

In
urban planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportatio ...
, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of
city
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
plan in which
street
A street is a public thoroughfare in a city, town or village, typically lined with Building, buildings on one or both sides. Streets often include pavements (sidewalks), pedestrian crossings, and sometimes amenities like Street light, streetligh ...
s run at
right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s to each other, forming a
grid
Grid, The Grid, or GRID may refer to:
Space partitioning
* Regular grid, a tessellation of space with translational symmetry, typically formed from parallelograms or higher-dimensional analogs
** Grid graph, a graph structure with nodes connec ...
.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogonal geometry, facilitate movement. The geometry helps with orientation and
wayfinding
Wayfinding (or way-finding) encompasses all of the ways in which people (and animals) Orientation (mental), orient themselves in physical space and navigation, navigate from place to place.
Wayfinding software is a self-service computer program th ...
and its frequent intersections with the choice and directness of route to desired destinations.
In
ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, the grid plan method of land measurement was called
centuriation
Centuriation (in Latin ''centuriatio'' or, more usually, ''limitatio''), also known as Roman grid, was a method of land measurement used by the Romans. In many cases land divisions based on the survey formed a field system, often referred to in m ...
. The grid plan dates from antiquity and originated in multiple cultures; some of the earliest
planned cities
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
were built using grid plans in the Indian subcontinent.
History
Ancient grid plans
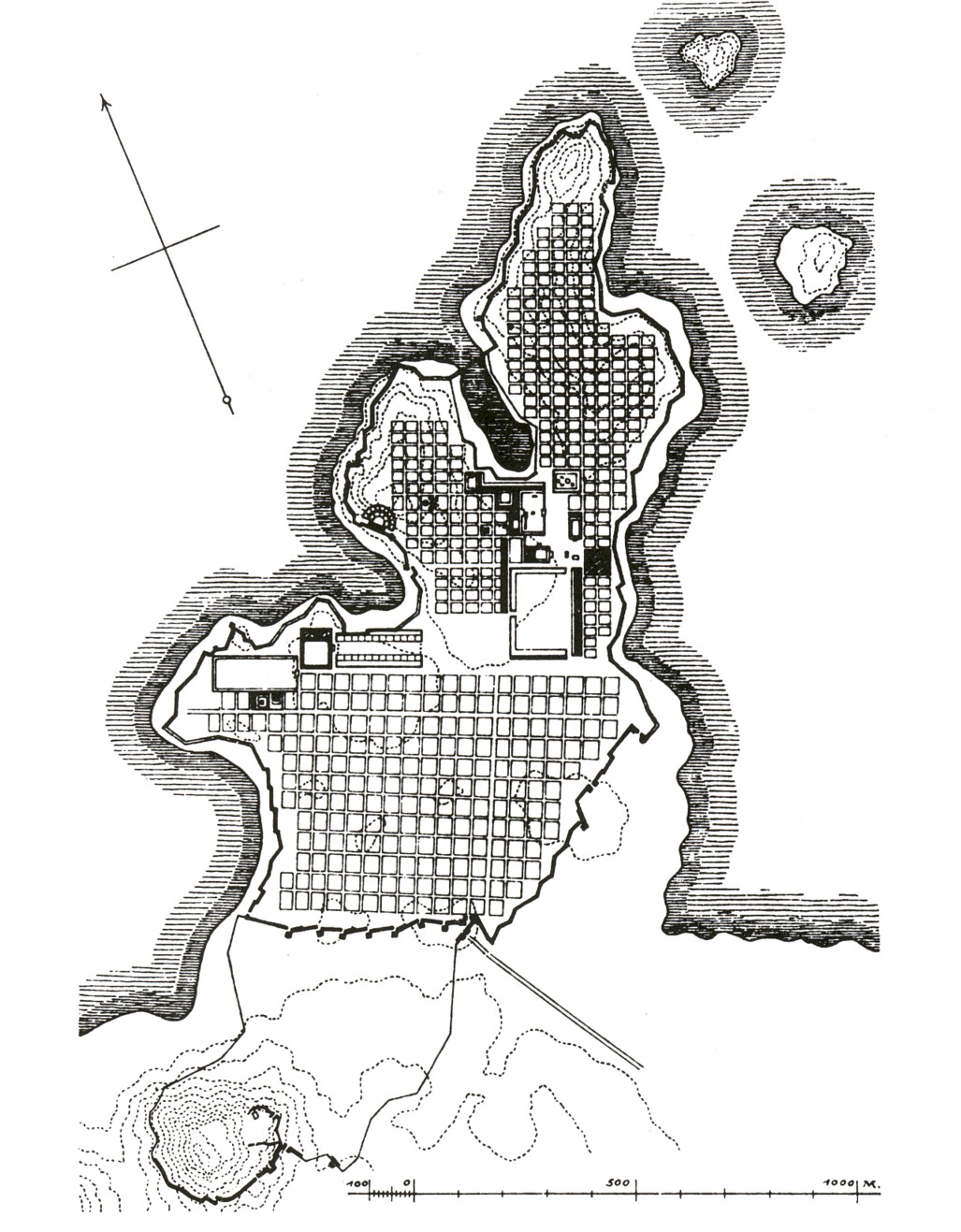
By 2600 BC,
Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; , ; ) is an archaeological site in Larkana District, Sindh, Pakistan. Built 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation, and one of the world's earliest major city, cities, contemp ...
and
Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
, major cities of the
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
, were built with blocks divided by a grid of straight streets, running north–south and east–west. Each block was subdivided by small lanes. The cities and monasteries of
Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
,
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the ...
and
Thimi (in the
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
and
Kathmandu Valley
The Kathmandu Valley (), also known as the Nepal Valley or Nepa Valley (, Newar language, Nepal Bhasa: 𑐣𑐾𑐥𑐵𑑅 𑐐𑐵𑑅, नेपाः गाः), National Capital Area, is a bowl-shaped valley located in the Himalayas, Hima ...
s), dating from the 1st millennium BC to the 11th century AD, also had grid-based designs.
A workers' village (2570–2500 BC) at
Giza
Giza (; sometimes spelled ''Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza''; , , ' ) is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of ...
,
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, housed a rotating labor force and was laid out in blocks of long galleries separated by streets in a formal grid. Many pyramid-cult cities used a common orientation: a north–south axis from the royal palace and an east–west axis from the temple, meeting at a central plaza where King and God merged and crossed.
Hammurabi
Hammurabi (; ; ), also spelled Hammurapi, was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered the ci ...
king of the
Babylonian Empire
Babylonia (; , ) was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorite-ru ...
in the 18th century BC, ordered the rebuilding of
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
: constructing and restoring temples, city walls, public buildings, and irrigation canals. The streets of Babylon were wide and straight, intersected approximately at right angles, and were paved with bricks and
bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
.
The tradition of grid plans is continuous in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
from the 15th century BC onward in the
traditional urban planning of various ancient Chinese states. Guidelines put into written form in the
Kaogongji
The ''Kaogongji'', ''Kaogong Ji'', or ''Kao Gong Ji'', variously translated as ''The Record of Trades'', ''Records of Examination of Craftsman'', ''Book of Diverse Crafts'', and ''The Artificers' Record'', is an ancient Chinese work on science a ...
during the
Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject t ...
(770-476 BC) stated: "a capital city should be square on plan. Three gates on each side of the perimeter lead into the nine main streets that crisscross the city and define its grid-pattern. And for its layout the city should have the Royal Court situated in the south, the Marketplace in the north, the Imperial Ancestral Temple in the east and the Altar to the Gods of Land and Grain in the west."
Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is ...
, near modern-day
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, is the largest ancient grid-plan site in the
Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
. The city's grid covered 21 square kilometres (8 square miles).
Perhaps the most well-known grid system is that spread through the colonies of the Roman Empire. The archetypal
Roman Grid was introduced to Italy first by the Greeks, with such information transferred by way of trade and conquest.
[Stanislawski, Dan (1946). "The Grid-Pattern Town", Geog. Rev., xxxvi, pp. 105-120, p. 116.]
Ancient Greece
Although the idea of the grid was present in Hellenic societal and city planning, it was not pervasive prior to the 5th century BC. However, it slowly gained primacy through the work of
Hippodamus of Miletus
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; c. 480– 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to ...
(498–408 BC), who planned and replanned many Greek cities in accordance with this form.
[Burns, Ross (2005), ''Damascus: A History'', Routledge, p. 39] The concept of a grid as the ideal method of town planning had become widely accepted by the time of Alexander the Great. His conquests were a step in the propagation of the grid plan throughout colonies, some as far-flung as Taxila in Pakistan,
that would later be mirrored by the expansion of the Roman Empire. The Greek grid had its streets aligned roughly in relation to the cardinal points
and generally looked to take advantage of visual cues based on the hilly landscape typical of Greece and Asia Minor.
[Higgins, Hannah (2009) ''The Grid Book''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. p.60. ] The street grid consisted of ''plateiai'' and ''stenophoi'' (equivalent to Roman ''
decumani'' and ''
cardines''). This was probably best exemplified in
Priene
Priene (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called the Büyük Menderes Rive ...
, in present-day western Turkey, where the orthogonal city grid was based on the cardinal points, on sloping terrain that struck views out towards a river and the city of
Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ...
.
Ancient Rome

The
Etruscan people, whose territories in Italy encompassed what would eventually become Rome, founded what is now the city of
Marzabotto at the end of the 6th century BC. Its layout was based on Greek Ionic ideas, and it was here that the main east–west and north–south axes of a town (the ''decumanus maximus'' and ''cardo maximus'' respectively) could first be seen in Italy. According to Stanislawski (1946), the Romans did use grids until the time of the late Republic or early Empire, when they introduced ''
centuriation
Centuriation (in Latin ''centuriatio'' or, more usually, ''limitatio''), also known as Roman grid, was a method of land measurement used by the Romans. In many cases land divisions based on the survey formed a field system, often referred to in m ...
'', a system which they spread around the Mediterranean and into northern Europe later on.
The military expansion of this period facilitated the adoption of the grid form as standard: the Romans established ''
castra
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified milita ...
'' (forts or camps) first as military centres; some of them developed into administrative hubs. The Roman grid was similar in form to the Greek version of a grid but allowed for practical considerations. For example, Roman ''castra'' were often sited on flat land, especially close to or on important nodes like river crossings or intersections of trade routes.
The dimensions of the ''castra'' were often standard, with each of its four walls generally having a length of . Familiarity was the aim of such standardisation: soldiers could be stationed anywhere around the Empire, and orientation would be easy within established towns if they had a standard layout. Each would have the aforementioned ''
decumanus maximus
In Roman urban planning, a ''decumanus'' was an east–west-oriented road in a Roman city or '' castrum'' (military camp). The main ''decumanus'' of a particular city was the ''decumanus maximus'', or most often simply "the ''decumanus''". In t ...
'' and ''
cardo maximus
A ''cardo'' (: ''cardines'') was a north–south street in ancient Roman cities and military camps as an integral component of city planning. The ''cardo maximus'', or most often the ''cardo'', was the main or central north–south-oriented str ...
'' at its heart, and their intersection would form the forum, around which would be sited important public buildings. Indeed, such was the degree of similarity between towns that Higgins states that soldiers "would be housed at the same address as they moved from ''castra'' to ''castra''".
Pompeii has been cited by both Higgins
and Laurence as the best-preserved example of the Roman grid.
Outside of the castra, large tracts of land were also divided in accordance with the grid within the walls. These were typically per side (called
''centuria'') and contained 100 parcels of land (each called
''heredium'').
[Gelernter, Mark (2001), ''A history of American architecture: buildings in their cultural and technological context'', p. 15.] The ''decumanus maximus'' and ''cardo maximus'' extended from the town gates out towards neighbouring settlements. These were lined up to be as straight as possible, only deviating from their path due to natural obstacles that prevented a direct route.
While the imposition of only one town form regardless of region could be seen as an imposition of imperial authority, there is no doubting the practical reasoning behind the formation of the Roman grid. Under Roman guidance, the grid was designed for efficiency and interchangeability, both facilitated by and aiding the expansion of their empire.
Asia from the first millennium AD

As
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and the
Korean peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
became politically centralized in the 7th century AD, those societies adopted Chinese grid-planning principles in numerous locations. In Korea,
Gyeongju
Gyeongju (, ), historically known as Seorabeol (, ), is a coastal city in the far southeastern corner of North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. It is the second largest city by area in the province after Andong, covering with a population of ...
, the capital of
Unified Silla
Unified Silla, or Late Silla, is the name often applied to the historical period of the Korean kingdom of Silla after its conquest of Goguryeo in 668 AD, which marked the end of the Three Kingdoms period. In the 7th century, a Silla–Tang alli ...
, and
Sanggyeong, the capital of
Balhae
Balhae,, , ) also rendered as Bohai or Bohea, and called Jin (; ) early on, was a multiethnic kingdom established in 698 by Dae Joyeong (Da Zuorong). It was originally known as the Kingdom of Jin (震, Zhen) until 713 when its name was changed ...
, adapted the
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
Chinese model. The ancient capitals of Japan, such as
Fujiwara-Kyô (AD 694–710),
Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an independent agency of the United States government within the executive branch, charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It is also task ...
(Heijô-Kyô, AD 710–784), and
Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
(Heian-Kyô, AD 794–1868) also adapted from Tang's capital,
Chang'an
Chang'an (; zh, t=長安, s=长安, p=Cháng'ān, first=t) is the traditional name of the city now named Xi'an and was the capital of several Chinese dynasties, ranging from 202 BCE to 907 CE. The site has been inhabited since Neolithic time ...
. However, for reasons of defense, the planners of
Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
eschewed the grid, opting instead for an irregular network of streets surrounding the
Edo Castle
is a flatland castle that was built in 1457 by Ōta Dōkan in Edo, Toshima District, Musashi Province. In modern times it is part of the Tokyo Imperial Palace in Chiyoda, Tokyo, and is therefore also known as .
Tokugawa Ieyasu established th ...
grounds. In later periods, some parts of Tokyo were grid-planned, but grid plans are generally rare in Japan, and the
Japanese addressing system
The Japanese addressing system is used to identify a specific location in Japan.
When written in Japanese characters, addresses start with the largest geographical entity and proceed to the most specific one. The Japanese system is complex, the ...
is accordingly based on increasingly fine subdivisions, rather than a grid.
The grid-planning tradition in Asia continued through the beginning of the 20th century, with
Sapporo
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in Hokkaido, Japan. Located in the southwest of Hokkaido, it lies within the alluvial fan of the Toyohira River, a tributary of the Ishikari River. Sapporo is the capital ...
, Japan (est. 1868) following a grid plan under American influence.
Europe and its colonies (12th-17th centuries)
New
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an towns were planned using grids beginning in the 12th century, most prodigiously in the
bastides
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the 13th and 14th centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the first bastides ...
of southern
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
that were built during the 13th and 14th centuries. Medieval European
new town
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz (South Korean band), The Boyz
* New (album), ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** New (Paul McCartney song), "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* New (EP), ''New'' (EP), ...
s using grid plans were widespread, ranging from
Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
to the
Florentine region. Many were built on ancient grids originally established as Roman colonial outposts. In the British Isles, the planned new town system involving a grid street layout was part of the system of
burgage
Burgage is a medieval land term used in Great Britain and Ireland, well established by the 13th century.
A burgage was a town ("borough" or "burgh") rental property (to use modern terms), owned by a king or lord. The property ("burgage tenement ...
. An example of a medieval planned city in The Netherlands is
Elburg.
Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as ''Bury,'' is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk District, West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St. Edmunds an ...
is an example of a town planned on a grid system in the late 11th century.
The Roman model was also used in Spanish settlements during the
Reconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
of Ferdinand and Isabella. It was subsequently applied in the new cities established during the
Spanish colonization of the Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began in 1493 on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (now Haiti and the Dominican Republic) after the initial 1492 voyage of Genoa, Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus under license from Queen Isabella ...
, after the founding of
San Cristóbal de La Laguna
San Cristóbal de La Laguna (commonly known as La Laguna, ) is a city and municipality in the northern part of the island of Tenerife in the Province of Santa Cruz de Tenerife, on the Canary Islands, Spain. The former capital of the Canary Islan ...
(Canary Islands) in 1496. In 1573, King Philip II of Spain compiled the Laws of the Indies to guide the construction and administration of colonial communities. The Laws specified a square or rectangular central plaza with eight principal streets running from the plaza's corners. Hundreds of grid-plan communities throughout the Americas were established according to this pattern, echoing the practices of earlier Indian civilizations.
The
baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
capital city of
Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
,
Valletta
Valletta ( ; , ) is the capital city of Malta and one of its 68 Local councils of Malta, council areas. Located between the Grand Harbour to the east and Marsamxett Harbour to the west, its population as of 2021 was 5,157. As Malta’s capital ...
, dating back to the 16th century, was built following a rigid grid plan of uniformly designed houses, dotted with palaces, churches and squares.
The grid plan became popular with the start of the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
in Northern Europe. In 1606, the newly founded city of
Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (), is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, second-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, the States of Ger ...
in
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
was the first Renaissance city laid out on the grid plan. Later came the New Town in
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
and almost the entire city centre of
Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
, and many
planned communities
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
and cities in
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
,
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry, is the second-largest City status in the United Kingdom, city in Northern Ireland, and the fifth-largest on the island of Ireland. Located in County Londonderry, the city now covers both banks of the River Fo ...
, constructed in 1613–1618, was the first
planned city
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
in
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
. The central diamond within a walled city with four gates was considered a good design for defence. The grid pattern was widely copied in the colonies of
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
.
Russia (18th century)

In
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
the first
planned city
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
was
St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
founded in 1703 by
Peter I. Being aware of the modern European construction experience which he examined in the years of his
Grand Embassy to Europe, the Czar ordered
Domenico Trezzini
Domenico Trezzini (; – 1734) was an Italian Swiss architect who elaborated the Petrine Baroque style of Russian architecture.
Biography
Domenico was born in Astano, Landvogtei of Lugano (at that time a condominium of the Old Swiss C ...
to elaborate the first general plan of the city. The project of this architect for
Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in Saint Petersburg, St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva River, Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south and northeast ...
was a typical rectangular grid of streets (originally intended to be canals, like in
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
), with three lengthwise thoroughfares, rectangularly crossed with about 30 crosswise streets.
The shape of street blocks on
Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in Saint Petersburg, St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva River, Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south and northeast ...
are the same, as was later implemented in the
Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march upto ...
for
Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
: elongated rectangles. The longest side of each block faces the relatively narrow street with a numeric name (in Petersburg they are called
''Liniya'' (Line)) while the shortest side faces wide avenues. To denote avenues in Petersburg, a special term ''
prospekt'' was introduced. Inside the grid of Vasilyevsky Island there are three prospekts, named ''Bolshoi'' (''Big''), ''Sredniy ''(''Middle'') and ''Maly'' (''Small'') while the far ends of each line cross with the embankments of
Bolshaya Neva
The Great Neva or Bolshaya Neva () is the largest armlet of the river Neva. It starts near the Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange and Rostral Columns, Spit of Vasilievsky Island (easternmost tip of the island).
The Great Neva is long; the width ...
and
Smolenka rivers in the delta of the
Neva River
The Neva ( , ; , ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it is the fourth-l ...
.
The peculiarity of 'lines' (streets) naming in this grid is that are each side of street has its own number, so one 'line' is a side of a street, not the whole street. The numbering is latently zero-based, however the supposed "zero line" has its proper name ''Kadetskaya liniya'', while the opposite side of this street is called the '1-st Line'. Next street is named the '2-nd Line' on the eastern side, and the '3-rd Line' on the western side. After the reorganization of house numbering in 1834 and 1858 the even house numbers are used on the odd-numbered lines, and respectively odd house numbers are used for the even-numbered lines. The maximum numbers for 'lines' in Petersburg are 28-29th lines.
Later in the middle of the 18th century another grid of rectangular blocks with the numbered streets appeared in the continental part of the city: 13 streets named from the '1-st Rota' up to the '13-th Rota', where the
companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether natural, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specifi ...
(, ) of the
Izmaylovsky Regiment were located.
Early United States (17th-19th centuries)



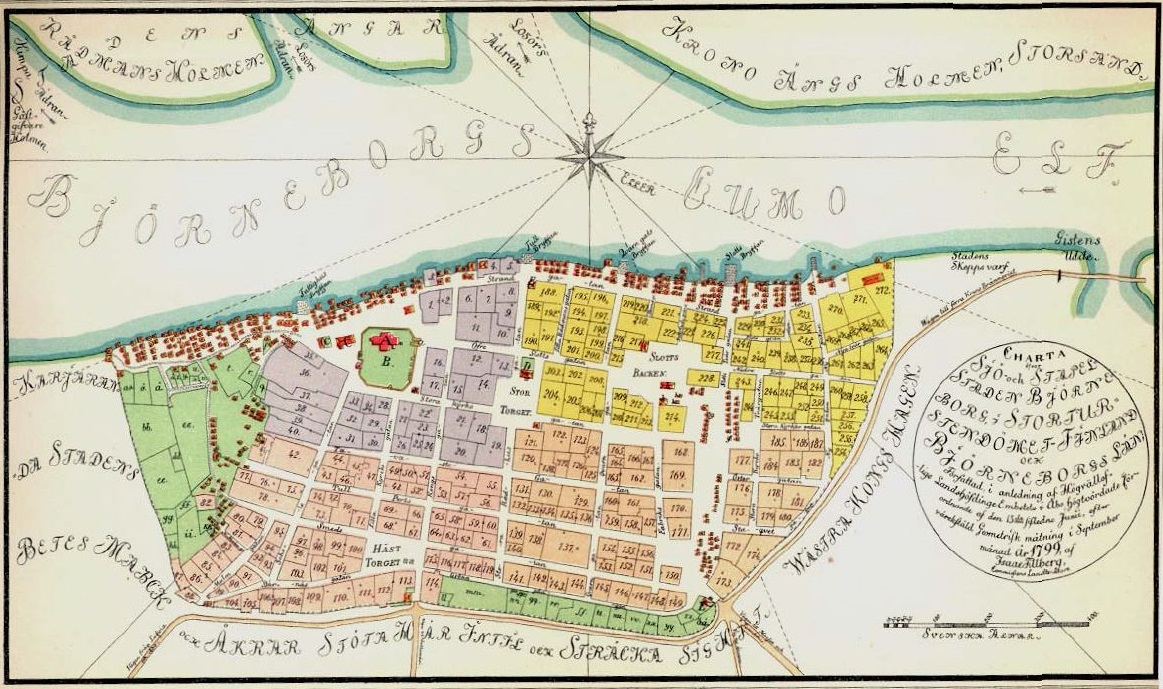
Many of the earliest cities in the United States, such as
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, did not start with a grid system. However, even in pre-revolutionary days some cities saw the benefits of such a layout.
New Haven Colony
New Haven Colony was an English colony from 1638 to 1664 that included settlements on the north shore of Long Island Sound, with outposts in modern-day New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware. The colony joined Connecticut Colony in 16 ...
, one of the earliest colonies in America, was designed with a tiny 9-square grid at its founding in 1638. On a grander scale,
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
was designed on a rectilinear street grid in 1682, one of the first cities in North America to use a grid system.
At the urging of city founder
William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
, surveyor
Thomas Holme
Thomas Holme (1624–1695) was the first surveyor general of the colonial-era Province of Pennsylvania. He laid out the first and original plan for the city of Philadelphia. Holme was a member of the Valiant Sixty, a group of early leaders and ...
designed a system of wide streets intersecting at right angles between the
Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river in eastern Pennsylvania. It flows for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map(). accessed April 1, 2011. from Pottsville, Pennsylvania, Pottsville ...
to the west and the
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
to the east, including five squares of dedicated parkland. Penn advertised this orderly design as a safeguard against overcrowding, fire, and disease, which plagued European cities. Holme drafted an ideal version of the grid, but alleyways sprouted within and between larger blocks as the city took shape. As the United States expanded westward, grid-based city planning modeled on Philadelphia's layout would become popular among frontier cities, making grids ubiquitous across the country.
Another well-known grid plan is the plan for
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
formulated in the
Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march upto ...
, a proposal by the state
legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
of
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
for the development of most of
Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
above
Houston Street
Houston Street ( ) is a major east–west thoroughfare in Lower Manhattan in New York City, New York. It runs the full width of the island of Manhattan, from FDR Drive along the East River in the east to the West Side Highway along the Hudson ...
.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, the capital of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, was planned under
French-American architect
Pierre Charles L'Enfant
Pierre "Peter" Charles L'Enfant (; August 2, 1754June 14, 1825) was a French-American artist, professor, and military engineer. In 1791, L'Enfant designed the baroque-styled plan for the development of Washington, D.C., after it was designated ...
. Under the L'Enfant plan, the original
District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
was developed using a grid plan that is interrupted by diagonal avenues, most famously
Pennsylvania Avenue
Pennsylvania Avenue is a primarily diagonal street in Washington, D.C. that connects the United States Capitol with the White House and then crosses northwest Washington, D.C. to Georgetown (Washington, D.C.), Georgetown. Traveling through So ...
. These diagonals are often connected by
traffic circle
A roundabout, a rotary and a traffic circle are types of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junct ...
s, such as
Dupont Circle
Dupont Circle is a historic roundabout park and Neighborhoods in Washington, D.C., neighborhood of Washington, D.C., located in Northwest (Washington, D.C.), Northwest D.C. The Dupont Circle neighborhood is bounded approximately by 16th St ...
and
Washington Circle. As the city grew, the plan was duplicated to cover most of the remainder of the capital. Meanwhile, the core of the city faced disarray and the
McMillan Plan
The McMillan Plan (formally titled The Report of the Senate Park Commission. The Improvement of the Park System of the District of Columbia) is a comprehensive planning document for the development of the monumental core and the park system of Was ...
, led by Senator
James McMillan, was adopted to build a
National Mall
The National Mall is a Landscape architecture, landscaped park near the Downtown, Washington, D.C., downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums of the Smithsonian Institu ...
and a parks system that is still today a jewel of the city.
Often, some of the streets in a grid are numbered (First, Second, etc.), lettered, or arranged in alphabetical order. Downtown
San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
uses all three schemes: north–south streets are numbered from west to east, and east–west streets are split between a lettered series running southward from A through L and a series of streets named after trees or plants, running northward alphabetically from Ash to Walnut. As in many cities, some of these streets have been given new names violating the system (the former D Street is now Broadway, the former 12th Avenue is now Park Boulevard, etc.); this has meant that 2nd, not 1st, is the most common street name in the United States.
An exception to the typical, uniform grid is the plan of
Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Brita ...
(1733), known as the
Oglethorpe Plan. It is a composite, cellular city block consisting of four large corner blocks, four small blocks in between and a public square in the centre; the entire composition of approximately ten acres (four hectares) is known as a ward. Its cellular structure includes all the primary land uses of a neighborhood and has for that reason been called
fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scale ...
. Its street configuration presages modern traffic calming techniques applied to uniform grids where certain selected streets become discontinuous or narrow, thus discouraging through traffic. The configuration also represents an example of functional
shared space
Shared space is an urban design approach that minimises the segregation between modes of road user. This is done by removing features such as curb (road), curbs, road surface markings, traffic signs, and traffic lights. Hans Monderman and othe ...
, where pedestrian and vehicular traffic can safely and comfortably coexist.
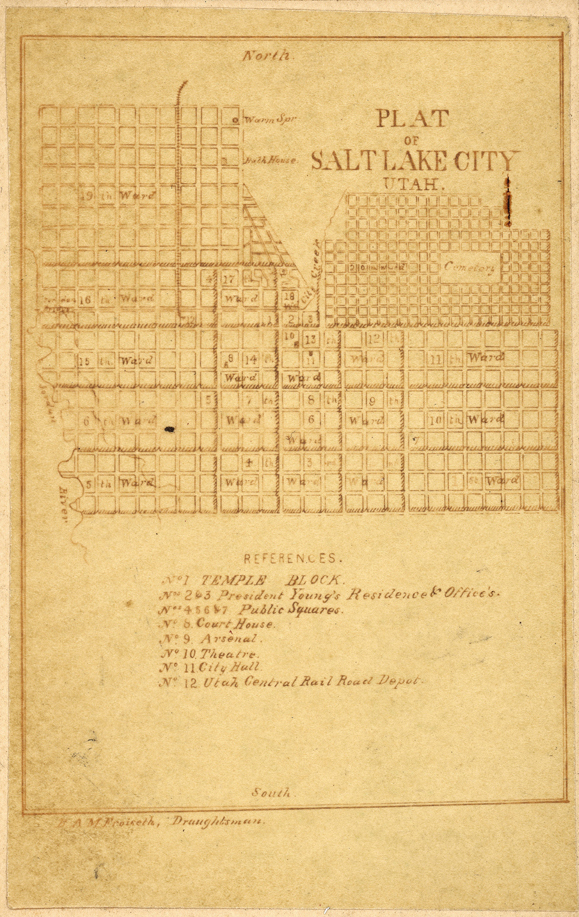
In the westward development of the United States, the use of the grid plan was nearly universal in the construction of new settlements, such as in
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
(1870),
Dodge City
Dodge City is a city in and the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. It was named after nearby Fort Dodge, which was named in honor of Grenville Dodge. The city ...
(1872) and
Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Oklahoma, most populous city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat ...
(1890). In these western cities the streets were numbered even more carefully than in the east to suggest future prosperity and metropolitan status.
One of the main advantages of the grid plan was that it allowed the rapid
subdivision
Subdivision may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Subdivision (metre), in music
* ''Subdivision'' (film), 2009
* "Subdivision", an episode of ''Prison Break'' (season 2)
* ''Subdivisions'' (EP), by Sinch, 2005
* "Subdivisions" (song), by Rush ...
and
auction
An auction is usually a process of Trade, buying and selling Good (economics), goods or Service (economics), services by offering them up for Bidding, bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from th ...
of a large parcel of land. For example, when the legislature of the
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
decided in 1839 to move the capital to a new site along the
Colorado River
The Colorado River () is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The river, the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), 5th longest in the United St ...
, the functioning of the government required the rapid population of the town, which was named
Austin
Austin refers to:
Common meanings
* Austin, Texas, United States, a city
* Austin (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin (surname), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin Motor Company, a British car manufac ...
. Charged with the task,
Edwin Waller
Edwin Leonard Waller (November 4, 1800 – January 3, 1881) was an American businessman, signer of the Texas Declaration of Independence, the first mayor of Austin, Texas, and the designer of its downtown grid plan.
Texas independence
He ...
designed a fourteen-block grid that fronted the river on 640 acres (exactly 1 square mile; about 2.6 km
2). After surveying the land, Waller organized the almost immediate sale of 306 lots, and by the end of the year the entire Texas government had arrived by
oxcart at the new site. Apart from the speed of surveying advantage, the rationale at the time of the grid's adoption in this and other cities remains obscure.
Early 19th century – Australasia
In 1836
William Light
William Light (27 April 1786 – 6 October 1839) was a British military officer and colonial administrator. He was the first Surveyor General of South Australia, Surveyor-General of the History of South Australia#British preparation for est ...
drew up his plans for
Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to ei ...
, South Australia, spanning the
River Torrens
The River Torrens (Karrawirra Parri / Karrawirraparri) is the most significant river of the Adelaide Plains. It was one of the main reasons for the siting of the city of Adelaide, capital of South Australia. It flows from its source in the Ad ...
. Two areas south (
the city centre) and north (
North Adelaide
North Adelaide is a predominantly residential precinct (Australia), precinct and suburb of the City of Adelaide in South Australia, situated north of the River Torrens and within the Adelaide Park Lands. Laid out in a grid plan in three section ...
) of the river were laid out in grid pattern, with the city surrounded by the
Adelaide Park Lands
The Adelaide Park Lands comprise the figure-eight configuration of land, spanning both banks of the River Torrens between Hackney and Thebarton, which encloses and separates the City of Adelaide area (including both the Adelaide city centre and ...
.
Hoddle Grid
The Hoddle Grid is the contemporary name given to the approximately grid of streets that form the Melbourne central business district, Australia. Bounded by Flinders Street, Spring Street, La Trobe Street, and Spencer Street, it lies at a ...
is the name given to the layout of
Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, Victoria, named after the surveyor
Robert Hoddle
Robert Hoddle (21 April 1794 – 24 October 1881)
was a surveyor and artist. He was the first Surveyor-General of Victoria from 1851 to 1853. He was previously the Surveyor-in-Charge of the Port Phillip District from 1837 to 1851. He became ...
, who marked it out in 1837 establishing the first formal town plan. This grid of streets, laid out when there were only a few hundred settlers, became the nucleus for what is now a city of over 5 million people, the city of Melbourne. The unusual dimensions of the allotments and the incorporation of narrow 'little' streets were the result of compromise between Hoddle's desire to employ the regulations established in 1829 by previous
New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
Governor Ralph Darling, requiring square blocks and wide, spacious streets and Bourke's desire for rear access ways (now the 'little' streets, for example
Little Collins Street
Little Collins Street is a minor road, street in the Melbourne central business district, Victoria, Australia.
The street runs parallel to and to the north of Collins Street, Melbourne, Collins Street and as a narrow one way lane takes on the ...
).
The city of
Christchurch
Christchurch (; ) is the largest city in the South Island and the List of cities in New Zealand, second-largest city by urban area population in New Zealand. Christchurch has an urban population of , and a metropolitan population of over hal ...
, New Zealand, was planned by
Edward Jollie in 1850.
Town acre
The term "town acre" (often spelt with initial capital letters) may have originated with
Edward Gibbon Wakefield
Edward Gibbon Wakefield (20 March 179616 May 1862) was an English politician in colonial Canada and New Zealand. He is considered a key figure in the establishment of the colonies of South Australia and New Zealand (where he later served as a ...
who, in the 1830s, was involved in various schemes to promote the
colonisation of South Australia
British colonisation of South Australia describes the planning and establishment of the colony of South Australia by the British government, covering the period from 1829, when the idea was raised by the then-imprisoned Edward Gibbon Wakefield, ...
and its capital,
Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to ei ...
,
and, as founder of the
New Zealand Company
The New Zealand Company, chartered in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, was a company that existed in the first half of the 19th century on a business model that was focused on the systematic colonisation of New Ze ...
, the plans for
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
,
New Plymouth
New Plymouth () is the major city of the Taranaki region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after the English city of Plymouth, in Devon, from where the first English settlers to New Plymouth migrated. The New Pl ...
and
Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
. All of these towns were laid out on a grid plan, so it was easy to divide the land into acre plots of one
chain
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A ...
by one
furlong
A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one-eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 foot (unit), feet, 220 yards, 40 rod (unit), rods, 10 chain (unit), chains, or a ...
, (approximately 0.4 ha.), and these became known as town acres.
Adelaide was divided into 1042 Town Acres. Maps showing the divisions of the town acres are available for Adelaide, Nelson, and Wellington.
Late 19th century to the present
 Ildefons Cerdà
Ildefons Cerdà, a Spanish civil engineer, defined a concept of urban planning, based on the grid, that he applied to the
Eixample
The Eixample (, ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and what were once surrounding small towns (Sants, Gràcia, Sant Andreu, etc.), constructed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its population was 262,000 at ...
of
Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
. The Eixample grid introduced innovative design elements which were exceptional at the time and even unique among subsequent grid plans:
* a very large block measuring , far larger than the old city blocks and larger than any Roman, Greek blocks and their mutations (see drawing below);
* a road width (right of way) compared with mostly 3 m in the old city;
* square blocks with truncated corners; and
* major roads, perpendicular and diagonal, measuring in width.
Cerda formulated these innovations in response to changing functional needs. As cities grew larger, through traffic, travel distance, noise, and pollution from carts became significant issues. Larger blocks with major perpendicular roads enables the creation of a quiet interior open space (60 m by 60 m) and allow ample sunlight and ventilation to its perimeter buildings; the rectilinear geometry, the wide streets and boulevards to sustain high mobility and the truncated corners to facilitate turning of carts and coaches and particularly vehicles on fixed rails. As buildings became taller, the new design also permitted a more natural sense of scale to the buildings from the street and reduced wind speeds.
In the early 1900s, urban planners such as New York architect
Charles Lamb
Charles Lamb (10 February 1775 – 27 December 1834) was an English essayist, poet, and antiquarian, best known for his '' Essays of Elia'' and for the children's book '' Tales from Shakespeare'', co-authored with his sister, Mary Lamb (1764� ...
, who was one of the first to sketch out a city plan with
hexagonal grid and Rudolf Muller, Austrian architect who iterated upon Lamb's hexagonal grid system, demonstrated their application and value to city grids. During the 1920s
a Canadian planner and engineer, further refined and optimized the hexagonal model—even showing how it can be integrated into existing cities.
With growing concerns over vehicle flow, this model provided a reduction in collision points; from 16 to just 3 by reducing the 4-way intersection of a traditional orthogonal grid, to a 3-way intersection that allows for better sightline with its obtuse 120° angle.
However
Thomas Adamswho was "pivotal in making urban planning a separate profession and in codifying residential design practice"
preferred square grids and suburban cul-de-sacs. Adam's rebutted Cauchon's work in his co-authored
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher lear ...
book: ''The Design of Residential Areas: Basic Considerations, Principles, and Methods'' (1934), modifying Cauchon's drawings to disfavour hexagonal grids, despite them being the most efficient grid model.
This publishment received widespread attention, and led to the adoption of square grids in the downtown areas of most large American colonial cities.
These areas represent the original land dimensions of the founded city, generally around one square mile. Some cities expanded the grid further out from the centre, but maps also show that, in general, as the distance from the centre increases, a variety of patterns emerge in no particular discernible order. In juxtaposition to the grid, they appear random. These new patterns have been systematically classified and their design characteristics measured.
In the United States, the grid system was widely used in most major cities and their
suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area. They are oftentimes where most of a metropolitan areas jobs are located with some being predominantly residential. They can either be denser or less densely populated ...
s until the 1960s. However, during the 1920s, the rapid adoption of the
automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
caused a panic among
urban planners
An urban planner (also known as town planner) is a professional who practices in the field of town planning, urban planning or city planning.
An urban planner may focus on a specific area of practice and have a title such as city planner, tow ...
, who, based on observation, claimed that speeding cars would eventually kill tens of thousands of small children per year. Apparently, at this early stage of the car's entry into the grid, the streets of major cities worldwide were the scene of virtual "slaughter" as the fatality rate in proportion to population was more than double the current rate. In 2009, after several decades of road safety improvements and a continuous decline in fatalities, an estimated 33,963 people died in motor vehicle traffic crashes and, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, "Motor vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death for children from 3 to 14 years old." Planners, therefore, called for an inwardly focused "
superblock" arrangement that minimized through automobile traffic and discouraged cars from traveling on anything but
arterial road
An arterial road or arterial thoroughfare is a high-capacity urban road that sits below highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It includes not just major roads, but also other public roads and rights o ...
s; traffic generators, such as apartment complexes and shops, would be restricted to the edges of the superblock, along the arterial. This paradigm prevailed between about 1930 and 1960, especially in
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, where notable examples include
Leimert Park
Leimert Park (; ) is a neighborhood in the South Los Angeles region of Los Angeles, California.
Developed in the 1920s as a mainly residential community, it features Spanish Colonial Revival homes and tree-lined streets. The Life Magazine/Leim ...
(an early example) and
Panorama City (a late-period one).

A prominent 20th century urbanist,
Lewis Mumford
Lewis Mumford (October 19, 1895 – January 26, 1990) was an American historian, sociologist, philosopher of technology, and literary critic. Particularly noted for his study of cities and urban architecture, he had a broad career as a ...
, severely criticized some of the grid's characteristics: "With a T-square and a triangle, finally, the municipal engineer could, without the slightest training as either an architect or a sociologist, 'plan' a metropolis, with its standard lots, its standard blocks, its standard street widths, in short, with its standardized comparable, and replaceable parts. The new gridiron plans were spectacular in their inefficiency and waste. By usually failing to discriminate sufficiently between main arteries and residential streets, the first were not made wide enough while the second were usually too wide for purely neighborhood functions... as for its contribution to the permanent social functions of the city, the anonymous gridiron plan proved empty."
In the 1960s,
traffic engineers and urban planners abandoned the grid virtually wholesale in favor of a "
street hierarchy
The street hierarchy is an urban planning technique for laying out road networks that exclude automobile through-traffic from developed areas. It is conceived as a hierarchy of roads that embeds the link importance of each road type in the ne ...
". This is a thoroughly "asymmetric" street arrangement in which a residential subdivision—often surrounded by a
noise wall or a
security gate—is completely separated from the road network except for one or two connections to arterial roads. In a way, this is a return to
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
styles: as noted in
Spiro Kostof
Spiro Konstantine Kostof (7 May 1936, Istanbul – 7 December 1991, Berkeley) was a Turkish-born American leading architectural historian, and educator. He was a professor at the University of California, Berkeley. His books continue to be widel ...
's seminal history of
urban design
Urban design is an approach to the design of buildings and the spaces between them that focuses on specific design processes and outcomes based on geographical location. In addition to designing and shaping the physical features of towns, city, ...
, ''The City Shaped'', there is a strong resemblance between the street arrangements of modern American suburbs and those of medieval
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
and
Moorish
The term Moor is an exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a single, distinct or self-defi ...
cities. In each case, the community unit at hand—the clan or extended family in the
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
world, the economically homogeneous
subdivision
Subdivision may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Subdivision (metre), in music
* ''Subdivision'' (film), 2009
* "Subdivision", an episode of ''Prison Break'' (season 2)
* ''Subdivisions'' (EP), by Sinch, 2005
* "Subdivisions" (song), by Rush ...
in modern suburbia—isolates itself from the larger urban scene by using dead ends and ''
culs-de-sac''.
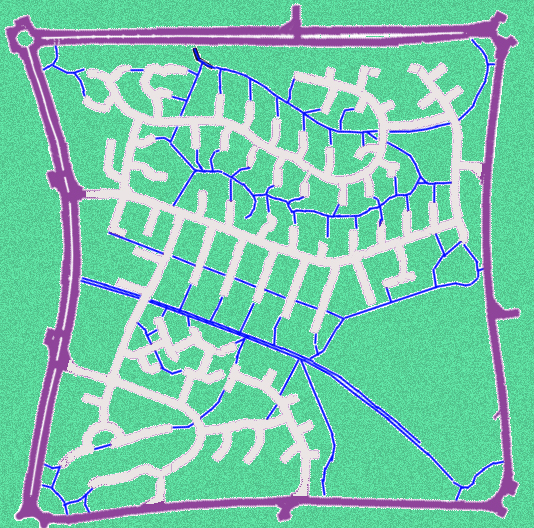
Milton Keynes
One famous grid system is in the British new town of
Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of Milton Keynes urban area, its urban area was 264,349. The River Great Ouse forms t ...
. In this planned city, which began construction in 1967, a system of ten "horizontal" (roughly east–west) and eleven "vertical" (roughly north–south) roads was used, with
roundabout
A roundabout, a rotary and a traffic circle are types of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junct ...
s at each intersection. The horizontal roads were all given names ending in 'way' and H numbers (for 'horizontal', e.g., H3 Monks Way). The vertical roads were given names ending in 'street' and V numbers (for 'vertical', e.g.,
V6 Grafton Street). Each grid road was spaced roughly one kilometre along from the next, forming squares of approximately one square kilometre. Each square and each roundabout was given its own name. The system provided very easy transport within the city, although it confused visitors who were unfamiliar with the system. The grid squares thus formed are far larger than the city blocks described earlier, and the road layouts within the grid squares are generally 'organic' in form – matching the street hierarchy model described above.
Benefits and criticisms
Financial cost

''Street width'', or right of way (ROW), influences the amount of land that is devoted to streets, which becomes unavailable for development and therefore represents an
opportunity cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best alternative forgone where, given limited resources, a choice needs to be made between several mutually exclusive alternatives. Assuming the best choice is made, ...
. The wider the street, the higher the opportunity cost. Street width is determined by circulation and aesthetic considerations and is not dependent on the pattern configuration. Any configuration can have wide or narrow streets.
''Street length'' influences proportionately the number of street components that have to be constructed such as pavement, curbs and sidewalks, storm sewers and drains, light poles, and trees. The street length of a given area of development depends on the frequency at which streets occur which in turn depends on the length and width of a block. The higher the frequency of streets the longer is their total length. The smaller the block dimensions the higher the frequency of the streets. As the frequency of street increases so does the number of intersections. Intersections normally cost more than straight street length because they are labour-intensive and require street and traffic signage.
''Pavement width'' influences the cost by affecting the amount of materials and labour required to provide a finished road surface. Pavement width is generally based on traffic engineering considerations and is not dependent on pattern configuration. As with the street width, any pattern can have wide or narrow pavements.
Of all three factors that affect cost, street width, street length and pavement width, only street length is pattern dependent. An objective cost comparison would, therefore, rely on this variable with the full understanding that the other variables, though optional, can play a role.
Not only do these street dimension factors increase infrastructure costs and inhibit land utilization and by turn, affordability, but they also impact a city's economic productivity. "Street width plays a crucial role in shaping our perception of scale, influencing how distant or accessible destinations appear".
Wider streets have less developable land within a square mile generating tax revenue (tax revenue falls) while having greater area of streets to maintain (expenses go up).
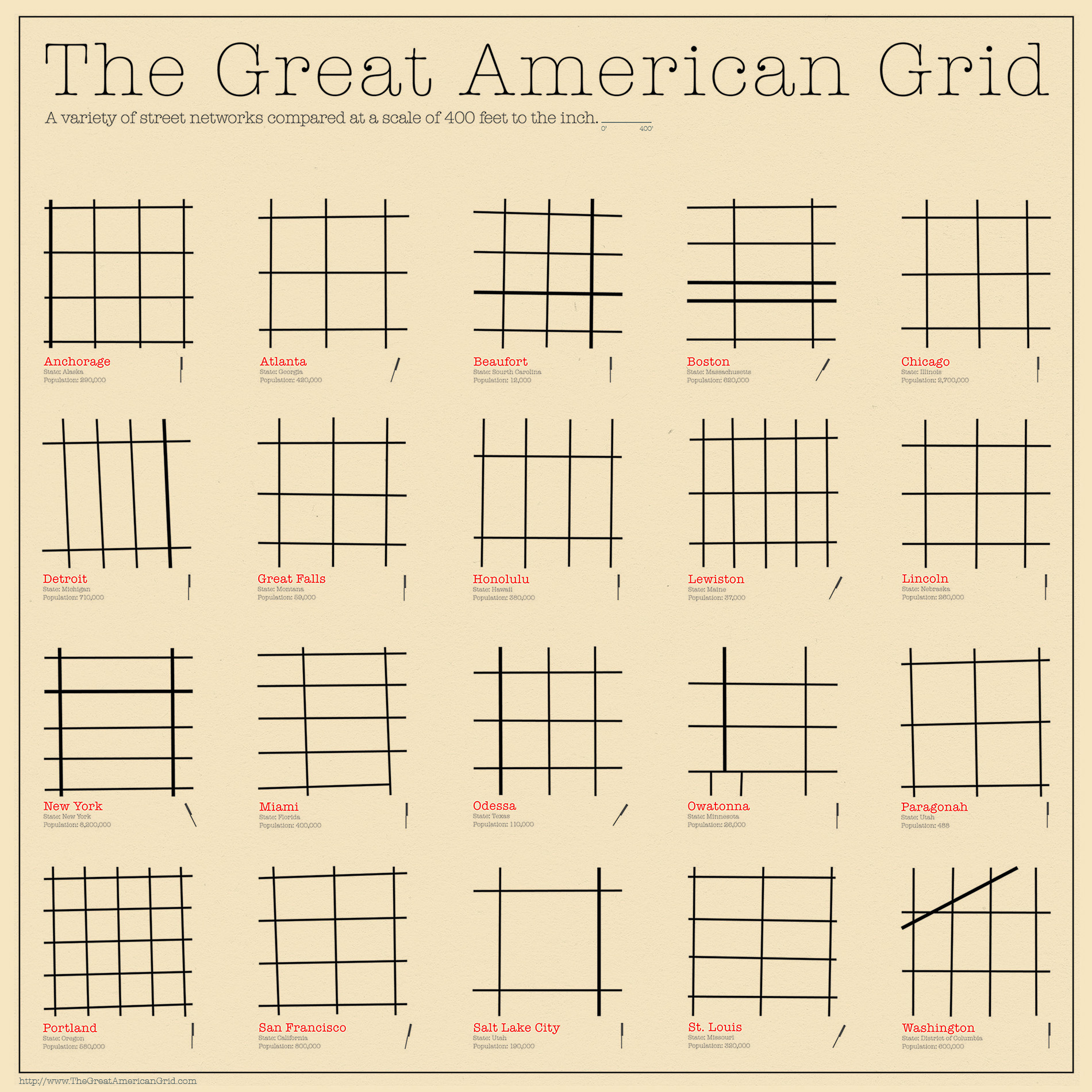
Traditional orthogonal grid patterns generally have greater street frequencies than discontinuous patterns. For example, Portland's block is 200 feet × 200 feet while Miletus' is half that size and Timgad's half again (see diagram). Houston, Sacramento and Barcelona are progressively bigger reaching up to four times the area of Portland's block. New York's 1811 plan (see above) has blocks of . in width and variable lengths ranging from about to feet. The corresponding frequency of streets for each of these block sizes affects the street length.
A simple example of a grid street pattern (see diagram) illustrates the progressive reduction in ''total'' street length (the sum of all individual street lengths) and the corresponding increase in block length. For a corresponding reduction of one, two, three and four streets within this parcel, the street length is reduced from an original total of to linear feet, a 39% reduction. Simultaneously, block lengths increase from 200 × 200 feet to 1240 × 200 feet. When all five blocks have reached the ultimate size of four street lengths out of total eight have been eliminated. Block lengths of or larger rarely appear in grid plans and are not recommended as they hinder pedestrian movement (Pedestrianism, below). From the pedestrian perspective, the smaller the block is, the easier the navigation and the more direct the route. Consequently, the finer grids are preferred.
Patterns that incorporate discontinuous street types such as crescents and
culs-de-sac have not, in general, regarded pedestrian movement as a priority and, consequently, have produced blocks that are usually in the range and often exceed it. As a result, street frequency drops and so does the ''total'' street length and, therefore, the cost. In general, it is not the street pattern per se that affects costs but the frequency of streets that it either necessitates or purposely incorporates.
An inherent advantage of the orthogonal geometry of a proper grid is its tendency to yield regular lots in well-packed sequences. This maximizes the use of the land of the block; it does not, however, affect street frequency. Any frequency of orthogonal streets produces the same
packing effect. Orthogonal geometry also minimizes disputes over lot boundaries and maximizes the number of lots that could front a given street.
John Randal said Manhattan's grid plan facilitated "buying, selling and improving real estate".
Another important aspect of street grids and the use of rectilinear blocks is that traffic flows of either pedestrians, cars, or both, only cross at right angles. This is an important traffic safety feature, since no one entering the intersection needs to look over their shoulder to see oncoming traffic. Any time traffic flows meet at an acute angle, someone cannot see traffic approaching them. The grid is thus a geometric response to our human physiology. It is very likely the original purpose of grid layouts comes from the Athenian Agora. Before the grid organization, markets were laid out randomly in a field with traffic approaches at odd angles. This caused carts and wagons to turn over due to frequent collisions. Laying out the market stalls into regularized rows at right angles solved this problem and was later built into the Athenian Agora and copied ever since.
Ecological features, rainwater absorption, and pollutant generation
Typical uniform grids are unresponsive to
topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
.
Priene
Priene (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called the Büyük Menderes Rive ...
's plan, for example, is set on a hill side and most of its north–south streets are stepped, a feature that would have made them inaccessible to carts, chariots and loaded animals. Many modern cities, such as
San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
,
Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, and
Saint John, New Brunswick
Saint John () is a port#seaport, seaport city located on the Bay of Fundy in the province of New Brunswick, Canada. It is Canada's oldest Municipal corporation, incorporated city, established by royal charter on May 18, 1785, during the reign ...
, follow Priene's example. In a modern context, steep grades limit accessibility by car, and more so by bicycle, on foot, or wheelchair, particularly in cold climates.
The same inflexibility of the grid leads to disregarding
environmentally sensitive areas such as small streams and
creeks or mature woodlots in preference for the application of the immutable geometry. It is said of the New York City grid plan that it flattened all obstacles in its way. By contrast, recent discontinuous street patterns follow the configuration of natural features without disrupting them. The grid represents a rationalist,
reductionist
Reductionism is any of several related philosophical ideas regarding the associations between phenomena which can be described in terms of simpler or more fundamental phenomena. It is also described as an intellectual and philosophical posit ...
solution to a multifaceted issue.
The grid's inherent high street and intersection frequencies produce large areas of
impermeable surfaces in the street pavement and the
sidewalk
A sidewalk (North American English),
pavement (British English, South African English), or footpath (Hiberno-English, Irish English, Indian English, Australian English, New Zealand English) is a path along the side of a road. Usually constr ...
s. In comparison with recent networks with discontinuous street types, grids can be up to 30% higher in impermeable surfaces attributable to roads. The emerging environmental priority of retaining as much as 90% of
rain water
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
on site becomes problematic with high percentages of impermeable surfaces. And since roads constitute the largest share of the total impermeable surfaces of a development, the difficulty is compounded by the grid type of layout. For these reasons modern planners have attempted to modify the rigid, uniform, classic grid.
Some cities, notably
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
, have devised means to improve a street's retention capacity. However, frequent intersections as they occur in a regular grid would pose an obstacle to their effective application.
A street network pattern can affect the production of pollutants by the amount of car travel that it necessitates and the speed at which cars can travel. The grid plan with its frequent intersections may displace a portion of the local car trips with walking or biking due to the directness of route that it offers to
pedestrian
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, by wheelchair or with other mobility aids. Streets and roads often have a designated footpath for pedestrian traffic, called the '' sidewalk'' in North American English, the ''pavement'' in British En ...
s. But, as long as cars are also allowed on those streets, it makes the same routes more direct for cars, which could be an enticement for driving. The potential car trip displacement would result in a reduction of
pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oi ...
emissions. The advantage of the intersection density for pedestrians, however, can have a contrary effect for cars due to its potential for reducing speeds. Low speeds below have a significantly higher coefficient of pollutant production than above , though the coefficient after leveling off tends to increase gradually after . This effect is accentuated with high traffic density in areas with commercial uses where speeds come to a crawl. Since the grid plan is non-hierarchical and intersections are frequent, all streets can be subject to this potential reduction of average speeds, leading to a high production of pollutants. Greenhouse and noxious gases can be detrimental to the environment and to resident health.
Social environment and security
In his seminal 1982 study on livable streets that was conducted in neighbourhoods with a grid, Donald Appleyard showed that social networking and street playing degraded as traffic increased on a street. His research provided the groundwork for
traffic calming
Traffic calming uses physical design and other measures to improve safety for motorists, car drivers, pedestrians and bicycle-friendly, cyclists. It has become a tool to combat speeding and other unsafe behaviours of drivers. It aims to encour ...
and for several initiatives such as
living street
A living street or residential street is a street designed with the interests of pedestrians and Cycling, cyclists in mind. Living streets also act as social spaces, allowing children to play and encouraging social interactions on a human scale, ...
s and
Home Zone
A home zone (or play street) is a living street (or group of streets) as implemented in the United Kingdom, which are designed primarily to meet the needs of pedestrians, cyclists, children and residents and where the speeds and dominance of cars ...
s, all of which are aimed at improving a street's social milieu. The amount of traffic on a street depends on variables such as the population density of the neighbourhood, car ownership and its proximity to commercial, institutional or recreational edifices. Most importantly, however, it depends on whether a street is or could become a through road to a destination. As a through road, it could sustain unpredictable levels of traffic that may fluctuate during the day and increase over time.
A key characteristic of the grid pattern is that any and all streets are equally accessible to traffic (non-hierarchical) and could be chosen at will as alternative routes to a destination. Cut-through driving, or shortcutting, has been resisted by residents. Cities responded by making modifications to prevent it. Current recommended design practice suggests the use of 3-way intersections to alleviate it.
The geometry of the normal, open grid is evidently unsuitable for protecting or enhancing the social environment of a street from the negative influence of traffic. The scale of the block, as argued by
Jane Jacobs
Jane Isabel Jacobs (''née'' Butzner; 4 May 1916 – 25 April 2006) was an American-Canadian journalist, author, theorist, and activist who influenced urban studies, sociology, and economics. Her book ''The Death and Life of Great American Ci ...
—writer and activist, in her landmark ''The Death and Life of Great American Cities'' (1961), is "one of the four most important factors in generating diversity".
Blocks longer than 400 feet (about 120 meters) disrupt the “intricate pools of fluid street use” that are necessary to support diverse economic and cultural interactions, and to maintain a “fabric of intimate economic cross-use”.
Another key aspect is the overall street connectivity pattern, where smaller block sizes are crucial for enhancing accessibility, in addition to irregular block dimensions that emulate pedestrian movement
Bill Hillier a professor of Architectural and Urban Morphology and his colleagues developed a “space syntax” model for street design, demonstrating that natural pedestrian movement—including trips to commercial areas—relies on the broader structure of the street grid. This supports Jacobs’ observation that block sizes directly influence economic activity and social interactions.
Similarly, a 1972 ground-breaking study by
Oscar Newman on a
Defensible Space Theory described ways to improve the social environment and security of neighbourhoods and streets. In a practical application of his theory at Five Oaks, the neighbourhood's grid pattern was modified to prevent through traffic and create identifiable smaller enclaves while maintaining complete pedestrian freedom of movement. The positive outcome of these changes reinforces Appleyard's findings and the need to reduce or prevent through traffic on neighbourhood streets; a need that cannot be met with a typical, uniform, open grid.
The question of neighbourhood security has been a constant focus of research since Oscar Newman's work. New research has expanded the discussion on this disputed issue. A recent study did extensive spatial analysis and correlated several building, site plan and social factors with crime frequencies and identified subtle nuances to the contrasting positions. The study looked at, among others, dwelling types, unit density (site density) movement on the street, culs–de-sac or grids and the permeability of a residential area. Among its conclusions are, respectively, that flats are always safer than houses and the wealth of inhabitants matters, density is generally beneficial but more so at ground level, local movement is beneficial, but not larger scale movement, relative affluence and the number of neighbours have a greater effect than either being on a cul-de-sac or being on a through street. It also re-established that simple, linear cul-de-sac with good numbers of dwellings that are joined to through streets tend to be safe. As for permeability, it suggests that residential areas should be permeable enough to allow movement in all directions but no more. The overprovision of poorly used permeability is a crime hazard. The open, uniform grid could be seen as an example of undifferentiated permeability.
A recent study in California examined the amount of child play that occurred on the streets of neighbourhoods with different characteristics; grid pattern and culs-de-sac. The findings indicate that the open grid streets showed substantially lower play activity than the cul-de-sac street type. Culs-de-sac reduce
perceived danger from traffic, and thereby encourage more outdoor play. It pointed the way toward the development of hybrid street network patterns that improve pedestrian movement but restrict cut-through driving. Similar studies in Europe and most recently in Australia found that children's outdoor play is significantly reduced on through roads where traffic is, or perceived by parents to be, a risk. As a result of this misperception of risk, children living in cul-de-sac communities are more likely to be killed by vehicles. This increased risk of death is due to multiple factors, including the families driving longer distances to reach their destinations, parents spending less time teaching their children to be as wary of traffic, and an increased risk of the parents accidentally driving over the children in their "safe" driveways and cul-de-sac streets.
Traditional street functions such as kids' play, strolling and socializing are incompatible with traffic flow, which the open, uniform grid geometry encourages. For these reasons, cities such as
Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland, Cali ...
, and
Vancouver, British Columbia
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, among many others, transformed existing residential streets part of a grid plan into permeable, linked culs-de-sac. This transformation retains the
permeability and connectivity of the grid for the active modes of transport but filters and restricts car traffic on the cul-de-sac street to residents only.
Pedestrian and bicycle movement
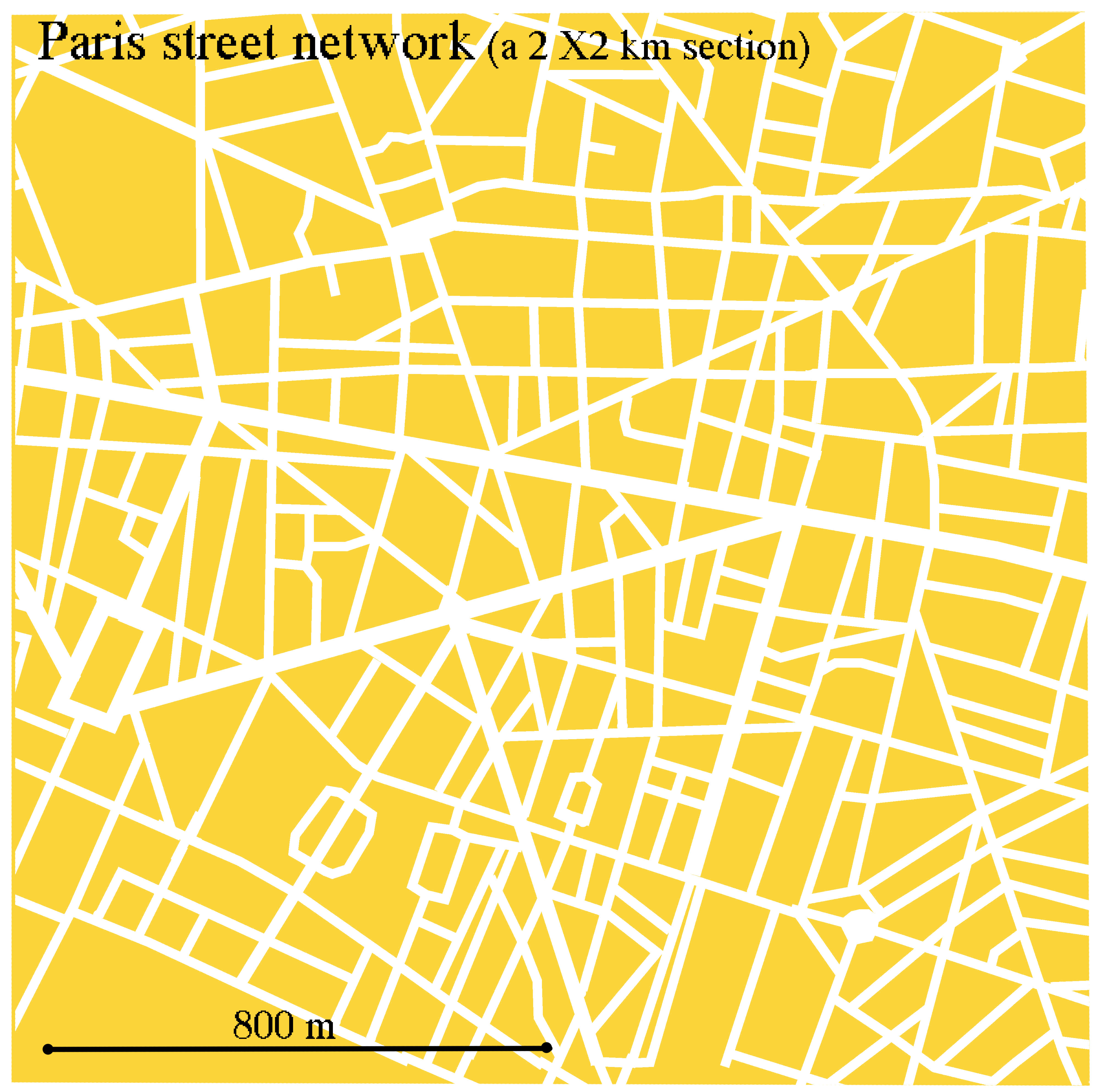
Street networks of old cities that grew organically, though admired for being picturesque, can be confusing for visitors but rarely for the original inhabitants (see plan). Similarly confusing to visitors are the plans of modern subdivisions with discontinuous and curvilinear streets. Change of street orientation, particularly when gradual or arbitrary, cannot be "mapped" in the mind. Impasses, crescents or
cul-de-sacs frustrate the traveler especially when they are long, forcing an arduous retracing of steps.
Frequency of intersections, however, becomes also a disadvantage for pedestrians and bicycles. It disrupts the relaxed canter of walking and forces pedestrians repeatedly onto the road, a hostile, anxiety-generating territory. People with physical limitations or frailties, children and seniors for example, can find a regular walk challenging. For bicycles this disadvantage is accentuated as their normal speed is at least double that of pedestrians. Frequent stops negate the speed advantage and the physical benefit of bicycling and add to frustration. Intersections are not only unpleasant but also dangerous. Most
traffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
s and injuries occur at intersections and the majority of the injuries to pedestrians crossing ''with'' the right of way.
A dilemma arises from trying to meet important planning objectives when using the grid: pedestrianism, cost efficiency and environmental responsiveness. To serve pedestrians well, a rectangular configuration and high frequency of streets and intersections is the preferred route, which the orthogonal grid geometry provides. To reduce development costs and environmental impact, lower frequency of streets is the logical path. Since these two design objectives are contradictory a balance needs to be struck. Such balance has been achieved in leading modern projects such as
Vauban, Freiburg
Vauban () is a neighbourhood (''Stadtteil'') to the south of the town centre in Freiburg, Germany. It was built as "a sustainable model district" on the site of a former French military base named after Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, the 17th ce ...
and
Village Homes, Davis. Both score high in pedestrian and bike mode share and, at the same time, in reducing negative development externalities. Their layout configurations represent a fusion of the classic grid plan with recent street network patterns.
Examining the issue of
walkability
In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities within a reasonable walking distance. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it s ...
, a recent comparison of seven neighbourhood layouts found a 43 and 32 percent increase in walking with respect to a grid plan and conventional suburban layout in a
fused grid layout, which has greater permeability for pedestrians than for cars due to its inclusion of dedicated pedestrian paths. It also showed a 7 to 10 percent range of reduction in driving with respect to the remainder six neighbourhood layouts in the set, an environmental benefit.
Safety
Perceived and actual safety play a role in the use of the street. Perceived safety, though perhaps an inaccurate reflection of the number of injuries or fatalities, influences parents' decision to allow their children to play, walk or bike on the street. Actual levels of safety as measured by the total number of collisions and the number and severity of injuries are a matter of public concern. Both should inform the layout, if the street network is to achieve its optimum use.
Recent studies have found higher traffic fatality rates in outlying suburban areas than in central cities and inner suburbs with smaller blocks and more-connected street patterns.
An earlier study found significant differences in recorded accidents between residential neighborhoods that were laid out on a grid and those that included culs-de-sac and crescents. The frequency of accidents was significantly higher in the grid neighborhoods.
Two newer studies examined the frequency of collisions in two regional districts using the latest analytical tools. They investigated the potential correlation between street network patterns and frequency of collisions. In one study, cul-de-sac networks appeared to be much safer than grid networks, by nearly three to one.
A second study found the grid plan to be the least safe by a significant margin with respect to all other street patterns.
A 2009 study suggests that land use patterns play a significant role in traffic safety and should be considered in conjunction with the network pattern. While all intersection types in general reduce the incidence of fatal crashes, four-way intersections, which occur regularly in a grid, increase total and injurious crashes significantly. The study recommends hybrid street networks with dense concentrations of T-intersections and concludes that a return to the 19th century gridiron is undesirable.
Stringent adherence to the grid plan can cause steep inclines since the topology of the land is not taken into account. This may be unsafe for drivers, pedestrians and bicycles since it is more difficult to control speed and braking, particularly in winter conditions.
Reconstruction and development
One of the greatest difficulties with grid plans is their lack of specialization, most of the important amenities being concentrated along the city's main arteries. Often grid plans are found in
linear settlements, with a main street connecting between the perpendicular roads. However, this can be mitigated by allowing mixed use development so that destinations become closer to home. Many cities, especially in Latin America, still successfully retain their grid plans. Recently, planners in the United States and Canada have revisited the idea of reintroducing grid patterns to many cities and towns.
Cities and towns with a grid plan
North America
United States
= Alabama
=
*
Anniston
*
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
= Arizona
=
*
Phoenix
*
Tucson
Tucson (; ; ) is a city in Pima County, Arizona, United States, and its county seat. It is the second-most populous city in Arizona, behind Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, with a population of 542,630 in the 2020 United States census. The Tucson ...
= Arkansas
=
*
Alicia
*
Altheimer
*
Arkadelphia
*
Arkansas City
*
Ashdown
*
Atkins
*
Augusta
*
Austin
Austin refers to:
Common meanings
* Austin, Texas, United States, a city
* Austin (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin (surname), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin Motor Company, a British car manufac ...
*
Bald Knob
*
Batesville
*
Beebe
*
Benton
*
Bigelow
*
Booneville
*
Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdo ...
*
Brinkley
*
Bryant
*
Cabot
*
Camden
*
Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
*
Clarendon
*
Clarksville
*
College Station
*
Conway
Conway may refer to:
Places
United States
* Conway, Arkansas
* Conway County, Arkansas
* Lake Conway, Arkansas
* Conway, Florida
* Conway, Iowa
* Conway, Kansas
* Conway, Louisiana
* Conway, Massachusetts
* Conway, Michigan
* Conway Townshi ...
*
Corning
*
Danville
*
Dardanelle
*
Delaplaine
*
DeWitt
*
Dumas
*
El Dorado
El Dorado () is a mythical city of gold supposedly located somewhere in South America. The king of this city was said to be so rich that he would cover himself from head to foot in gold dust – either daily or on certain ceremonial occasions � ...
*
Emmet
*
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
*
Fayetteville
*
Forrest City
Forrest City is a city in and the county seat of St. Francis County, Arkansas, United States. It was named for General Nathan Bedford Forrest, a notable Confederate war hero who later became the first Grand Wizard of the Ku Klux Klan. Shortly ...
*
Fort Smith
*
Fordyce
*
Garner
*
Georgetown
*
Gurdon
*
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
*
Harrison
*
Hazen
*
Heber Springs
*
Helena–West Helena
*
Hope
Hope is an optimistic state of mind that is based on an expectation of positive outcomes with respect to events and circumstances in one's own life, or the world at large.
As a verb, Merriam-Webster defines ''hope'' as "to expect with confid ...
*
Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
*
Hoxie
*
Humnoke
*
Jacksonville
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
*
Jonesboro
*
Kensett
*
Kingsland
*
Knobel
*
Leslie
*
Letona
*
Little Rock
Little Rock is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Arkansas, most populous city of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The city's population was 202,591 as of the 2020 census. The six-county Central Arkan ...
*
Lonoke
*
Malvern
*
McCrory
*
McGehee
*
McRae
*
Mena
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA), also referred to as West Asia and North Africa (WANA) or South West Asia and North Africa (SWANA), is a geographic region which comprises the Middle East (also called West Asia) and North Africa together ...
*
Monticello
Monticello ( ) was the primary residence and plantation of Thomas Jefferson, a Founding Father, author of the Declaration of Independence, and the third president of the United States. Jefferson began designing Monticello after inheriting l ...
*
Morrilton
*
Mountain Home
*
Mountain View
*
Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
*
Newport
*
Ozark
*
O'Kean
*
Pangburn
*
Paragould
*
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
*
Peach Orchard
*
Perryville
*
Pine Bluff
*
Pocahontas
Pocahontas (, ; born Amonute, also known as Matoaka and Rebecca Rolfe; 1596 – March 1617) was a Native American woman belonging to the Powhatan people, notable for her association with the colonial settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. S ...
*
Poyen
*
Prescott
*
Redfield
*
Rison
*
Russell
*
Russellville
*
Searcy
*
Sheridan
*
Smackover
*
Strong
Strong may refer to:
Education
* The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States
* Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas
* Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United ...
*
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of ...
*
Swifton
*
Texarkana
The Texarkana metropolitan statistical area (MSA), as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget, is a two-county region anchored by the Twin cities (geographical proximity), twin cities of Texarkana, Texas (population 37,33 ...
*
Tuckerman
*
Van Buren
*
Waldron
*
Walnut Ridge
*
Ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
*
West Memphis
*
Wrightsville
= California
=
*
Fresno
Fresno (; ) is a city in the San Joaquin Valley of California, United States. It is the county seat of Fresno County, California, Fresno County and the largest city in the greater Central Valley (California), Central Valley region. It covers a ...
*
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
**
Panorama City
*
Sacramento
Sacramento ( or ; ; ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the seat of Sacramento County. Located at the confluence of the Sacramento and American Rivers in Northern California's Sacramento Valley, Sacramento's 2020 p ...
*
San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
*
San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
*
San Jose
= Connecticut
=
*
New Haven
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is the third largest city in Co ...
= Delaware
=
*
Wilmington
= District of Columbia
=
*
Washington D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
(see
L'Enfant Plan
The L'Enfant Plan for the city of Washington, D.C. is the urban plan developed in 1791 by Major Pierre (Peter) Charles L'Enfant for George Washington, the first president of the United States. It is regarded as a landmark in urban design and h ...
)
= Florida
=
*
Jacksonville
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
*
Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
*
Orlando
Orlando commonly refers to:
* Orlando, Florida, a city in the United States
Orlando may also refer to:
People
* Orlando (given name), a masculine name, includes a list of people with the name
* Orlando (surname), includes a list of people wit ...
*
St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
*
Tampa
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
*
Windermere
Windermere (historically Winder Mere) is a ribbon lake in Cumbria, England, and part of the Lake District. It is the largest lake in England by length, area, and volume, but considerably smaller than the List of lakes and lochs of the United Ki ...
*
Winter Park
= Georgia
=
*
Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
*
Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
(see
Oglethorpe Plan)
= Iowa
=
*
Cedar Falls
= Illinois
=
*
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
= Indiana
=
*
Indianapolis
Indianapolis ( ), colloquially known as Indy, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Indiana, most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the county seat of Marion County, Indiana, Marion ...
= Kansas
=
*
Wichita, Kansas
Wichita ( ) is the List of cities in Kansas, most populous city in the U.S. state of Kansas and the county seat of Sedgwick County, Kansas, Sedgwick County. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population of the city was 397, ...
= Louisiana
=
*
Lake Charles
= Massachusetts
=
*
Holyoke
Holyoke is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, that lies between the western bank of the Connecticut River and the Mount Tom Range. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 38,247. Loca ...
= Michigan
=
*
Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
*
Traverse City
= Minnesota
=
*
Minneapolis
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Locat ...
= Missouri
=
*
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more t ...
*
St. Louis
St. Louis ( , sometimes referred to as St. Louis City, Saint Louis or STL) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a populatio ...
= Montana
=
*
Billings
*
Missoula
Missoula ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Missoula County, Montana, Missoula County, Montana, United States. It is located along the Clark Fork River near its confluence with the Bitterroot River, Bitterroot and Blackfoot River (Montana), ...
= Nebraska
=
*
Omaha
Omaha ( ) is the List of cities in Nebraska, most populous city in the U.S. state of Nebraska. It is located in the Midwestern United States along the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's List of United S ...
= Nevada
=
*
Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
= New Hampshire
=
*
Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
= New York
=
*
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
(see
Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march upto ...
)
= North Carolina
=
*
Charlotte
*
Raleigh
Raleigh ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, second-most populous city in the state (after Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte) ...
*
Wilmington
*
Morehead City
Morehead City is a port city in Carteret County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 8,661 at the 2010 census. Morehead City celebrated the 150th anniversary of its founding on May 5, 2007. It forms part of the Crystal Coast.
Hi ...
= North Dakota
=
*
Fargo
= Oklahoma
=
*
Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Oklahoma, most populous city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat ...
*
Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa ( ) is the List of municipalities in Oklahoma, second-most-populous city in the U.S. state, state of Oklahoma, after Oklahoma City, and the List of United States cities by population, 48th-most-populous city in the United States. The po ...
= Ohio
=
*
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
*
Columbus
= Oregon
=
*
Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
*Portland, Oregon, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon
*Portland, Maine, the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maine
*Isle of Portland, a tied island in the English Channel
Portland may also r ...
= Pennsylvania
=
*
Pittsburgh (former Allegheny City section), Pennsylvania
*
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
= Rhode Island
=
*
Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
*
Providence
= South Carolina
=
*
Columbia, South Carolina
Columbia is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of South Carolina. With a population of 136,632 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is List of municipalities in South Carolina, the second-mo ...
= South Dakota
=
*
Sioux Falls
Sioux Falls ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of South Dakota and the 117th-most populous city in the United States. It is the county seat of Minnehaha County and also extends into northern Lincoln County. The population was 192 ...
= Tennessee
=
*
Memphis
= Texas
=
*
Austin
Austin refers to:
Common meanings
* Austin, Texas, United States, a city
* Austin (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin (surname), a list of people and fictional characters
* Austin Motor Company, a British car manufac ...
*
Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
*
Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
*
Lubbock
*
Tyler
= Utah
=
*
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
= Virginia
=
*
Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, California, a city in the United States
* Richmond, London, a town in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, England
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town ...
= Washington
=
*
Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
(see
Street layout of Seattle)
= Wisconsin
=
*
Milwaukee
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States ...
Canada
= Alberta
=
*
Calgary
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in C ...
*
Edmonton
Edmonton is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Central Alberta ...
= British Columbia
=
*
Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
*
Victoria
= Manitoba
=
*
Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Manitoba. It is centred on the confluence of the Red River of the North, Red and Assiniboine River, Assiniboine rivers. , Winnipeg h ...
= New Brunswick
=
*
Saint John
= Nova Scotia
=
*
Halifax
*
Saskatoon
Saskatoon () is the largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It straddles a bend in the South Saskatchewan River in the central region of the province. It is located along the Trans-Canada Hig ...
= Ontario
=
*
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
*
Oshawa
Oshawa is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the Lake Ontario shoreline. It lies in Southern Ontario, approximately east of downtown Toronto. It is commonly viewed as the eastern anchor of the Greater Toronto Area and of the Golden Horseshoe. It ...
*
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
*
Sudbury
*
Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario. Its population i ...
*
Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
(see
Concession road
In Upper Canada, Upper and Lower Canada, concession roads were laid out by the colonial government through undeveloped Crown land#Canada, Crown land to provide access to rows of newly surveyed Land lot, lots intended for farming by new settlers. T ...
)
*
Windsor
= Quebec
=
*
Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
*
Quebec City, Quebec
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
*
Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
= Saskatchewan
=
*
Regina
Mexico
*
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
*
Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
South America
Argentina
*
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
*
Mar del Plata
Mar del Plata is a city on the coast of the Argentine Sea, Atlantic Ocean, in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is the seat of General Pueyrredón Partido, General Pueyrredón district. Mar del Plata is the second largest city in Buenos Aires ...
*
La Plata
La Plata () is the capital city of Buenos Aires province, Argentina. According to the 2022 Argentina census, census, the La Plata Partido, Partido has a population of 772,618 and its metropolitan area, the Greater La Plata, has 938,287 inhabit ...
*
Bahía Blanca
Bahía Blanca (; English: ''White Bay''), colloquially referred to by its own local inhabitants as simply Bahía, is a city in the Buenos Aires Province, Buenos Aires province of Argentina, centered on the northwestern end of the eponymous Blanc ...
Most cities and towns in Argentina follow a traditional square grid.
Chile
*
Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Regi ...
Peru
*
Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
Venezuela
*
Barquisimeto
Barquisimeto (; ) is a city in Venezuela. Barquisimeto is located in the Central-Western Region, Venezuela. It is the capital of the state of Lara (state), Lara and head of Iribarren Municipality. It is an important urban, industrial, commercial a ...
Europe
Spain
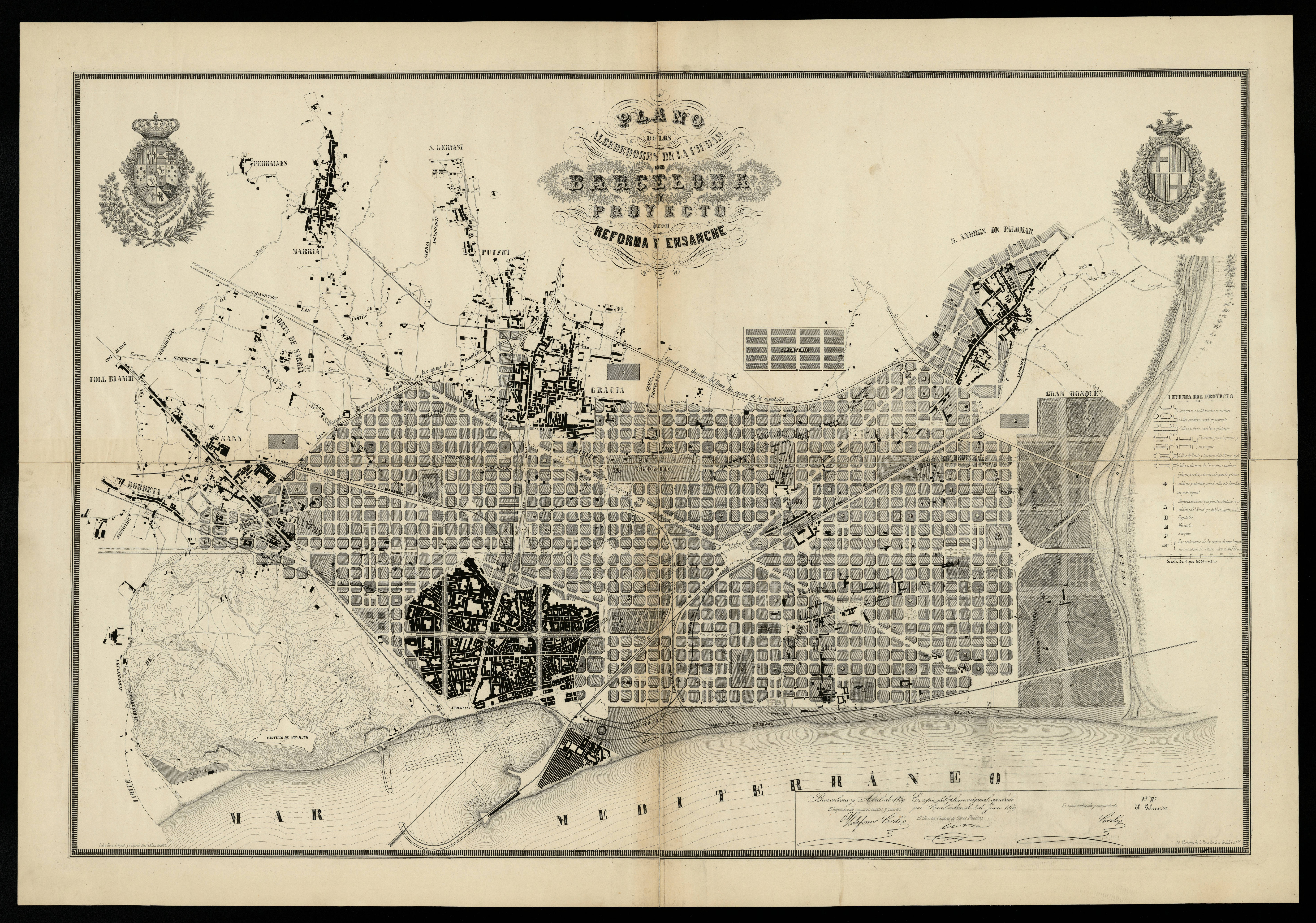
*
Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
(see
Eixample
The Eixample (, ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and what were once surrounding small towns (Sants, Gràcia, Sant Andreu, etc.), constructed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its population was 262,000 at ...
and )
*
Madrid
Madrid ( ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in Spain, most populous municipality of Spain. It has almost 3.5 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 7 million. It i ...
(see )
*
Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
(see
Eixample, Valencia)
*
San Sebastián
San Sebastián, officially known by the bilingual name Donostia / San Sebastián (, ), is a city and municipality located in the Basque Autonomous Community, Spain. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Biscay, from the France–Spain border ...
United Kingdom
*
Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
*
Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as ''Bury,'' is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk District, West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St. Edmunds an ...
(medieval grid)
*
Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of Milton Keynes urban area, its urban area was 264,349. The River Great Ouse forms t ...
(see
Milton Keynes grid road system
The Milton Keynes grid road system is a network of predominantly national speed limit, fully landscaped routes that form the top layer of the street hierarchy for both private and public transport in Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire. The system is ...
)
*
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street ...
*
Plymouth
Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Devon, South West England. It is located on Devon's south coast between the rivers River Plym, Plym and River Tamar, Tamar, about southwest of Exeter and ...
*
Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and civil parish in the Cumberland (unitary authority), Cumberland district of Cumbria, England. It is a port on the north-west coast, and lies outside the Lake District National parks of England and Wales, National Park. ...
*
Winchelsea
Winchelsea () is a town in the county of East Sussex, England, located between the High Weald and the Romney Marsh, approximately south west of Rye and north east of Hastings. The current town, which was founded in 1288, replaced an earli ...
Switzerland
*
La Chaux-de-Fonds
La Chaux-de-Fonds (; archaic ) is a Swiss city in the canton of Neuchâtel. It is located in the Jura Mountains at an altitude of 992 metres, a few kilometres south of the French border. After Geneva, Lausanne, Biel/Bienne, and Fribourg, ...
Italy
*
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
*
Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is main ...
