps even heresy, and renewed their incursions on the pretext that pagan
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
s remained in Lithuania. From then on, however, the Order found it harder to sustain the cause of a crusade and faced the growing threat to its existence posed by the Kingdom of Poland and a genuinely Christian Lithuania alliance. Władysław sponsored the creation of the diocese of Vilnius under bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
Andrzej Wasilko, the former confessor of Elizabeth of Poland. The bishopric, which included Samogitia, then largely controlled by the Teutonic Order, was subordinated to the see of Gniezno
Gniezno (; ; ) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The city is the administrative seat of Gniezno County (''powiat'') ...
and not to that of Teutonic Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
. The decision may not have improved Władysław's relations with the Order, but it served to introduce closer ties between Lithuania and Poland, enabling the Polish church to freely assist its Lithuanian counterpart.
In 1389, Władysław's rule in Lithuania faced a revived challenge from Vytautas, who resented the power given to Skirgaila in Lithuania at the expense of his own patrimony. Vytautas started a civil war in Lithuania, aiming to become the Grand Duke. On 4 September 1390, the joint forces of Vytautas and Grand Master Konrad von Wallenrode of the Teutonic Order, laid siege to Vilnius, which was held by Władysław's regent Skirgaila with combined Polish, Lithuanian and Ruthenian troops. Although the Knights lifted the siege of the castle after a month, they reduced much of the outer city to ruins. This bloody conflict was eventually brought to a temporary halt in 1392 with the Treaty of Ostrów, by which Władysław handed over the government of Lithuania to his cousin in exchange for peace: Vytautas was to rule Lithuania as the grand duke (''magnus dux'') until his death, under the overlordship of the Supreme Duke (''dux supremus'') in the person of the Polish monarch. Skirgaila was moved from the Duchy of Trakai
Duchy of Trakai () was a subdivision of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania during the 14th and early 15th centuries. The Duke of Trakai was an important position held either by the Grand Duke of Lithuania himself or his second-in-command.
History
After ...
to become prince of Kiev. Vytautas initially accepted his status but soon began to pursue Lithuania's independence from Poland.
The protracted period of war between the Lithuanians and the Teutonic Knights was ended on 12 October 1398 by the Treaty of Salynas, named after the islet in the Neman River
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its s ...
where it was signed. Lithuania agreed to cede Samogitia and assist the Teutonic Order in a campaign to seize Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
, while the Order agreed to assist Lithuania in a campaign to seize Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
. Shortly afterwards, Vytautas was crowned as a king by local nobles; but the following year his forces and those of his ally, Khan Tokhtamysh of the White Horde, were crushed by the Timurids at the Battle of the Vorskla River, ending his imperial ambitions in the east and obliging him to submit to Władysław's protection once more.
King of Poland
Early actions
On 22 June 1399, Jadwiga gave birth to a daughter, baptised Elizabeth Bonifacia, but within a month the mother and daughter died, leaving Władysław sole ruler of the Kingdom of Poland and without an heir nor much legitimacy to rule the kingdom. Jadwiga's death undermined Władysław's right to the throne, and as a result old conflicts between the nobility ofLesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
, generally sympathetic to Władysław, and the gentry of Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
began to surface. In 1402, Władysław answered the rumblings against his rule by marrying Anna of Cilli, a granddaughter of Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
, a political match that re-legitimized his reign.
The Union of Vilnius and Radom of 1401 confirmed the status of Vytautas as grand duke under Władysław's overlordship while assuring the title of grand duke to the heirs of Władysław rather than those of Vytautas: should Władysław die without heirs, the Lithuanian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Bulgaria, Kievan Rus' (and later Russia), Moldavia and Wallachia (and later Romania), Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. C ...
s were to elect a new monarch. Since no heir had yet been produced by either monarch, the implications of the union were unforeseeable, but it forged bonds between the Polish and Lithuanian nobility and a permanent defensive alliance between the two states, strengthening Lithuania's hand for a new war against the Teutonic Order in which Poland officially took no part. While the document left the liberties of the Polish nobles untouched, it granted increased power to the boyars of Lithuania, whose grand dukes had till then been unencumbered by checks and balances of the sort attached to the Polish monarchy. The Union of Vilnius and Radom therefore earned Władysław a measure of support in Lithuania.
In late 1401, the new war against the Order overstretched the resources of the Lithuanians, who found themselves fighting on two fronts after uprisings in the eastern provinces. Another of Władysław's brothers, the malcontent Švitrigaila
Švitrigaila (before 1370 – 10 February 1452; sometimes spelled Svidrigiello) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1430 to 1432. He spent most of his life in largely unsuccessful dynastic struggles against his cousins Vytautas and Sigismund K� ...
, chose this moment to stir up revolts behind the lines and declare himself grand duke. On 31 January 1402, he presented himself in Marienburg, where he won the backing of the Knights with concessions similar to those made by Jogaila and Vytautas during earlier leadership contests in the Grand Duchy.
Against the Teutonic Order
The war ended in the Treaty of Raciąż on 22 May 1404. Władysław acceded to the formal cession of Samogitia and agreed to support the Order's designs onPskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
; in return, Konrad von Jungingen undertook to sell Poland the disputed Dobrzyń Land
Dobrzyń Land () is a historical region in central-northern Poland. It lies northeast of the Vistula River, south of the Drwęca, and west of the Skrwa. The territory approximately corresponds with the present-day powiats of Lipno, Rypin, and ...
and the town of Złotoryja
Złotoryja (; , ; Latin: ''Aureus Mons'', ''Aurum'') is a historic town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwestern Poland, the administrative seat of Złotoryja County, and of the smaller Gmina Złotoryja. Złotoryja is the first town in Pola ...
, once pawned to the Order by Władysław Opolski, and to support Vytautas in a revived attempt on Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
. Both sides had practical reasons for signing the treaty at that point: the Order needed time to fortify its newly acquired lands, the Poles and Lithuanians to deal with territorial challenges in the east and in Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
.
Also in 1404, Władysław held talks at Vratislav with Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia
Wenceslaus IV (also ''Wenceslas''; ; , nicknamed "the Idle"; 26 February 136116 August 1419), also known as Wenceslaus of Luxembourg, was King of Bohemia from 1378 until his death and King of Germany from 1376 until he was deposed in 1400. As he ...
, who offered to return Silesia to Poland if Władysław supported him in his power struggle within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. Władysław turned the deal down with the agreement of both Polish and Silesian nobles, unwilling to burden himself with new military commitments in the west.
Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic war
In December 1408, Władysław and Vytautas held strategic talks inNavahrudak Castle
The former castle in Navahrudak, Belarus (, , ) was one of the strongholds of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, cited by Maciej Stryjkowski as the location of Mindaugas's coronation as King of Lithuania as well as his likely burial place.Tomas Baranau ...
, where they decided to foment a Samogitian uprising against Teutonic rule to draw German forces away from Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
. Władysław promised to repay Vytautas for his support by restoring Samogitia to Lithuania in any future peace treaty. The uprising, which began in May 1409, at first provoked little reaction from the Knights, who had not yet consolidated their rule in Samogitia by building castles; but by June their diplomats were busy lobbying Władysław's court at Oborniki
Oborniki is a town in west-central Poland, in Greater Poland Voivodeship, about north of Poznań. It is the capital of Oborniki County and of Gmina Oborniki. Its population is 18,176 (2005).
History
Oborniki was granted town rights before 129 ...
, warning his nobles against Polish involvement in a war between Lithuania and the Order. Władysław, however, bypassed his nobles and informed the new Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen that if the Knights acted to suppress Samogitia, Poland would intervene. This stung the Order into issuing a declaration of war against Poland on 6 August, which Władysław received on 14 August in Nowy Korczyn.
The castles guarding the northern border were in such bad condition that the Knights easily captured those at Złotoryja, Dobrzyń and Bobrowniki, the capital of Dobrzyń Land, while German burghers invited them into Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its bank (geography), left-bank tributary, the Brda (river), Brda, the strategic location of Byd ...
(German: Bromberg). Władysław arrived on the scene in late September, retook Bydgoszcz within a week, and came to terms with the Order on 8 October. During the winter, the two armies prepared for a major confrontation. Władysław installed a strategic supply depot at Płock
Płock (pronounced ), officially the Ducal Capital City of Płock, is a city in central Poland, on the Vistula river, in the Masovian Voivodeship. According to the data provided by Central Statistical Office (Poland), GUS on 31 December 2021, the ...
in Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
and had a pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, is a bridge that uses float (nautical), floats or shallow-draft (hull), draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the support ...
constructed and transported north down the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
.
Meanwhile, both sides unleashed diplomatic offensives. The Knights dispatched letters to the monarchs of Europe, preaching their usual crusade against the heathens; Władysław countered with his letters to the monarchs, accusing the Order of planning to conquer the whole world. Such appeals successfully recruited many foreign knights to each side. Wenceslas IV of Bohemia signed a defensive treaty with the Poles against the Teutonic Order; his brother, Sigismund of Luxembourg
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in 1437. He was elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) in 1410, and was also King of Bohemia from 1419, as well as prince-elec ...
, allied himself with the Order and declared war against Poland on 12 July, though his Hungarian vassals refused his call to arms.
Battle of Grunwald
When the war resumed in June 1410, Władysław advanced into the Teutonic heartland at the head of an army of about 20,000 mounted nobles, 15,000 armed commoners, and 2,000 professional cavalry mainly hired from Bohemia. After crossing the Vistula over the pontoon bridge at Czerwińsk, his troops met up with those ofVytautas
Vytautas the Great (; 27 October 1430) was a ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was also the prince of Grodno (1370–1382), prince of Lutsk (1387–1389), and the postulated king of the Hussites.
In modern Lithuania, Vytautas is revere ...
, whose 11,000 light cavalry included Lithuanians, Ruthenians, and Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
. The Teutonic Order's army had about 18,000 cavalry, mostly Germans, and 5,000 infantry. On 15 July, at the in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), a ...
after one of the largest and most ferocious battles of the Middle Ages, the allies won a victory so overwhelming that the Teutonic Order's army was virtually annihilated, with most of its key commanders killed in combat, including Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen and Grand Marshal Friedrich von Wallenrode. Thousands of troops were reportedly slaughtered on either side.
The road to the Teutonic capital Marienburg now lay open, the city undefended; but for reasons the sources do not explain, Władysław hesitated to pursue his advantage. On 17 July, his army began a laboured advance, arriving at Marienburg only on 25 July, by which time the new Grand Master, Heinrich von Plauen, had organised a defence of the fortress. The apparent half-heartedness of the ensuing siege, called off by Władysław on 19 September, has been variously ascribed to the impregnability of the fortifications, high Lithuanian casualties, to Władysław's unwillingness to risk further casualties, or to his desire to keep the Order weakened but undefeated so as to not upset the balance of power between Poland (which would most likely acquire most of the Order possessions if it was totally defeated) and Lithuania; but a lack of sources precludes a definitive explanation.
Dissent
 The war ended in 1411 with the Peace of Thorn, in which neither Poland nor Lithuania drove home negotiating advantages home to the full, much to the discontent of the Polish nobility. Poland regained
The war ended in 1411 with the Peace of Thorn, in which neither Poland nor Lithuania drove home negotiating advantages home to the full, much to the discontent of the Polish nobility. Poland regained Dobrzyń Land
Dobrzyń Land () is a historical region in central-northern Poland. It lies northeast of the Vistula River, south of the Drwęca, and west of the Skrwa. The territory approximately corresponds with the present-day powiats of Lipno, Rypin, and ...
, Lithuania regained Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five ...
, and Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
regained a small territory beyond the Wkra river. Most of the Teutonic Order's territory, however, including towns that had surrendered, remained intact. Władysław then released many high-ranking Teutonic Knights and officials for apparently modest ransoms. The cumulative expense of the ransoms, however, proved a drain on the Order's resources. This failure to exploit the victory to his nobles' satisfaction provoked growing opposition to Władysław's regime after 1411, further fueled by the granting of Podolia
Podolia or Podillia is a historic region in Eastern Europe located in the west-central and southwestern parts of Ukraine and northeastern Moldova (i.e. northern Transnistria).
Podolia is bordered by the Dniester River and Boh River. It features ...
, disputed between Poland and Lithuania, to Vytautas
Vytautas the Great (; 27 October 1430) was a ruler of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was also the prince of Grodno (1370–1382), prince of Lutsk (1387–1389), and the postulated king of the Hussites.
In modern Lithuania, Vytautas is revere ...
, and by the king's two-year absence in Lithuania.
In an effort to outflank his critics, Władysław promoted the leader of the opposing faction, bishop Mikołaj Trąba, to the archbishopric of Gniezno
Gniezno (; ; ) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The city is the administrative seat of Gniezno County (''powiat'') ...
in autumn 1411 and replaced him in Kraków with Vytautas supporter Wojciech Jastrzębiec. He also sought to create more allies in Lithuania. The Union of Horodło
The Union of Horodło or Pact of Horodło was a set of three acts signed in the town of Horodło on 2 October 1413. The first act was signed by Władysław II Jagiełło, King of Poland, and Vytautas, Grand Duke of Lithuania. The second and thir ...
on 2 October 1413 decreed that the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was "tied to our Kingdom of Poland permanently and irreversibly", and granted the Catholic nobles of Lithuania privileges equal to those of Polish szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (; ; ) were the nobility, noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Depending on the definition, they were either a warrior "caste" or a social ...
. The act included a clause prohibiting the Polish nobility from electing a monarch without the consent of the Lithuanian nobility, and the Lithuanian nobility from electing a grand duke without the consent of the Polish monarch.
Last conflicts
In 1414, a sporadic new war broke out, known as the " Hunger War" from the Knights'scorched-earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and i ...
tactics of burning fields and mills; but both the Knights and the Lithuanians were too exhausted from the previous war to risk a major battle, and the fighting petered out in the autumn. Hostilities did not flare up again until 1419, during the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance (; ) was an ecumenical council of the Catholic Church that was held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance (Konstanz) in present-day Germany. This was the first time that an ecumenical council was convened in ...
, when they were called off at the papal legate's insistence.
The Council of Constance proved a turning point in the Teutonic crusades, as it did for several European conflicts. Vytautas sent a delegation in 1415, including the metropolitan of Kiev and Samogitian witnesses; they arrived at Constance at the end of that year to express their preference for being "baptised with water and not with blood". The Polish envoys, among them Mikołaj Trąba, Zawisza Czarny, and Paweł Włodkowic, lobbied for an end to the forced conversion of heathens and to the Order's aggression against Lithuania and Poland. As a result of the Polish–Lithuanian diplomacy, the council, though scandalised by Włodkowic's questioning of the legitimacy of the monastic state, denied the Order's request for a further crusade and instead entrusted the conversion of the Samogitians to Poland–Lithuania.
The diplomatic context at Constance included the revolt of the Bohemian Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century
file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the ...
s, who looked upon Poland as an ally in their wars against Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it ''Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
, the emperor elect and new king of Bohemia. In 1421, the Bohemian Diet declared Sigismund deposed and formally offered the crown to Władysław on condition that he accept the religious principles of the Four Articles of Prague, which he was not prepared to do. After Władysław's refusal, Vytautas was postulated (elected in absentia) as Bohemian king, but he assured the pope that he opposed the heretics. Between 1422 and 1428, Władysław's nephew, Sigismund Korybut, attempted a regency in war-torn Bohemia, with little success. Vytautas accepted Sigismund's offer of a royal crown in 1429—apparently with Władysław's blessing—but Polish forces intercepted the crown in transit and the coronation was cancelled.
In 1422, Władysław fought another war, known as the Gollub War, against the Teutonic Order, defeating them in under two months before the Order's imperial reinforcements had time to arrive. The resulting Treaty of Melno ended the Knights' claims to Samogitia once and for all and defined a permanent border between Prussia and Lithuania. Lithuania was given the province of Samogitia, with the port of Palanga, but the city of Klaipėda
Klaipėda ( ; ) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the List of cities in Lithuania, third-largest city in Lithuania, the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, fifth-largest city in the Baltic States, and the capi ...
was left to the Order. This border remained largely unchanged for roughly 500 years, until 1920. The terms of this treaty have, however, been seen as turning a Polish victory into defeat, as a result of Władysław's renunciation of Polish claims to Pomerania, Pomerelia, and Chełmno Land, for which he received only the town of Nieszawa
Nieszawa (Polish pronunciation: ) is a town and a commune in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. As of June 30, 2014, the town has a population of 1,985 people. It is located in the historic region of Kuyavia.
History
...
in return. The Treaty of Melno closed a chapter in the Knights' wars with Lithuania but did little to settle their long-term issues with Poland. Further sporadic warfare broke out between Poland and the Knights between 1431 and 1435.
Cracks in the cooperation between Poland and Lithuania after the death of Vytautas in 1430 had offered the Knights a revived opportunity for interference in Poland. Władysław supported his brother Švitrigaila
Švitrigaila (before 1370 – 10 February 1452; sometimes spelled Svidrigiello) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1430 to 1432. He spent most of his life in largely unsuccessful dynastic struggles against his cousins Vytautas and Sigismund K� ...
as grand duke of Lithuania, but when Švitrigaila, with the support of the Teutonic Order and dissatisfied Rus' nobles, rebelled against Polish overlordship in Lithuania, the Poles, under the leadership of Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków, occupied Podolia
Podolia or Podillia is a historic region in Eastern Europe located in the west-central and southwestern parts of Ukraine and northeastern Moldova (i.e. northern Transnistria).
Podolia is bordered by the Dniester River and Boh River. It features ...
, which Władysław had awarded to Lithuania in 1411, and Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in ...
. In 1432, a pro-Polish party in Lithuania elected Vytautas's brother Žygimantas as grand duke, leading to an armed struggle over the Lithuanian succession which stuttered on for years after Władysław's death.
Succession and death
At the dying request of the childless Jadwiga, he married aStyria
Styria ( ; ; ; ) is an Austrian Federal states of Austria, state in the southeast of the country. With an area of approximately , Styria is Austria's second largest state, after Lower Austria. It is bordered to the south by Slovenia, and cloc ...
n lady, Anna of Celje. She died in 1416, leaving a daughter:
* Hedwig (1408–1431).
In 1417, Władysław married Elisabeth of Pilica, who died in 1420 without bearing him a child.Two years later, he married Sophia of Halshany (niece of Uliana Olshanska), who bore him two surviving sons : * Władysław (1424–1444) *
Casimir
Casimir is a Latin version of the Polish male name Kazimierz (). The original Polish feminine form is Kazimiera, in Latin and other languages rendered as Casimira. It has two possible meanings: "preacher of peace" or alternatively "destroyer of p ...
(1427–1492)
The death in 1431 of his daughter Hedwig (Jadwiga), the last heir of Piast blood, released Władysław to make his sons by Sophia of Halshany his heirs, though he had to placate the Polish nobility
The ''szlachta'' (; ; ) were the nobility, noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Depending on the definition, they were either a warrior "caste" or a social ...
with concessions to ensure their agreement since the monarchy was elective. In 1427 the Polish nobles had initiated an anti-Jagiellonian movement, seeking to have Władysław and Casimir excluded from the Polish throne as they had no blood link to the previous ruling Polish dynasty, the Piasts.
During an excursion into Przemyśl Land in the 48th year of his reign, Władysław caught a cold from which he was unable to recover. He finally died in Grodek in 1434, leaving Poland to his elder son, Władysław III, and Lithuania to his younger, Casimir, both still minors at the time. The Lithuanian inheritance, however, could not be taken for granted. Władysław's death ended the personal union between the two realms, and it was not clear what would take its place.
Legacy
Władysław is depicted on the obverse of the modernized 100 Polish złoty banknote. The Jagiełło Oak, an ancient tree inBiałowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest is a large forest complex on the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and the largest remaining part of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain. The forest is home to more ...
, is named in honour of the fact that he initiated the tradition of royal hunting in the area.
In 2021, asteroid 2004 TP17 was officially named as Jogaila (the Lithuanian language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of t ...
variant of his name).
Gallery
Effigy
An effigy is a sculptural representation, often life-size, of a specific person or a prototypical figure. The term is mostly used for the makeshift dummies used for symbolic punishment in political protests and for the figures burned in certain ...
of Władysław II Jagiełło at Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral (), formally titled the Archcathedral Basilica of Stanislaus of Szczepanów, Saint Stanislaus and St. Wenceslas, Saint Wenceslaus, () is a Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it ...
in Kraków
File:Uładzisłaŭ Jagajła, Jadwiga Andegaweńska. Уладзіслаў Ягайла, Ядвіга Анжуйская (XVII).jpg, A 17th-century depiction of Władysław II Jagiełło and Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig (from German) and in , was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. Born in Buda, she was the youngest daught ...
by the cross by Tommaso Dolabella
File:Jagajła. Ягайла (M. Godlewski, 1863).jpg, Portrait of Jagiełło holding a cross and sword, by Michał Godlewski, 1863.
File:Władysław Jagiełło (Wizerunki książąt i królów polskich).jpg, Władysław Jagiełło as depicted in Ksawery Pillati's ''Portraits of Polish Princes and Kings'', 1888
File:Wladyslaw II Jagiello (275169).jpg, ''Władysław II Jagiełło'' by Jan Matejko
Jan Alojzy Matejko (; also known as Jan Mateyko; 24 June 1838 – 1 November 1893) was a Polish painter, a leading 19th-century exponent of history painting, known for depicting nodal events from Polish history. His works include large scale ...
, early 1890s
File:The Wladyslaw Jagiello monument in NYC 8.jpg, King Jagiello Monument, Central Park, New York
File:PomnikGrunwaldzki-PlacMatejki-POL, Kraków.jpg, Grunwald Monument, Kraków
Family tree
See also
*History of Lithuania
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categ ...
* History of Poland (1385–1569)
* Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A person ...
* for Jovian asteroid 202093 Jogaila
* List of Lithuanian rulers
The article is a list of heads of state of Lithuania over historical Lithuanian state. The timeline includes all heads of state of Lithuania as a sovereign entity, legitimately part of a greater sovereign entity, a client state, or a Republics o ...
* King Jagiello Monument
* List of Poles
This is a partial list of notable Polish people, Polish or Polish language, Polish-speaking or -writing people. People of partial Polish heritage have their respective ancestries credited.
Physics
*Miedziak Antal
* Czesław Białobrzesk ...
* Monument to Jadwiga and Jagiełło in Kraków
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Wladyslaw 02 Jagiello 14th-century births 1434 deaths Year of birth uncertain 14th-century Polish monarchs 15th-century Polish monarchs Adult adoptees Burials at Wawel Cathedral Converts to Roman Catholicism from pagan religions Gediminids Grand dukes of Lithuania Jagiellonian dynasty Kings of Poland Remarried jure uxoris kings Jure uxoris kings Lithuanian former pagans Lithuanian Roman Catholics Order of the Dragon People from Vilnius People in the Battle of Grunwald Polish Roman Catholics