|
Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest is a large forest complex on the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and the largest remaining part of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain. The forest is home to more than 800 European bison, Europe's heaviest land animal. UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme designated the Polish Białowieża National Park, Biosphere Reserve as ' in 1976, and the Belarusian Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, Biosphere Reserve as ' in 1993. In 2015, the Belarusian Biosphere Reserve spanned , subdivided into transition, buffer and core zones. The forest has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site and an EU Natura 2000 Special Area of Conservation. The World Heritage Committee, through its decision of June 2014, approved the extension of the UNESCO World Heritage site "Belovezhskaya Pushcha / Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Poland", which became "Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Poland". It straddles the border bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to that region. The capital and largest city is Białystok. It borders the Masovian Voivodeship to the west, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the northwest, Lublin Voivodeship to the south, Belarus to the east, and Lithuania to the northeast. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, from the former Białystok Voivodeship (1975–98), Białystok and Łomża Voivodeships and the eastern half of the former Suwałki Voivodeship. Etymology The voivodeship takes its name from the Polish historical regions, historic region of Poland called ''Podlasie'', or in Latin known as Podlachia. There are two opinions regarding the origin of the region's name. People often derive it from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podlachia
Podlachia, also known by its Polish name Podlasie (; ; ), is a historical region in north-eastern Poland. Its largest city is Białystok, whereas the historical capital is Drohiczyn. Similarly to several other historical regions of Poland, e.g. Greater Poland, Lesser Poland, Mazovia, Pomerania, Silesia, Warmia, Podlachia possesses its own folk costumes, unique traditional architecture and cuisine. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the capital in Drohiczyn. Now the part north of the Bug River is included in the modern Podlaskie Voivodeship with the capital in Białystok, whereas southern parts are located in the Masovian and Lublin Voivodeships. Names and etymology The region is called , or in Polish, in Lithuanian, ''Padliašša'' (Падляшша) in Belarusian, ''Podljas’e'' (Подлясье) in Russian, פּאָדליאַשע ''Podlyashe'' in Yiddish, and in Latin. There are two hypotheses regarding the origin of the name of the region. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition of Poland, First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772, after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition of Poland, Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition of Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". Tsar and its variants were the official titles in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), the Kingdom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), the Serbian Empire (1346–1371), and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). The first ruler to adopt the title ''tsar'' was Simeon I of Bulgaria. Simeon II, the last tsar of Bulgaria, is the last person to have held this title. Meaning in Slavic languages The title tsar is derived from the Latin title for the Roman emperors, ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puszcza Białowieska - Orientacyjne Położenie