*
Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
, partially with the Beruto plan
*
Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
*
Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
*
Bari
Bari ( ; ; ; ) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia Regions of Italy, region, on the Adriatic Sea in southern Italy. It is the first most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy. It is a port and ...
Ireland
*
Newtown Pery, Limerick
Newtown Pery (; ) is an area of central Limerick, Ireland, and forms the main city centre (or CBD) of the city. The district is known for its Georgian architectural heritage and is the core area of Limerick's Georgian Quarter. It is one of the ...
Malta
*
Valletta
Valletta ( ; , ) is the capital city of Malta and one of its 68 Local councils of Malta, council areas. Located between the Grand Harbour to the east and Marsamxett Harbour to the west, its population as of 2021 was 5,157. As Malta’s capital ...
Netherlands
*
Elburg
*
The Hague
The Hague ( ) is the capital city of the South Holland province of the Netherlands. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands. Situated on the west coast facing the North Sea, The Hague is the c ...
*
Nieuw-Vennep
Russia
* Old
St Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
*
Yeysk
Serbia
*
Kraljevo
Kraljevo ( sr-Cyrl, Краљево, ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Raška District in central Serbia. It is situated on the confluence of West Morava and Ibar River, Ibar, in the geographical region of ...
Finland
*
Pori
Pori (; ; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Satakunta. It is located on the west coast of the country, on the Gulf of Bothnia. The population of Pori is approximately , while the Pori sub-region, sub-region has a population of a ...
Germany
*
Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (), is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, second-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, the States of Ger ...
Bulgaria
*
Stara Zagora
Stara Zagora (, ) is a city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of Stara Zagora Province. It is located in the Upper Thracian Plain, near the cities of Kazanlak, Plovdiv, and Sliven. Its population is 121,582 making it the sixth largest c ...
*
Byala Slatina
Byala Slatina ( ) is a town in Northwestern Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of ...
Oceania
Australia
= New South Wales
=
*
Ballina
*
Newcastle
Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area ...
(see
Dangar Grid)
*
Tamworth
*
Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
suburbs of
Smithfield,
Austral,
Auburn and
Canley Heights in the
greater west
= South Australia
=
*
Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to ei ...
(see
Light's Vision
William Light (27 April 1786 – 6 October 1839) was a British military officer and colonial administrator. He was the first Surveyor General of South Australia, Surveyor-General of the History of South Australia#British preparation for est ...
)
= Victoria
=

*
Ballarat
Ballarat ( ) () is a city in the Central Highlands of Victoria, Australia. At the 2021 census, Ballarat had a population of 111,973, making it the third-largest urban inland city in Australia and the third-largest city in Victoria.
Within mo ...
*
Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
(see
Hoddle Grid
The Hoddle Grid is the contemporary name given to the approximately grid of streets that form the Melbourne central business district, Australia. Bounded by Flinders Street, Spring Street, La Trobe Street, and Spencer Street, it lies at a ...
)
*
Mildura
Mildura ( ) is a regional city in north-west Victoria, Australia. Located on the Victorian side of the Murray River, Mildura had a population of 34,565 at the 2021 census. When nearby Wentworth, Irymple, Nichols Point, Merbein and Red ...
= Queensland
=
*
Cairns
Cairns (; ) is a city in the Cairns Region, Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. In the , Cairns had a population of 153,181 people.
The city was founded in 1876 and named after William Cairns, Sir W ...
= Tasmania
=
*
Hobart
Hobart ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the island state of Tasmania, Australia. Located in Tasmania's south-east on the estuary of the River Derwent, it is the southernmost capital city in Australia. Despite containing nearly hal ...
= Western Australia
=
*
Perth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The ...
in many of the older inner suburbs.
New Zealand
*
Ashburton
*
Christchurch
Christchurch (; ) is the largest city in the South Island and the List of cities in New Zealand, second-largest city by urban area population in New Zealand. Christchurch has an urban population of , and a metropolitan population of over hal ...
*
Invercargill
Invercargill ( , ) is the southernmost and westernmost list of cities in New Zealand, city in New Zealand, and one of the Southernmost settlements, southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland Region, Southlan ...
*
Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
*
New Plymouth
New Plymouth () is the major city of the Taranaki region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after the English city of Plymouth, in Devon, from where the first English settlers to New Plymouth migrated. The New Pl ...
*
Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
Africa
Egypt
*
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
*
Port Said
Port Said ( , , ) is a port city that lies in the northeast Egypt extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, straddling the west bank of the northern mouth of the Suez Canal. The city is the capital city, capital of the Port S ...
Senegal
*
Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 mill ...
Somalia
*
Mogadishu
Mogadishu, locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Ocean for millennia and has ...
South Africa
*
Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
*
Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
Tanzania
*
Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (, ; from ) is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of the Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over 7 million people, Dar es Salaam is the largest city in East Africa by population and the ...
in the market district of
Kariakoo
Zimbabwe
*
Harare
Harare ( ), formerly Salisbury, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Zimbabwe. The city proper has an area of , a population of 1,849,600 as of the 2022 Zimbabwe census, 2022 census and an estimated 2,487,209 people in its metrop ...
*
Gweru
*
Bulawayo
Bulawayo (, ; ) is the second largest city in Zimbabwe, and the largest city in the country's Matabeleland region. The city's population is disputed; the 2022 census listed it at 665,940, while the Bulawayo City Council claimed it to be about ...
Asia
Japan
*
Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
*
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region of Japan. It is the list of cities in Japan, fourth-most populous city in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020, and the principal city of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, which is the List of ...
*
Sapporo
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in Hokkaido, Japan. Located in the southwest of Hokkaido, it lies within the alluvial fan of the Toyohira River, a tributary of the Ishikari River. Sapporo is the capital ...
India
*
Amaravati
Amaravati ( , Telugu language, Telugu: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Guntur district on the right bank of the Krishna River, southwest of Vijayawada. The city derives its name from the nearby his ...
*
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the ...
*
Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar () is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the industrial corridor between the megacities of Delhi and Mumbai.
Gandhinagar ...
*
Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
*
Mulund, a suburb of
Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
*
Neyveli Township
Hong Kong
*
Kowloon
Kowloon () is one of the areas of Hong Kong, three areas of Hong Kong, along with Hong Kong Island and the New Territories. It is an urban area comprising the Kowloon Peninsula and New Kowloon. It has a population of 2,019,533 and a populat ...
peninsula
China
*
Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
*
Datong
Datong is a prefecture-level city in northern Shanxi Province, China. It is located in the Datong Basin at an elevation of and borders Inner Mongolia to the north and west and Hebei to the east. As of the 2020 census, it had a population o ...
*
Xi'an
Xi'an is the list of capitals in China, capital of the Chinese province of Shaanxi. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong plain, the city is the third-most populous city in Western China after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populou ...
Indonesia
*
Batam
Batam, officially the City of Batam (, not to be confused with ''Batam Kota'', a kecamatan, district within this city), is the largest List of regencies and cities of Indonesia, city in the Indonesian province of Riau Islands. The city administra ...
*
Gilimanuk
*
Kenyam
*
Kolaka
*
Lubuk Pakam
*
Medan
Medan ( , ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the Indonesian Provinces of Indonesia, province of North Sumatra. The nearby Strait of Malacca, Port of Belawan, and Kualanamu International Airport make Medan a regional hub and multi ...
*
Metro
* Nabire
* North Jakarta
* Palangka Raya
* Pematangsiantar
* Pinrang Regency, Pinrang
* Pontianak
* Siak Sri Indrapura
* Sibolga
* Sragen
* Surabaya
* Waingapu
* Wonogiri
* Towns and villages from the results of the transmigration program throughout Indonesia
Israel
* Old Beersheba
Malaysia
* Batu Pahat
* Ipoh
* Kota Kinabalu
* Muar (town), Muar
* Subang Jaya
* Taiping, Perak, Taiping
Pakistan
* Islamabad
* Karachi
* Jauharabad
Philippines
* Bacolod
* Banga, South Cotabato, Banga
* Basco, Batanes
* Bonifacio Global City
* Butuan
* Candelaria, Quezon, Candelaria
* Candon
* Cebu City
* Claveria, Cagayan
* Kidapawan
* Koronadal
* Lucena
* Intramuros, Manila
* Magalang
* Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Muñoz
* Pasay
* San Nicolas, Ilocos Norte, San Nicolas
* Santiago, Isabela, Santiago
* Tagum
* Tuguegarao
* Victoria, Tarlac, Victoria
* Vigan
Singapore
* Punggol as Fused grid
* Anchorvale as Fused grid
United Arab Emirates
* Abu Dhabi
* Dubai
* Sharjah
Vietnam
* District 1, Ho Chi Minh City
See also
* City block
*
Commissioners' Plan of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march upto ...
(Manhattan street grid)
* Comprehensive planning
* Fused grid
* Land Ordinance of 1785 (United States)
* Street hierarchy
* Urban planning
* Urban structure
References
External links
Superblocks, Barcelona Answer to Car-Centric CityHistorical Society of PennsylvaniaThe Great American GridCity Street Orientations around the World
{{DEFAULTSORT:Grid Plan
3rd-millennium BC introductions
City layout models
Road transport
Urban studies and planning terminology
Mohenjo-daro
Harappa
Indian inventions

 In
In  By 2600 BC,
By 2600 BC,  In
In 

 Many of the earliest cities in the United States, such as
Many of the earliest cities in the United States, such as  A prominent 20th century urbanist,
A prominent 20th century urbanist, 
 Typical uniform grids are unresponsive to
Typical uniform grids are unresponsive to  Street networks of old cities that grew organically, though admired for being picturesque, can be confusing for visitors but rarely for the original inhabitants (see plan). Similarly confusing to visitors are the plans of modern subdivisions with discontinuous and curvilinear streets. Change of street orientation, particularly when gradual or arbitrary, cannot be "mapped" in the mind. Impasses, crescents or cul-de-sacs frustrate the traveler especially when they are long, forcing an arduous retracing of steps.
Frequency of intersections, however, becomes also a disadvantage for pedestrians and bicycles. It disrupts the relaxed canter of walking and forces pedestrians repeatedly onto the road, a hostile, anxiety-generating territory. People with physical limitations or frailties, children and seniors for example, can find a regular walk challenging. For bicycles this disadvantage is accentuated as their normal speed is at least double that of pedestrians. Frequent stops negate the speed advantage and the physical benefit of bicycling and add to frustration. Intersections are not only unpleasant but also dangerous. Most
Street networks of old cities that grew organically, though admired for being picturesque, can be confusing for visitors but rarely for the original inhabitants (see plan). Similarly confusing to visitors are the plans of modern subdivisions with discontinuous and curvilinear streets. Change of street orientation, particularly when gradual or arbitrary, cannot be "mapped" in the mind. Impasses, crescents or cul-de-sacs frustrate the traveler especially when they are long, forcing an arduous retracing of steps.
Frequency of intersections, however, becomes also a disadvantage for pedestrians and bicycles. It disrupts the relaxed canter of walking and forces pedestrians repeatedly onto the road, a hostile, anxiety-generating territory. People with physical limitations or frailties, children and seniors for example, can find a regular walk challenging. For bicycles this disadvantage is accentuated as their normal speed is at least double that of pedestrians. Frequent stops negate the speed advantage and the physical benefit of bicycling and add to frustration. Intersections are not only unpleasant but also dangerous. Most  *
*  *
*  * Bacolod
* Banga, South Cotabato, Banga
* Basco, Batanes
* Bonifacio Global City
* Butuan
* Candelaria, Quezon, Candelaria
* Candon
* Cebu City
* Claveria, Cagayan
* Kidapawan
* Koronadal
* Lucena
* Intramuros, Manila
* Magalang
* Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Muñoz
* Pasay
* San Nicolas, Ilocos Norte, San Nicolas
* Santiago, Isabela, Santiago
* Tagum
* Tuguegarao
* Victoria, Tarlac, Victoria
* Vigan
* Bacolod
* Banga, South Cotabato, Banga
* Basco, Batanes
* Bonifacio Global City
* Butuan
* Candelaria, Quezon, Candelaria
* Candon
* Cebu City
* Claveria, Cagayan
* Kidapawan
* Koronadal
* Lucena
* Intramuros, Manila
* Magalang
* Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Muñoz
* Pasay
* San Nicolas, Ilocos Norte, San Nicolas
* Santiago, Isabela, Santiago
* Tagum
* Tuguegarao
* Victoria, Tarlac, Victoria
* Vigan