Puszcza is a Polish term for a large forest. It may also refer to the following villages: * Puszcza, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (north-central Poland) * Puszcza, Łódź Voivodeship (central Poland) * Puszcza, Lublin Voivodeship (east Poland) * Puszcza, Masovian Voivodeship (east-central Poland) * Puszcza, Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland) * Puszcza, Lubusz Voivodeship (west Poland) See also * {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution Of The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, formally establishing the dissolution of the Soviet Union as a state and subject of international law. It also brought an end to the Soviet Union's federal government and General Secretary (also President) Mikhail Gorbachev's effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of 15 top-level republics that served as the homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Language
Belarusian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language. It is one of the two Languages of Belarus, official languages in Belarus, the other being Russian language, Russian. It is also spoken in parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Ukraine, and the United States by the Belarusian diaspora. Before Belarus Dissolution of the Soviet Union, gained independence in 1991, the language was known in English language, English as ''Byelorussian'' or ''Belorussian'', or alternatively as ''White Russian''. Following independence, it became known as ''Belarusian'', or alternatively as ''Belarusan''. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Belarusian descends from a language generally referred to as Ruthenian language, Ruthenian (13th to 18th centuries), which had, in turn, descend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th to 18th centuries). The first Polish ruler whose existence is not debatable was Mieszko I, Duke Mieszko I, who Christianization of Poland, adopted Christianity under the authority of Rome in the year 966. He was succeeded by his son, Bolesław I the Brave, who greatly expanded the boundaries of the Polish state and ruled as the first king in 1025. The following centuries gave rise to the mighty Piast dynasty, consisting of both kings such as Mieszko II Lambert, Przemysł II or Władysław I the Elbow-high and dukes like Bolesław III Wrymouth. The dynasty's rule over Poland ceased with the death of Casimir III the Great in 1370. In the same year, the Capetian House of Anjou became the ruling house with Louis I t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke Of Lithuania
This is a list of Lithuanian monarchs who ruled Lithuania from its inception until the fall of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1795. The Lithuanian monarch bore the title of Grand duke, Grand Duke, with the exception of Mindaugas, who was crowned king in 1253. Other Lithuanian rulers, such as Vytautas the Great, also attempted to secure a royal coronation, but these efforts were unsuccessful.Nadveckė, Ineta (6 July 2019Trys Lietuvos karaliai: vienas tikras, vienas nelabai ir vienas beveik''Lithuanian National Radio and Television, LRT''. Until 1569, the Lithuanian monarchy was hereditary. In 1386, Grand Duke Jogaila was elected King of Poland. From that point onward, with some interruptions, the two states were united in a personal union, sharing a common ruler until 1569, when they were formally merged by the Union of Lublin to form the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The monarch of this new state was elected in a free election by the entire nobility. From the Christianizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
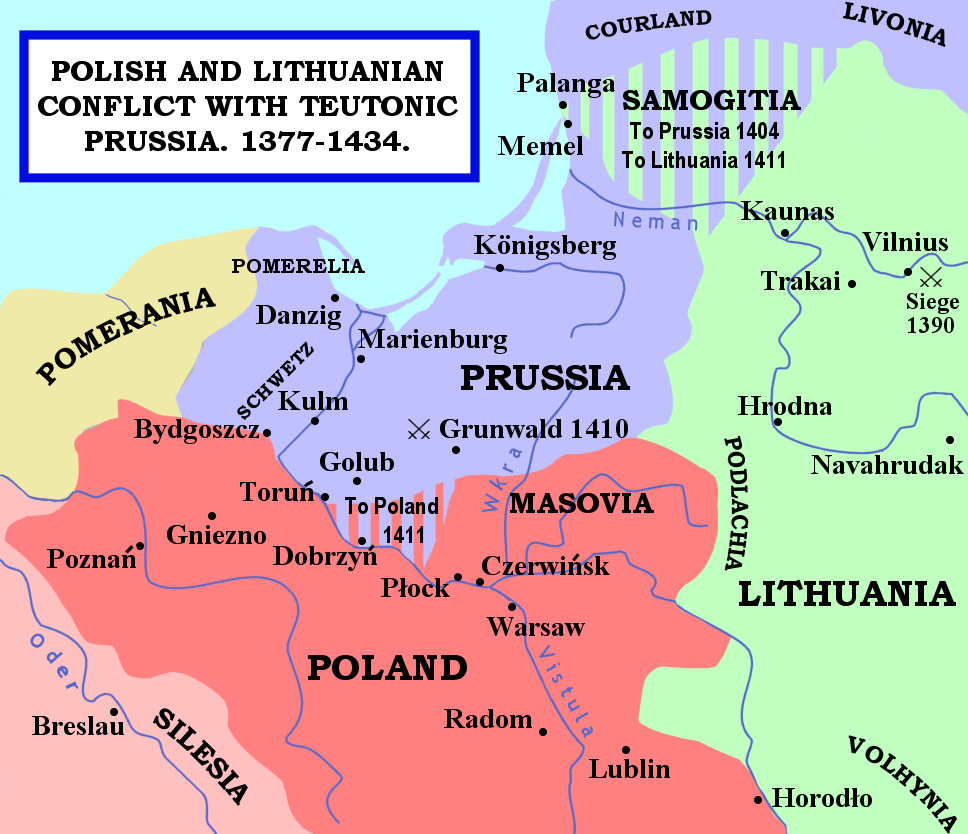
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło (),Other names include (; ) (see also Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło) was Grand Duke of Lithuania beginning in 1377 and starting in 1386, becoming King of Poland as well. As Grand Duke, he ruled Lithuania from 1377 to 1381 and from 1382 to 1401, at which time he became the Supreme Duke of Lithuania in exchange for naming his cousin Vytautas as the new Grand Duke. Władysław II initially served as King of Poland alongside his wife Jadwiga of Poland, Jadwiga until her death in 1399, and then the sole ruler until his own death in 1434. Raised a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and baptized as Ladislaus () in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he Christianization of Lithuania, converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |